

Innovative Ultrasonic Joining Technique Capable of Assessing Dissimilar Metals Quality using Acoustic Data
A Breakthrough in Ultrasonic Joining Technology
Recent advancements in ultrasonic joining technology have led to a remarkable method that can rapidly assess the quality of joints between dissimilar metals using only acoustic data. Developed by researchers at the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), this innovative technique promises to enhance product quality while reducing costs.
Ultrasonic welding is widely recognized in the industry for its ability to create strong, low-resistance joints quickly, making it ideal for applications like battery electrode connections. However, challenges arise when joining dissimilar metals, which can lead to inconsistencies in joint strength. Traditional inspection methods are often costly and time-consuming, requiring extensive testing to ensure quality. The new technology aims to mitigate these issues by leveraging sound data generated during the joining process.
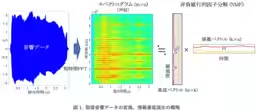
The research team, led by Chief Researcher Toyoharu Maruyama from AIST's Multi-Material Research Division, focused on the welding of aluminum (Al) and magnesium (Mg) alloys. By capturing and analyzing the acoustic signals produced during the joining process, the team set out to establish a reliable method for determining the quality of the joints without costly inspections.
The Methodology
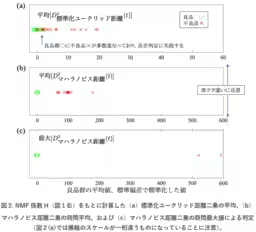
To develop this method, the researchers utilized spectrogram analysis and Non-negative Matrix Factorization (NMF) for data processing. They created a process that included various indicators to evaluate the quality of the joint. Among them, they identified the Mahalanobis distance as the most effective metric for accurately determining joint quality. The Mahalanobis distance allows for precise identification of whether a joint meets the necessary quality standards, significantly enhancing the efficiency of production process audits.
Implications for Industry
This technology offers a new approach to quality control in the ultrasonic joining of dissimilar metals. By enabling on-the-spot quality assessments without the need for destructive testing, manufacturers can ensure joints are sufficiently strong without increasing the energy input or processing time excessively. This method conserves energy and preserves the advantages of ultrasonic welding, potentially transforming quality assurance practices within the industry.
Moreover, the long-term prospects for this technique extend to improved production efficiency and cost reductions across various applications, particularly in industries that require lightweight and robust materials like aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
Future Developments
The research team aims to deepen their understanding of the relationship between acoustic data and joint strength. They plan to extend their studies to include combinations of other metals beyond aluminum and magnesium, while simultaneously developing analysis techniques suitable for operational manufacturing environments. Collaborative projects with industries where ultrasonic joining is actively used are also anticipated, paving the way for real-world applications of this technology.
A presentation detailing these findings is scheduled for May 22, 2025, during the AIST Chubu Center Lecture Meeting. This event will further showcase the potential of acoustic data in revolutionizing quality control in ultrasonic welding.
For additional insights, check out the full press release from AIST.

Topics Consumer Products & Retail)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.