

The Superiority of Natural Edible Bird's Nest Backed by Scientific Research
The Superiority of Natural Edible Bird's Nest Backed by Scientific Research
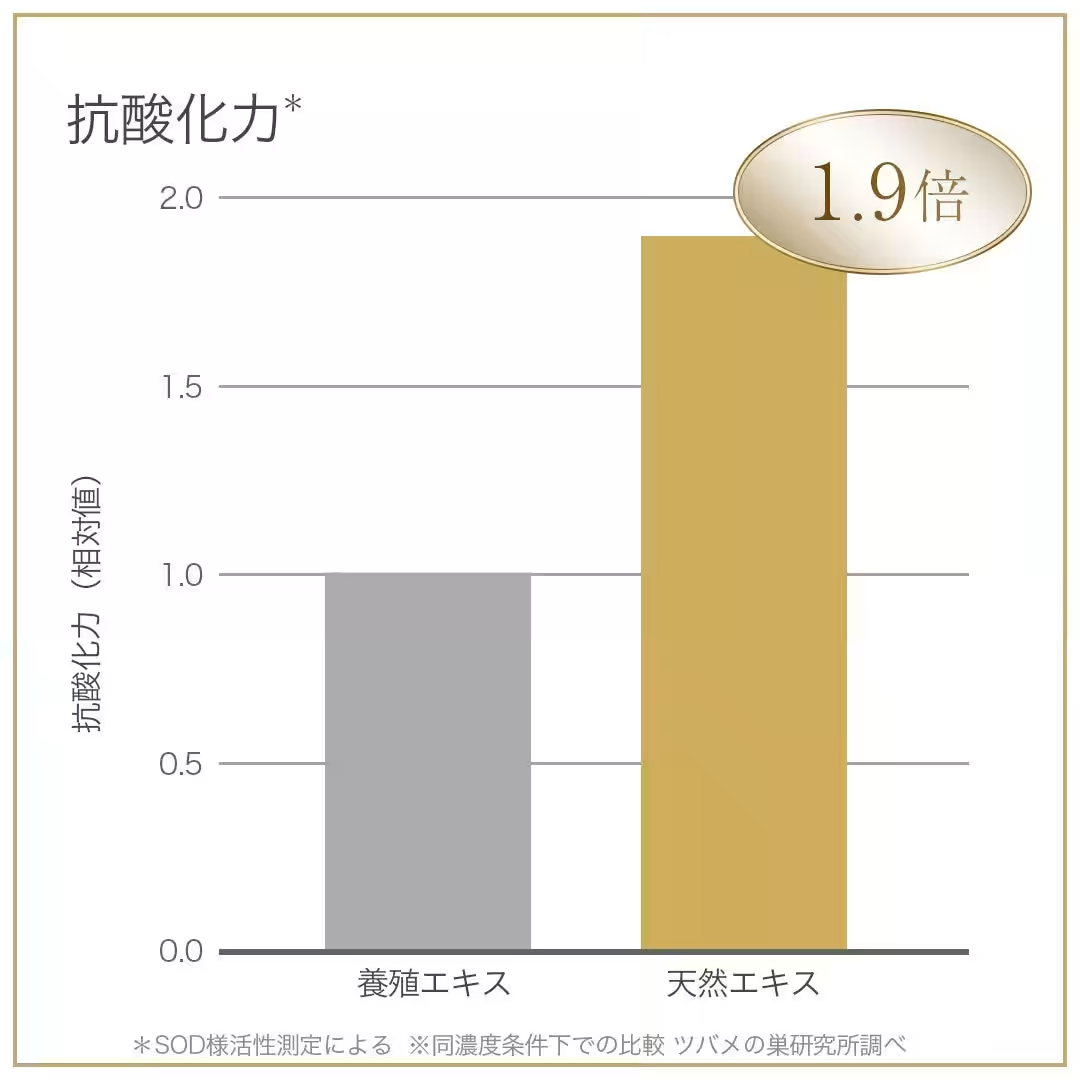
In a significant breakthrough, M Style Japan Co., Ltd., based in Fukuoka, has conducted a study proving that their natural edible bird's nest, sourced from Malaysia, possesses an impressive antioxidant power that is 1.9 times greater than that of commonly available farmed bird's nests. This research underscores the commitment of the BI-SU brand to quality and the value of natural ingredients, enhancing consumer trust in their products.
Overview of the Study
The research involved extracting essences from both natural edible bird's nests and farmed bird's nests available in the market. Their antioxidant capabilities were then compared using a measurement known as Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) activity. This measurement is critical because it gauges the ability to eliminate reactive oxygen species, which are associated with aging and various health issues. A higher SOD activity level indicates better potential for age-defying effects.
The results were striking: the extract from the natural edible bird's nest showed a clear superiority with 1.9 times more antioxidant power compared to its farmed counterpart. This finding highlights the incredible potential of natural edible bird's nests for those seeking to enhance their beauty and health.
Background of the Research
Three Types of Edible Bird's Nests
Edible bird's nests available in the market can be categorized into three main types, each differing in quality and characteristics:
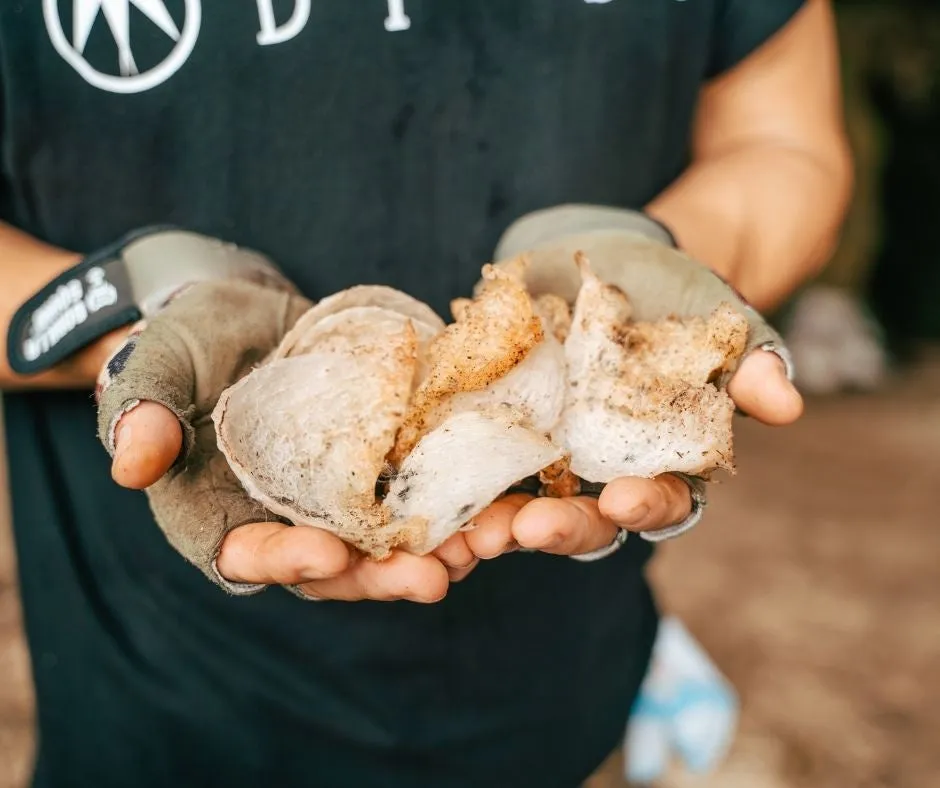
1. Natural: Built by swallows in a rich ecosystem without human intervention. These nests encapsulate the essence of untouched nature.
2. Artificial: Created using chemicals to mimic the texture and shape, lacking the unique properties found in actual swallow nests.
3. Farmed: Cultivated in 'birdhouses' specifically designed to boost production efficiency, these nests are also technically produced by swallows but under human control.
The aim of this research was to scientifically validate the inherent value of the


Topics Other)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.