
Sumitomo Bakelite Launches High Thermal Conductivity Substrate Material for Semiconductor Packages
Introduction
Sumitomo Bakelite Co., Ltd., headquartered in Shinagawa, Tokyo, has recently embarked on shipping samples of a new substrate material, LαZ®, designed specifically for semiconductor packages. This advanced material effectively dissipates heat generated by semiconductor chips, showcasing high thermal conductivity that is essential for modern high-performance devices.
Background
As the demands for cutting-edge semiconductors rise, particularly with technologies like AI, 5G, and edge computing, there is a concurrent increase in the output capacity and frequency of power devices. These advancements require more compact chips with reduced transmission loss and lower energy consumption. Integrating chips directly into substrates has been proposed as a solution to shorten wiring distances through via connections. However, the heat generated by the embedded semiconductor chips poses challenges, as it can damage products and diminish energy efficiency and overall performance. Thus, effective methods for heat suppression and dissipation are critical in the development of next-generation semiconductor packages.
Enhancing Heat Dissipation in Semiconductor Package Materials
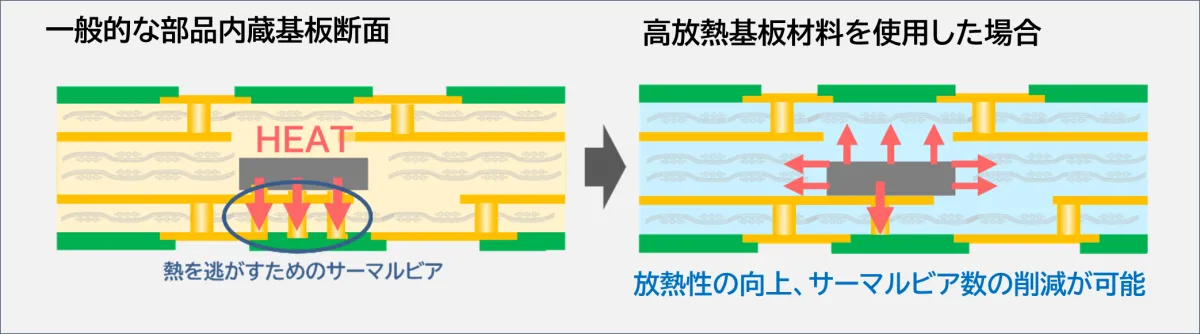
Traditionally, thermal vias were the primary method used for heat dissipation, relying on conductive vias to connect various layers. However, by increasing the thermal conductivity of the substrate material itself, we can significantly enhance heat dissipation capabilities. This improvement leads to a reduction in the number of thermal vias required, thereby increasing design flexibility and supporting the miniaturization of components.
Innovations in High Thermal Conductivity Substrate Materials
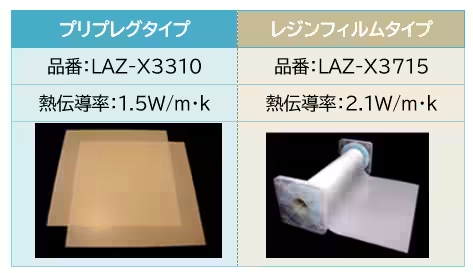
The innovative substrate material developed by Sumitomo Bakelite boasts impressive thermal conductivities: 1.5W for prepreg types and 2.1W for resin film types. In addition, the resin film type includes high flowability, which facilitates the embedding of chips within cavities in the substrate. This enhancement substantially improves the heat dissipation properties within the substrate itself.
Benefits of the New Material
1. Efficient Heat Dispersion
The new high thermal conductivity substrate materials are adept at efficiently dispersing heat generated from chips, contributing to the reduction of thermal buildup. This is particularly beneficial for substrates housing embedded chips and components.
2. Miniaturization of Packages
By elevating the thermal conductivity, it becomes feasible to embed chips directly within the substrate, leading to further miniaturization of the package design.
3. Increased Design Flexibility
The introduction of these high thermal conductivity materials allows a decrease in the number of thermal vias required, enhancing the freedom of circuit design. This enables more intricate and high-performance circuit designs that were previously challenging to achieve.
Future Prospects
With sample shipments of both prepreg and resin film materials currently underway, Sumitomo Bakelite aims for mass production of LαZ® by the fiscal year 2025. Furthermore, the company envisions expanding its product lineup to include core materials, continuing its dedication to meeting market and customer needs with innovative packaging materials. This would contribute significantly to the advancement of semiconductor high functionality and productivity.
Contact Information
For further inquiries on this product, please reach out to:
Sumitomo Bakelite Co., Ltd.
Information & Communication Materials Sales Department
Phone: 03-5462-4015
Contact Form
With these improvements, Sumitomo Bakelite stands poised to lead the semiconductor packaging industry into its next phase of development, reinforcing the importance of thermal management in future electronic devices.
Topics Consumer Products & Retail)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.