

Emerging Trends in AI Agents: Business Adoption and Expectations in Japan
Overview of AI Agent Adoption in Japan
A recent study by Allganize Japan, led by CEO Yasuhiro Sato, sheds light on the changing landscape of AI usage in Japanese companies. The survey, targeting 1,000 key employees from organizations that have adopted generative AI, aims to understand the practical applications of AI agents in business environments.
AI agents are gaining significant attention as firms increasingly turn to AI for high-level decision support and autonomous task management. The survey findings highlight both trends in the utilization of generative AI and the evolving expectations regarding the value AI agents are expected to bring to organizations.
Growing Utilization of Generative AI
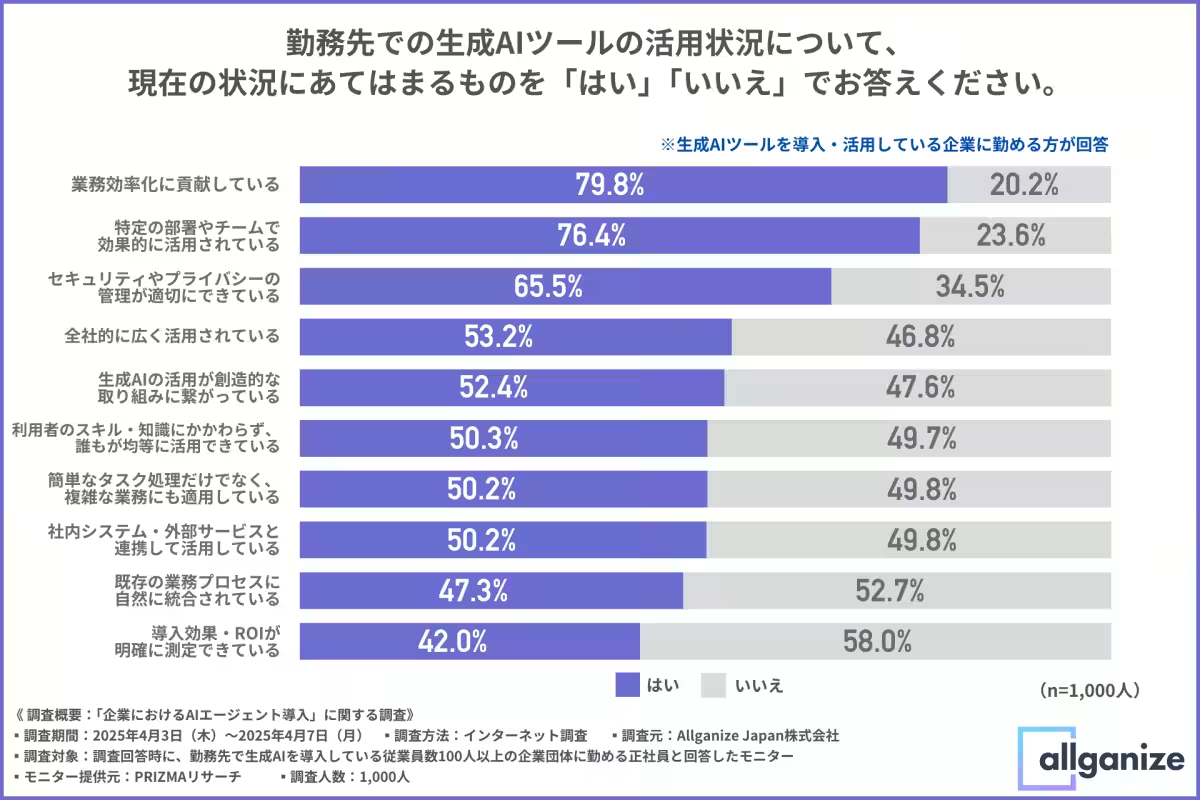
The survey reveals encouraging trends concerning the implementation of generative AI in businesses. Approximately 80% of respondents reported that their firms note enhanced operational efficiency due to AI tools. Additionally, a substantial 80% stated that these tools are effectively employed within specific departments or teams. However, only about half acknowledged that these tools are utilized at an enterprise-wide level, indicating that further integration is necessary. Disparities in AI tool usage among employees, linked to varied levels of knowledge and skills, also surfaced, suggesting challenges in achieving equitable access across the organization.
Specific Uses of Generative AI
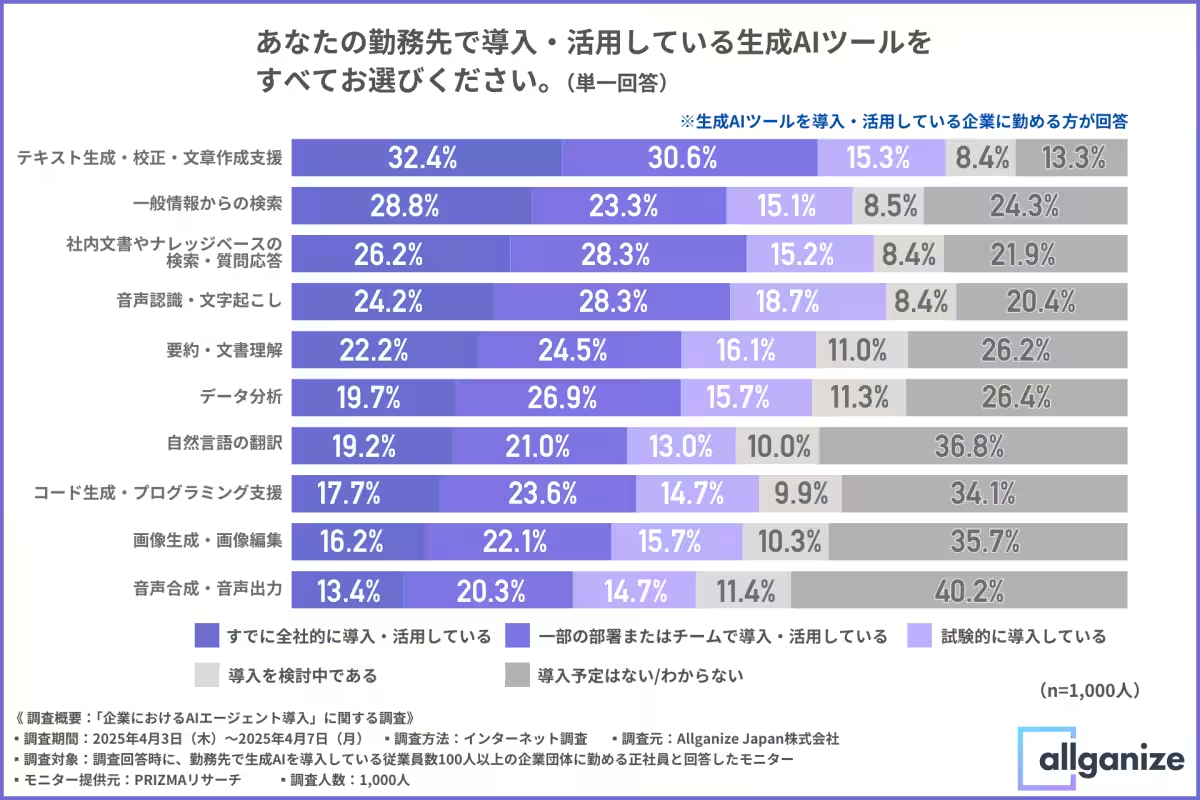
In analyzing how companies utilize generative AI, the survey noted that over 30% of firms incorporated tools for text generation, proofreading, and support in document creation. High adoption rates were also observed for general information searches (28.8%) and internal knowledge base queries (26.2%). Such functionalities are characterized by their versatility and clear return on investment (ROI), further encouraging their use.
Moreover, even for non-fully adopted categories, about 30% of organizations are either testing these tools or contemplating their implementation, suggesting that many are at a critical juncture toward broader adoption.
Awareness and Future Plans for AI Agents
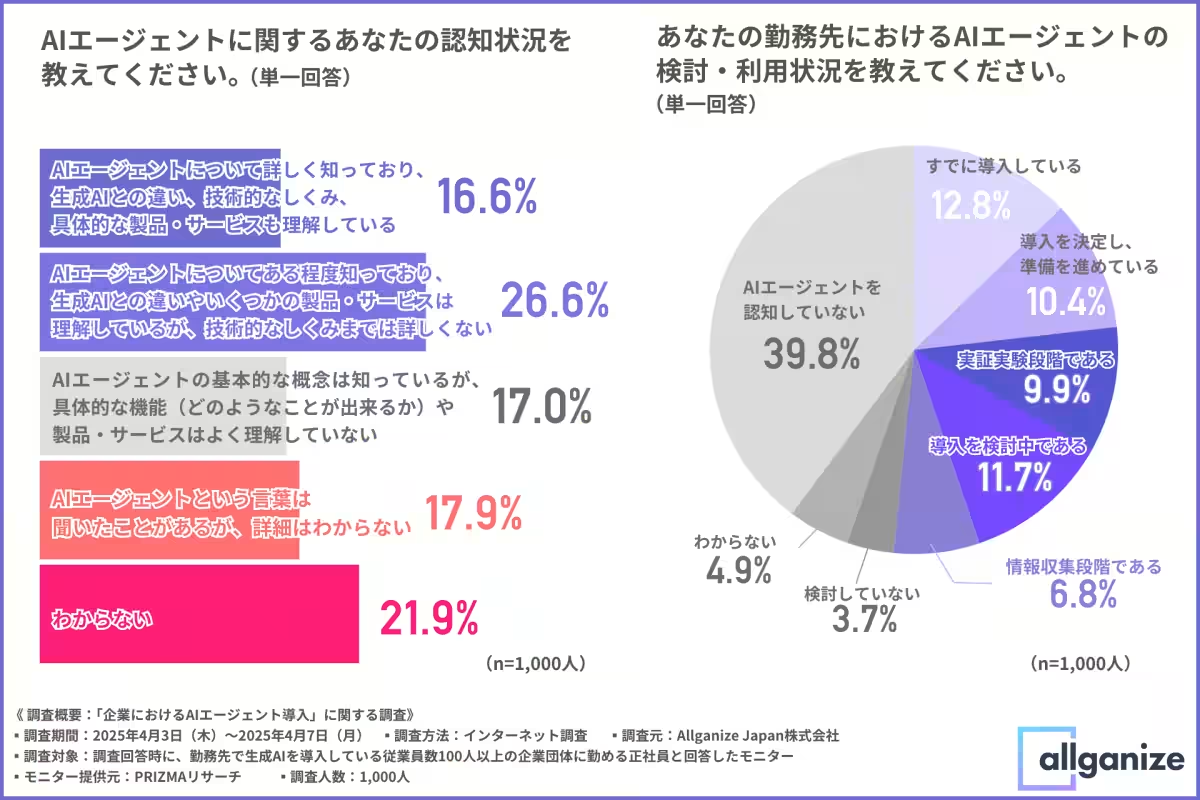
Among those company workers already employing generative AI, awareness of AI agents diverges sharply. Around 40% of respondents confirmed a solid understanding or familiarity with AI agents, while nearly 40% said they merely recognized the term or had no clarity about it. This indicates a split in comprehension, suggesting that while AI agent concepts are permeating discussions, detailed knowledge and practical examples are still not widespread.
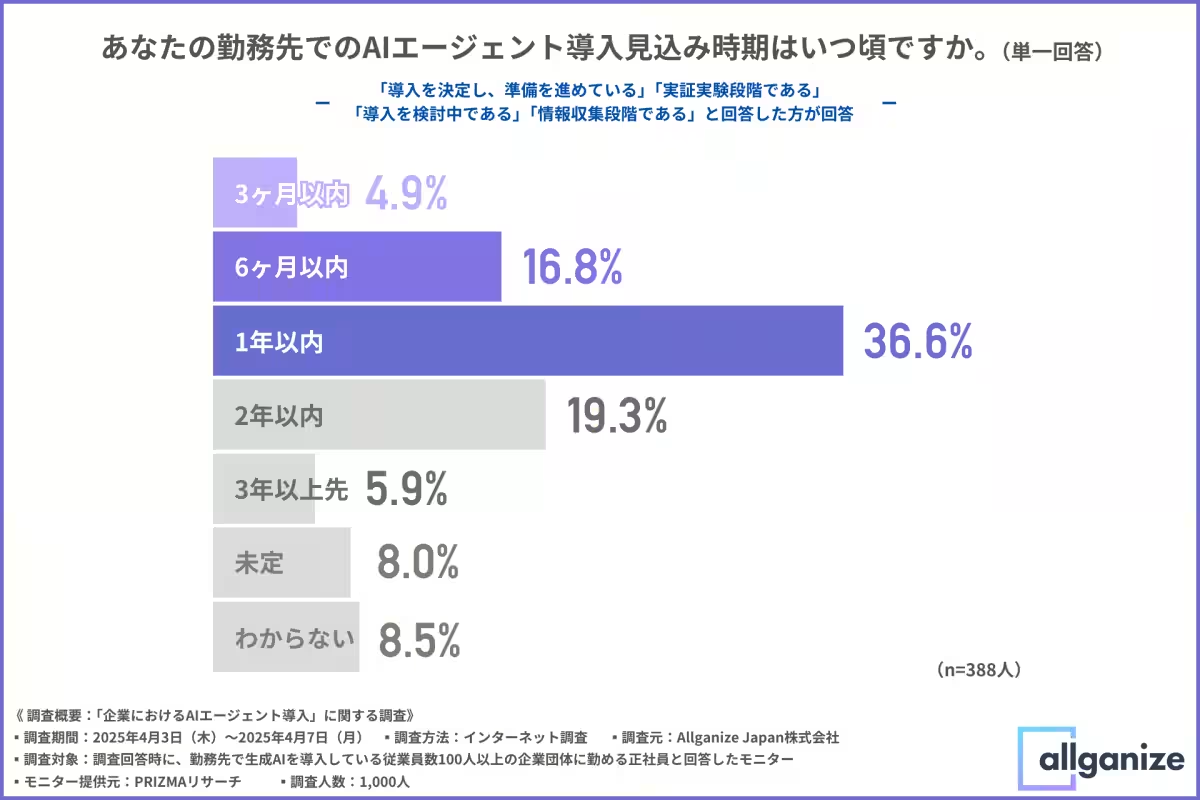
The survey revealed that over half of those aware of AI agents are actively exploring their implementation, with many at the stages of pilot testing or information gathering. It's clear that a growing number of companies recognize the potential benefits of AI agents, and advanced AI solutions are increasingly being considered for implementation.
Notably, among those intending to integrate AI agents, around 60% plan to do so within a year, capturing a rapid transition expected for 2025 and early 2026 when AI agents could gain traction in the market.
Key Expectations from AI Agents
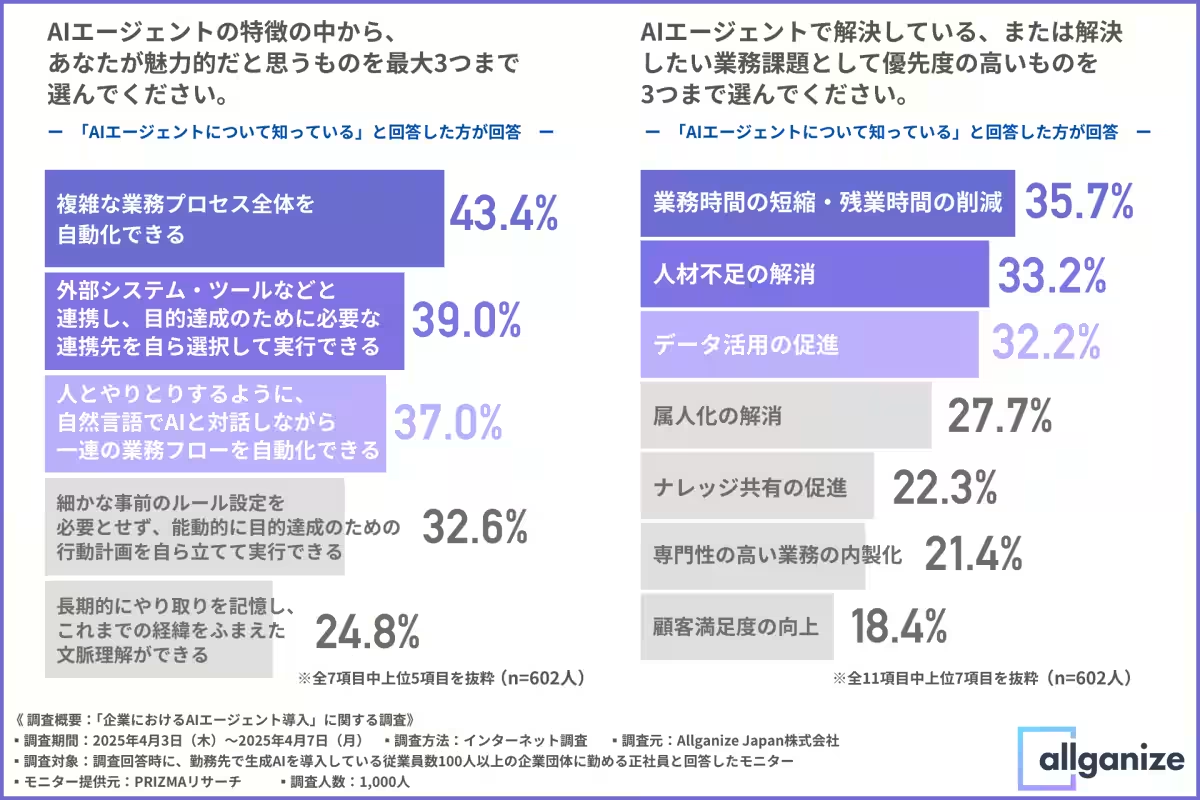
When inquired about the attractive characteristics of AI agents, respondents highlighted the capability to automate entire complex business processes (43.4%), autonomous integration with external systems (39.0%), and the potential to interact in natural language during task automation (37.0%). This reveals a strong desire for self-sufficient and integrative AI functionalities that promote organization-wide process transformation beyond mere task efficiency.
The emphasis on conversational interactions with AI underscores significant expectations for intuitive interfaces that facilitate use by individuals without specialized expertise. Many organizations hope this will reduce dependency on high-level skill sets and promote substantial operational efficiencies across the workforce.
Among the most pressing operational challenges that businesses seek to resolve with AI agents are reducing work hours (35.7%), addressing labor shortages (33.2%), and enhancing data utilization (32.2%). These identified issues reflect fundamental challenges organizations face and highlight AI agents’ pivotal role in fostering sustainability and competitive advantage in the corporate landscape.
Factors Influencing AI Agent Implementation
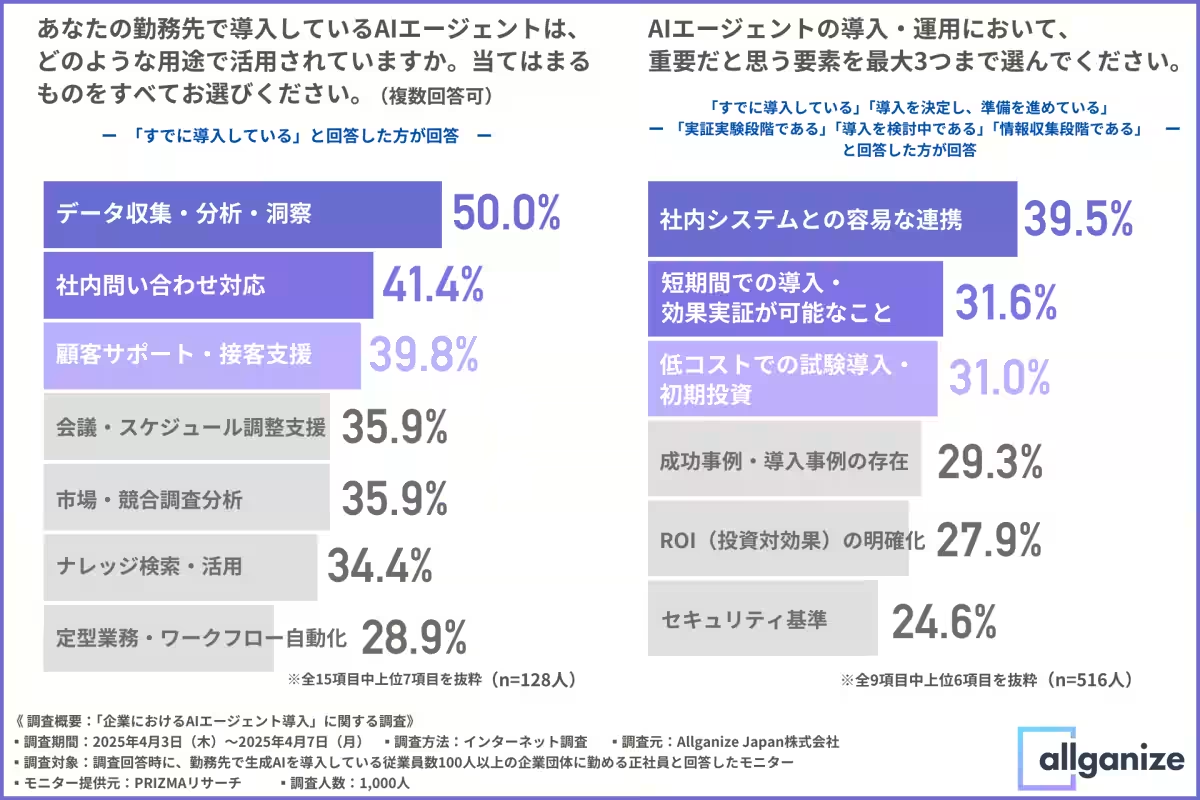
Businesses that have already adopted AI agents focus on areas including data collection, analysis, and customer support. Functions related to information handling demonstrate the value AI agents provide in communication and overall operational fluidity. Additionally, their application in scheduling and competitive analysis further cements their worth in streamlining organizational processes.
The survey also found that businesses regard ease of integration with existing systems (39.5%) as paramount, followed by the need for rapid proof of effectiveness (31.6%) and cost-efficient trial implementations (31.0%).
These responses highlight that for AI agents to maximize their value, ease of incorporating them into existing workflows and systems is essential. The smoothness of integrating these tools could significantly affect their overall adoption rates moving forward.
Conclusion: From Generative AI Tools to AI Agents
The study illustrates a pivotal shift in corporate AI use, evolving from individual efficiency to a more holistic approach aimed at transforming organizational capabilities. As firms steadily implement generative AI to enhance individual productivity, challenges remain in achieving broad organizational integration and enabling complex automation processes.
AI agents are emerging as next-gen solutions anticipated to meet earlier unmet demands, especially in automating sophisticated business workflows and seamlessly linking with legacy systems. With a substantial portion of surveyed companies expressing intentions to adopt AI agents within a year, the trajectory ahead looks promising for AI technologies, particularly in areas fostering collaboration and operational agility.
Allganize Japan underlines this opportunity, positioning itself to facilitate Japanese businesses’ transitions to AI agents, thereby fostering innovation and heightened productivity within the corporate sector. As organizations embrace the potential that AI agents can unlock, their evolution will play a crucial role in augmenting corporate prowess and sustainable growth in the digital age.
Topics Business Technology)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.