
FANCL's Health Big Data Study Reveals Links Between Memory Decline and Lifestyle Choices
FANCL's Insights on Memory Decline
FANCL Corporation has conducted an extensive health analysis, known as the Health Big Data Study, incorporating feedback from over 33,000 participants aged between 20 and 69. This investigation focuses on understanding how various lifestyle factors—including dietary habits, sleep duration, and exercise routines—correlate with perceived memory decline.
Key Findings
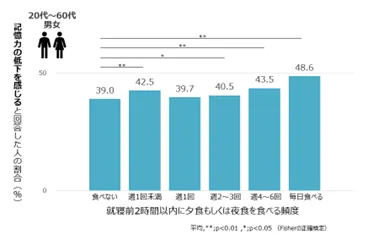
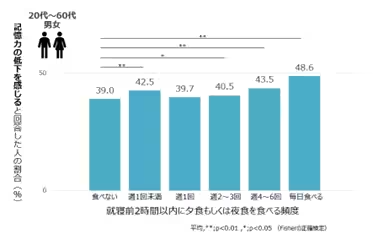
1. Meal Timing and Memory
The study revealed a significant relationship between meal timing and memory health. Individuals who reported frequent late-night eating—specifically within two hours before bedtime—were more likely to feel that their memory was declining. This connection suggests that even infrequent late-night snacks can adversely affect cognitive functions.
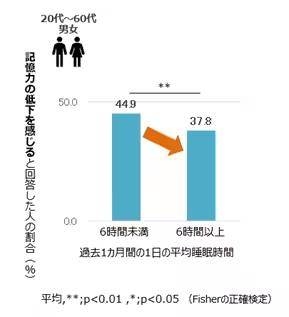
2. Sleep Duration's Impact
The results indicated that sufficient sleep plays a crucial role in preserving memory. Participants sleeping at least six hours a night reported a lower incidence of memory decline compared to those who slept less than six hours. Thus, adequate sleep might be essential for maintaining cognitive health and reducing the risk of memory issues.
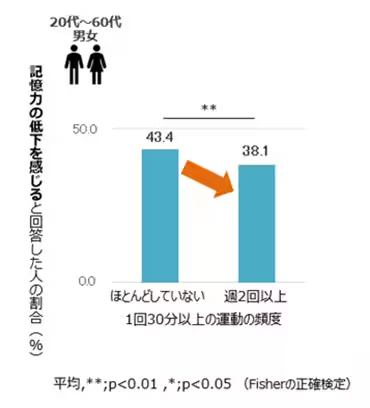
3. Exercise Frequency Matters
Regular physical activity is linked to better memory retention. Those who engaged in exercise at least twice a week were less likely to experience memory decline in comparison to individuals who exercised minimally or not at all. This highlights the importance of establishing a consistent workout regimen for cognitive health.
Background of FANCL's Research
Since its inception in 1994, FANCL has focused on supporting customers' health through dietary supplements. As lifestyles evolve, the importance of sleep and exercise is increasingly recognized. This 31-year milestone for FANCL marks a commitment to not only assist in dietary intake but also promote the significance of sleep and physical activity in holistic health.
To further enhance understanding of these factors, FANCL will continue to release regular analyses derived from extensive data, including over 50,000 survey responses related to lifestyle choices and health metrics by May 2024.
Expert Commentary
Dr. Katsumi Shibata, who contributed to establishing dietary intake standards, commented on the findings, stating that late-night meals negatively influence memory retention, while exercise and proper sleep could provide beneficial effects. He noted the connection between gut health and brain function, emphasizing how timely meals can interfere with sleep quality, thus affecting cognitive performance.
Dr. Shibata recommends that individuals maintain evening meal quantities and establish their sleep and exercise routines—focusing on personalized approaches to health.
Future Directions
FANCL aims to contribute to a sustainable society through comprehensive insights and innovative health products. By thoroughly analyzing survey results and urine tests gathered through its 'Personal One' supplement program, FANCL intends to uncover new perspectives on health to deliver higher quality support to customers. The ongoing initiative includes a commitment to promoting awareness regarding the interconnections of diet, sleep, and physical fitness.
Engage with Your Health
To cater to those struggling to incorporate exercise into their daily routines, FANCL offers an online fitness program that allows individuals to work out conveniently from home, enhancing accessibility to physical fitness without the need to visit gyms.
Study Details
- - Analyzed Data: Responses from FANCL's 'Personal One' lifestyle survey.
- - Study Period: January 27, 2020, to May 31, 2024.
- - Participants: 33,246 adults aged 20 to 69 upon initial purchase of 'Personal One'.
Topics Health)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.