

Hitachi Enhances Customer Support Quality with AI Agents in Quality Assurance
Introduction
Hitachi, Ltd. has recently made significant strides in improving its customer service capabilities through the application of AI agents in the quality assurance sector. This innovative move focuses on optimizing responses to customer inquiries related to equipment malfunctions and other operational issues by incorporating the tacit knowledge of experienced professionals into an easily accessible format. A pilot implementation has already demonstrated its potential at the company's Omika Works, a hub for systems that bolster critical infrastructure such as power generation, railways, and water management.
The Challenge
Traditionally, customer inquiries regarding equipment failures could be highly challenging to manage effectively, primarily due to the sheer volume of past incidents and manual processes involved in sifting through historical data. Quality assurance teams were heavily reliant on the expertise and intuitive judgment of seasoned staff members. Fresh faces in the workforce often struggled to keep pace with these demands, leading to slower response times and potentially unsatisfactory answers for customers. Recognizing this gap, Hitachi aimed to enhance its processes with AI.
Implementation of AI Agents
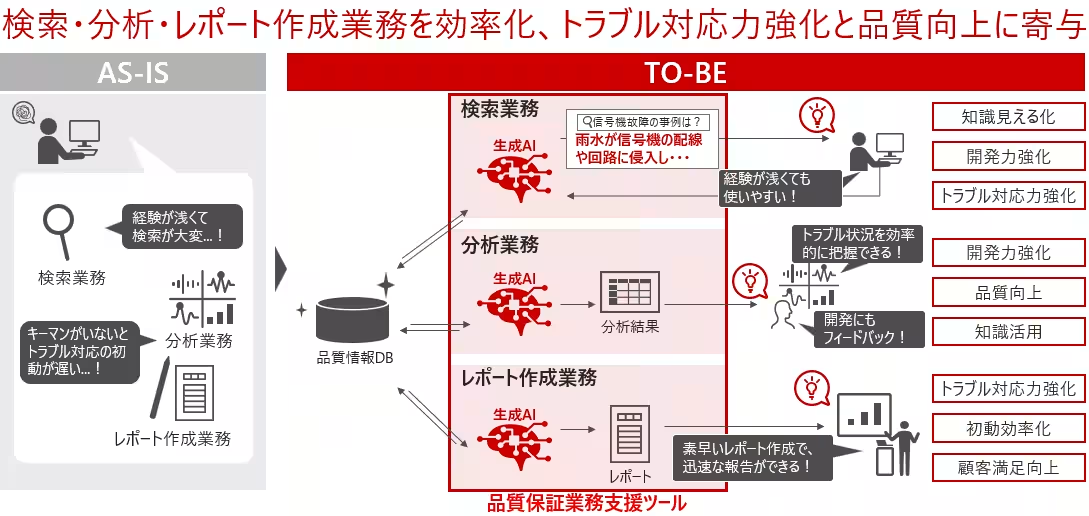
The deployment involved creating a powerful support tool powered by AI that could access a vast database of historical records. This tool is designed to facilitate the quality assurance process by allowing users to input a brief description of issues, which the AI interprets and uses to search for similar past cases. By understanding the search patterns and strategies of experienced professionals, an AI agent can simplify access to relevant data.
Over the course of a demonstration project slated from October 2024 to March 2025, this initiative has showcased the considerable advancements achieved through their generative AI technology. While still in its initial phases, feedback indicates a significant potential for refining quality assurance processes overall.
Results Achieved
The pilot program yielded three primary benefits:
1. Reduction in Search Time: The AI agent dramatically cut the time needed to locate necessary information in response to customer inquiries by nearly 90%. This improvement allows all staff, regardless of their experience level, to extract pertinent information effectively and efficiently.
2. Enhanced Analysis Capability: By utilizing AI in data analysis tasks, the quality of reporting and assessment not only improved but also reduced the time taken for such procedures by over 80%. This feature empowers team members to generate actionable insights more rapidly and accurately than before.
3. Faster Reporting: In instances where senior personnel are unavailable, the AI can assist in generating initial reports concerning customer issues. This capability facilitates quicker preliminary assessments, enabling the company to maintain high service standards even under challenging circumstances.
Future Directions
Encouraged by the outcomes from the pilot, Hitachi plans to expand the use of AI agents to bolster quality assurance practices across the entirety of Omika Works. With an eye toward the 2026 fiscal year, they aim to extend these implementations beyond the railway systems into other sectors, including electricity and water services. As they refine their technology, Hitachi envisions addressing the broader challenges facing the manufacturing industry, including personnel shortages and the need for operational consistency.
Conclusion
Hitachi's commitment to merging its extensive operational technology expertise with cutting-edge generative AI illustrates its dedication to solving pressing social issues. By promoting knowledge sharing and increasing productivity, the company is poised to enhance not just its internal operations but also the overall quality of service provided to its customers. For further information on Hitachi's generative AI initiatives, please visit their official site.

Topics Business Technology)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.