
The Impact of Class Closures on Student Achievement and Economic Disparities
The Impact of Class Closures on Academic Performance
In recent years, the issue of school closures due to influenza outbreaks has gained significant attention, given its notable impact on students' academic achievements. A recent study conducted by researchers from Waseda University and the University of Tokyo has shed light on how such closures affect particularly economically disadvantaged students. This insightful research illustrates the depth of the issues at hand and provides a clearer understanding of the academic inequalities stemming from class interruptions.
Findings from the Research
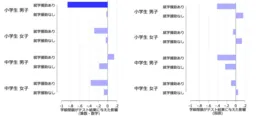
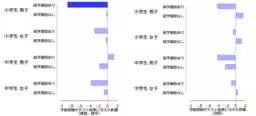
The study utilized government data from a local authority in the metropolitan area, focusing on the performance of elementary school students during periods of class closures. It was found that these interruptions negatively impacted the math skills of students, with a more pronounced effect observed among male students.
Key Insights:
- - Impact on Academic Performance: The study revealed that students from economically disadvantaged backgrounds suffered significant declines in their math scores as a result of class closures. The findings indicated that the reduction in instructional time and alterations in daily habits—such as increased screen time and decreased sleep—played critical roles in this decline.
- - Gender Disparities: The decline in academic performance was notably more significant among boys compared to girls, highlighting a concerning gender discrepancy. It was also noted that class closures conducted closer to the academic year’s end had more severe impacts. However, similar effects were not observed in middle school students.
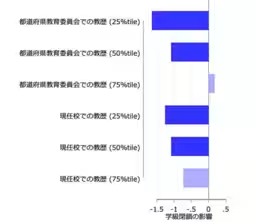
- - Role of Teacher Experience: Interestingly, the study suggested that experienced teachers could help mitigate the adverse effects that class closures had on students, particularly those from struggling economic backgrounds.
Contributing Factors to Learning Loss
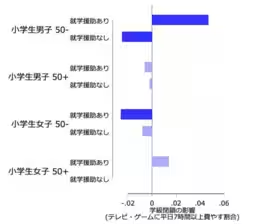
The research team determined that class closures contribute not only through the loss of classroom instruction but also via lifestyle changes that adversely affect students' learning capabilities. Students—especially boys from difficult economic situations—increased their TV and gaming time while simultaneously reducing their sleep hours, leading to diminished academic performance.
To illustrate these points, visual data from the study showed a correlation between class closures and increased time spent on non-educational activities. For instance, the percentage of economically disadvantaged boys spending more than seven hours on screens during weekdays rose significantly during closures.
This alarming trend underscores the need for targeted public educational support during periods of school disruption—helping to level the playing field for those in economic hardship.
Implications for Educational Policy
The implications of this research extend beyond mere classroom disruption, suggesting a pressing need for public policies that address the unique challenges faced by economically disadvantaged students. The need for intervention strategies is crucial, especially in light of the ongoing challenges posed by pandemics or health crises that lead to school closures.
The evidence supports the development of specific educational programs, including targeted tutoring and the strategic placement of experienced teachers in classrooms with higher concentrations of economically disadvantaged students.
Future Directions
While this study represents a valuable step towards understanding the consequences of class closures, it acknowledges the need for further research. Future inquiries could explore the connection between school closures and various other factors affecting educational outcomes, such as social dynamics among peers and family stressors.
To further enhance the empirical understanding of this issue, researchers aim to analyze how class closures affect not only academic skills but also aspects of physical development among children.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the findings of this research not only highlight the severe impacts of class closures on students—especially those who are economically disadvantaged—but also underscore the importance of proactive educational measures. Ensuring that every child has equal access to learning opportunities is vital for fostering a more equitable educational environment. As we move forward, it is imperative to take these findings into account when developing policies that protect children's educational rights, especially in times of crisis.
Topics Other)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.