

Exploring the Reality of AI Adoption in Japan: What Companies Need to Do Next
The Reality of AI Adoption: Success Rates and Future Steps for Japanese Companies
AI technology has often been heralded as a catalyst for efficiency and innovation in the business world. However, the recent findings from Japanese firm Helpfeel starkly reveal that while AI adoption rates have soared globally, the success of these implementations remains alarmingly low.
On October 1, 2025, Helpfeel introduced the outcomes of an extensive study during a seminar titled “Why Japanese Startups Fail: Insights from Global AI Trends and Success Factors” held in Tokyo. It was presented by the company's CEO, Issei Rakusai, alongside Benjamin Forden, who focuses on overseas operations. Together, they discussed over a hundred cases observed through North American business discussions and site visits, highlighting the realities of the global AI market and what it means for Japanese enterprises.
Current AI Adoption Landscape
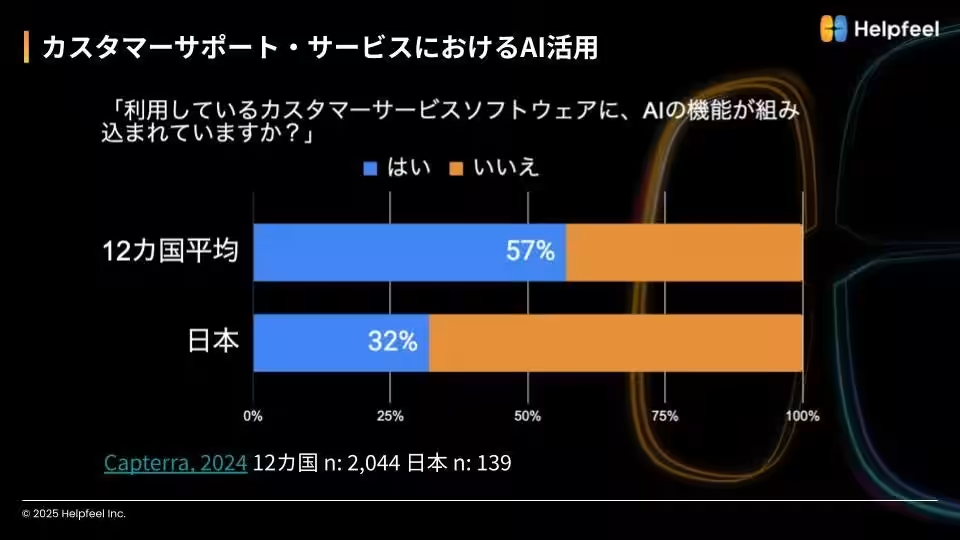
The statistics paint a sobering picture—while AI adoption rates in the U.S. are projected to leap from 55% in 2023 to 78% in 2024, Japan lags behind with only 32% adoption in customer service roles, compared to an international average of 57%. More critically, Japan's success rate with AI has dwindled to a mere 5%, indicating a concerning trend. No longer can firms expect immediate results simply from implementing AI; the mantra of “just adopting for adoption’s sake” has not only faded but left many companies without the expected improvements in efficiencies or customer experiences.
This trend reveals a pivotal moment for organizations to reflect on their AI strategies: understanding that success in AI is no longer about the mere act of implementation but rather about its effective operation.
Learning from Global Trends
Helpfeel’s findings underscore the importance of examining global trends in AI adoption, especially as concepts born overseas typically arrive in Japan within 1-2 years. For instance, one case discussed involved a major global company that replaced 700 operator roles with AI, only to revert due to declining customer satisfaction. This incident starkly illustrates that the goal of AI should not be merely reducing human labor but enhancing human capabilities through AI. Successful implementations observe a harmonious balance between human judgment and AI efficiency.
With this shift, the skill requirements for customer support roles are also evolving. The need for emotional intelligence is now coupled with technical skills; support engineers are expected to grasp concepts like APIs and SQL to drive automation within their organizations. Companies are on the lookout for talent that can adeptly utilize AI in a way that elevates overall performance and user satisfaction.
The Transition of AI Vendors
The landscape for AI vendors is also transforming. It is no longer sufficient to merely supply tools; companies like Helpfeel are moving towards a model that emphasizes ongoing operational support and consulting. One notable factor that raised Helpfeel’s profile among North American counterparts was its focus on providing personalized consultation services, emphasizing that successful adoption requires continuous engagement.
Moving Forward: Strategies for Global Success
During the seminar, Helpfeel identified common strategies employed by successful global companies, which can be distilled into three main points:
1. Understanding Local Markets: Organizations benefit from diverse teams that grasp the cultural nuances and decision-making preferences of their local markets.
2. Subtraction Philosophy: Companies that achieve success on a global scale often do so by stripping down products to their most essential and useful forms rather than adding unnecessary features.
3. Product-Centric Approach: Making technology the cornerstone of competitive advantage, companies emphasize continuously refining their core products to maintain relevance and marketability.
To thrive in international markets, firms should aim for swift product iterations based on minimum viable products, allowing them to respond efficiently to user feedback. A prominent example shared was that of “Gyazo,” a globally utilized image and video sharing service that refined its offerings based on critical input from its users.
Helpfeel's Initiatives for Global Expansion
Wrapping up the event, Helpfeel unveiled a new functionality for their AI-FAQ platform—an automatic translation feature that translates Japanese FAQs into over 50 languages in real time. This enhances accessibility for the company's diverse clientele, including nearly 2.3 million foreign employees in Japan and international tourists.
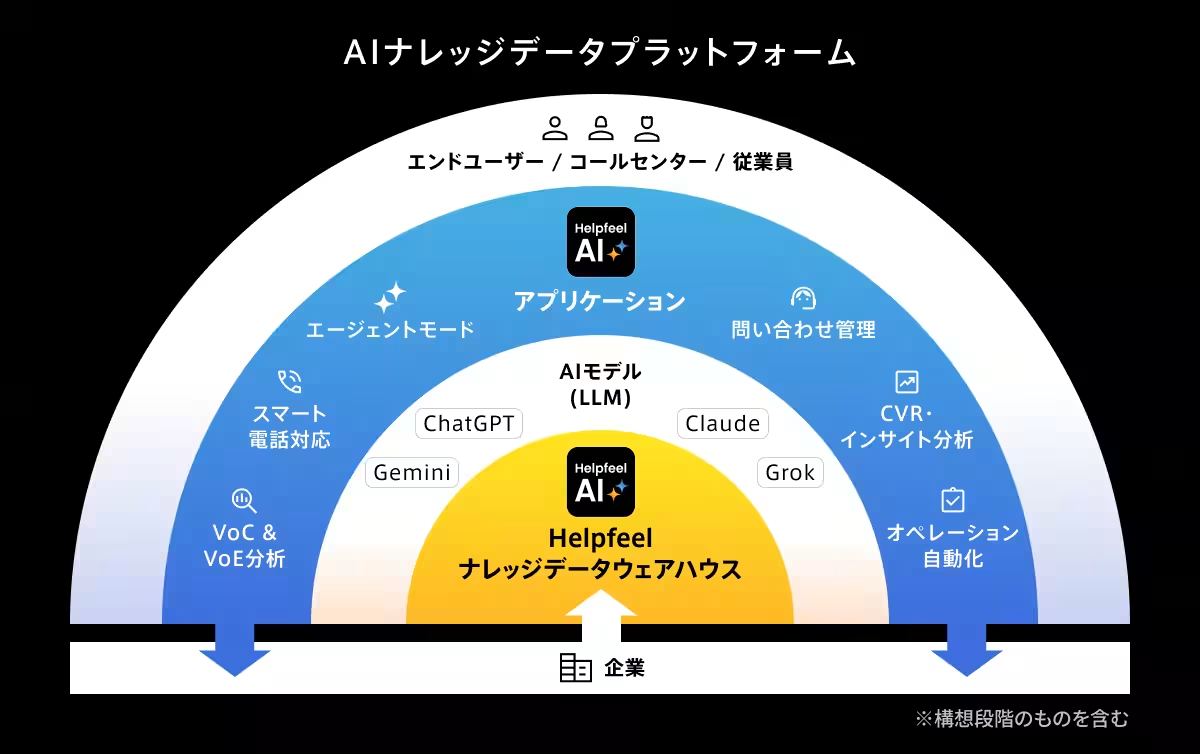
Moving forward, Helpfeel has successfully raised 2.6 billion yen in funding as of September 2025 and is now intensifying its global expansion efforts in North America. In October, they plan to showcase their solutions at international trade fairs, broadening their customer base while promoting their AI Knowledge Data Platform to overseas companies.
In an era where AI’s capabilities are rapidly advancing, Helpfeel seeks to build a solid knowledge foundation that allows organizations worldwide to harness AI effectively through their innovative platform.
Conclusion
As the AI landscape continues to evolve, Japan faces a crucial juncture in determining how to best implement and benefit from this technology. The insights from Helpfeel serve as a call to action for Japanese firms: to construct a robust knowledge infrastructure, nurture a blend of customer and technical orientation in their workforce, and ensure continuous operational improvement. Only then can they hope to elevate their AI initiatives from mere implementation to genuine success.




Topics Business Technology)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.