

Toyama Prefecture Launches Agricultural Worker Support Project Using Spot Work System
Toyama Prefecture's Agricultural Worker Support Initiatives
Toyama Prefecture has taken a significant step toward addressing its agricultural labor shortage by launching a new initiative that leverages spot work. The project, called "Toyama Aguri Matchbox," is operated under the governance of Toyama’s Prefectural Government, in partnership with Matchbox Technologies. This innovative platform enables local farmers and agricultural businesses to hire short-term workers efficiently and connects them with job seekers through a digital interface.
Background of the Initiative
Matchbox Technologies, based in Niigata City, has developed and provided a self-sourcing SaaS platform called "matchbox." This platform allows businesses to register and manage their own spot workers, independently sourcing human resources while adhering to labor compliance and safety standards. As part of a broader project named "Digi-PoC TOYAMA," the Toyama Aguri Matchbox was trialed from November 1, 2024, to February 28, 2025.
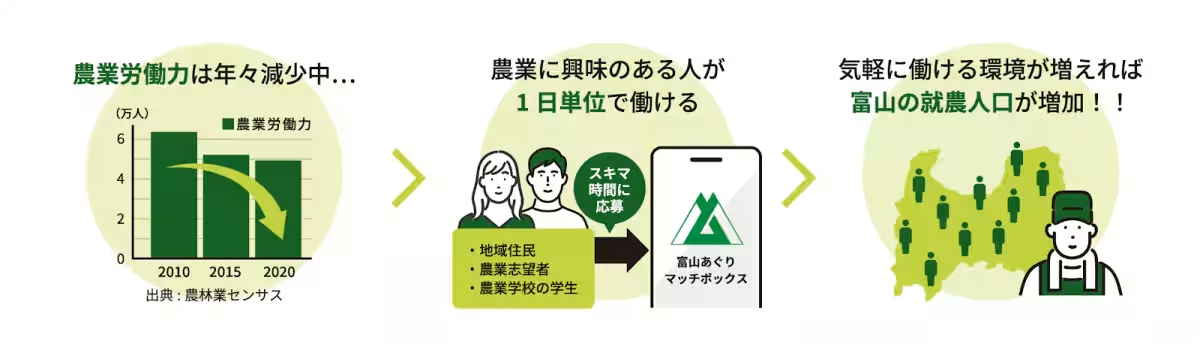
The results from this proof of concept were encouraging. Over 60 new agricultural workers engaged during the trial, which is comparable to the annual new farmers typically recorded in Toyama, indicating the program's potential effectiveness in revitalizing the local agricultural workforce.
Performance Metrics of Toyama Aguri Matchbox
During the trial period, approximately 15% of Toyama’s agricultural businesses, totaling 116 entities, registered on the Toyama Aguri Matchbox platform. In total, 229 job placements were made, with contributing workers logging over 1,140 hours of labor. Additionally, the platform includes features to foster repeat employment; 61 workers utilized the system to re-engage with agricultural businesses, highlighting its effectiveness in creating a sustainable labor pool.
Young Workers Embrace Spot Work
Interestingly, the age distribution among job seekers showed that individuals in their 20s constituted the majority of applications. This is noteworthy considering the ongoing narrative about the aging agricultural labor force. By allowing flexible work hours through both short day and hourly contracts, the Toyama Aguri Matchbox program successfully attracted a younger workforce, which is pivotal for the industry’s longevity and evolution.
Positive Feedback from Farmers
Feedback from participating farmers underscores the platform's speed and efficiency—from job posting to worker hiring. Many expressed surprise at the diversity of applicants coming from different age groups, while also noting that some of these connections have already transitioned into long-term employment arrangements.
The Role of Local Government in Employment Platforms
Officials like Nakamura Kazuhiro from Toyama's Agriculture Management Division emphasize that the aging agricultural workforce and the associated decline in the farming population are critical issues. They believe that establishing platforms like the Toyama Aguri Matchbox is essential for building connections between aspirational farmers and the agricultural sector.
Building Confidence Through Compliance
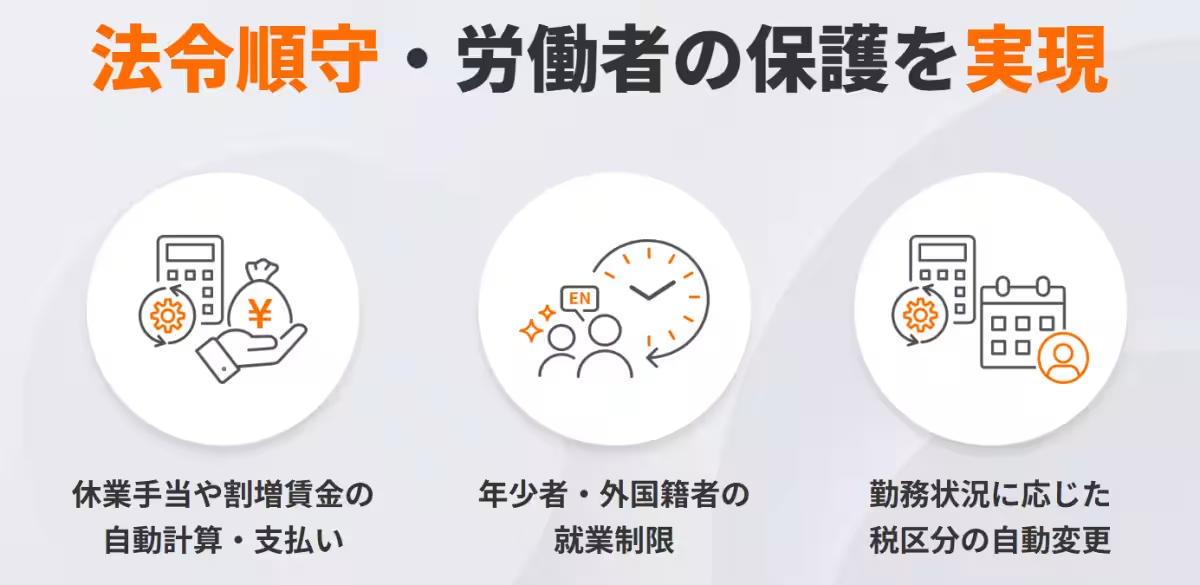
One of the key features of the matchbox platform is its focus on providing a reliable and secure working environment. By conducting thorough background checks on all registered businesses, it encourages applicants to seek jobs without fear of exploitation. Such efforts strengthen trust between workers and employers, thus creating a robust community around spot work initiatives.
A Future-Oriented Perspective
The future of the Toyama Aguri Matchbox indicates potential for expansion beyond agriculture. The local government envisions replicating this model in hospitality and welfare sectors to address labor shortages comprehensively. The strategy aims not only to fortify the agricultural integrity but also to open doors for various employment opportunities in local communities.
In conclusion, the Toyama Aguri Matchbox initiative, backed by the advanced technology of Matchbox Technologies, marks a significant leap toward securing the future of agriculture in Toyama Prefecture. As the program transitions from a trial phase to a fully operational model in fiscal year 2025, it’s poised to create a lasting impact on the region’s economy and workforce structure. The collaboration between local governments and technological innovation illustrates a forward-thinking approach to solving pressing local issues.

Topics Other)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.