

The Key Challenges of On-the-Job Training According to HR Professionals
Exploring the Challenges of On-the-Job Training in Organizations
Recently, ALL DIFFERENT Co., Ltd., a consulting firm focused on organizational development and human resource training, collaborated with the Learning Innovation Institute to conduct an extensive survey on the topic of On-the-Job Training (OJT) among HR professionals. With over 20,000 companies and more than 4.2 million individuals benefiting from their expertise, their findings shed light on critical issues facing companies today.
Background and Context
The issue of early resignations among new employees has garnered significant attention, with data from Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare indicating that over 30% of new graduates, both from high schools and universities, leave their jobs within three years of joining. This phenomenon not only reflects troubled youth adaptation but also manifests as a potential setback for organizations that have invested substantial time and resources in training these individuals. The survey revealed that young employees often experience gaps between expectations and reality, leading to increased turnover intentions.
The study aimed to explore OJT as a pivotal method for nurturing young talent, highlighting the importance of both individual resilience and organizational support in facilitating employee retention and growth.
Survey Highlights
Main Challenges Identified by HR
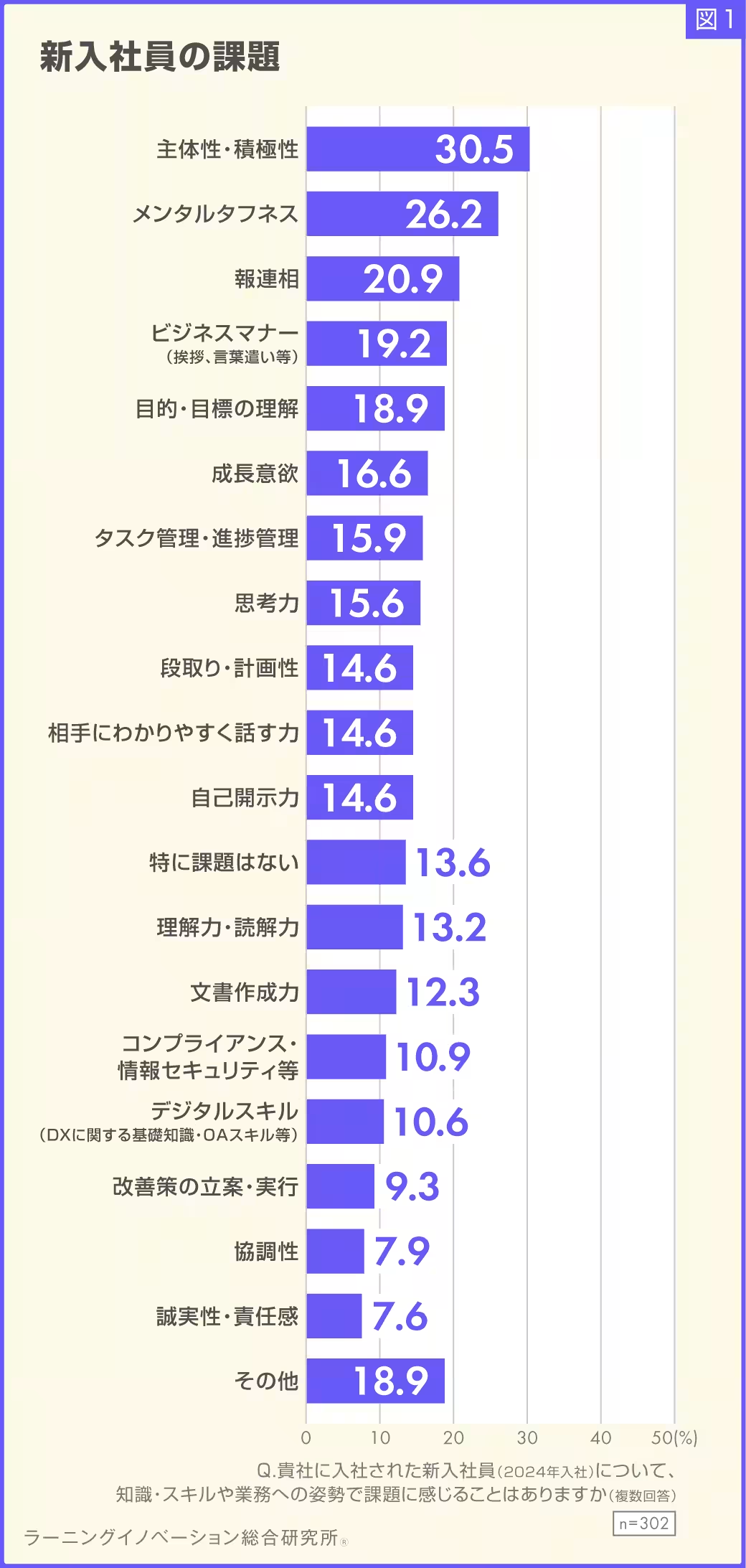
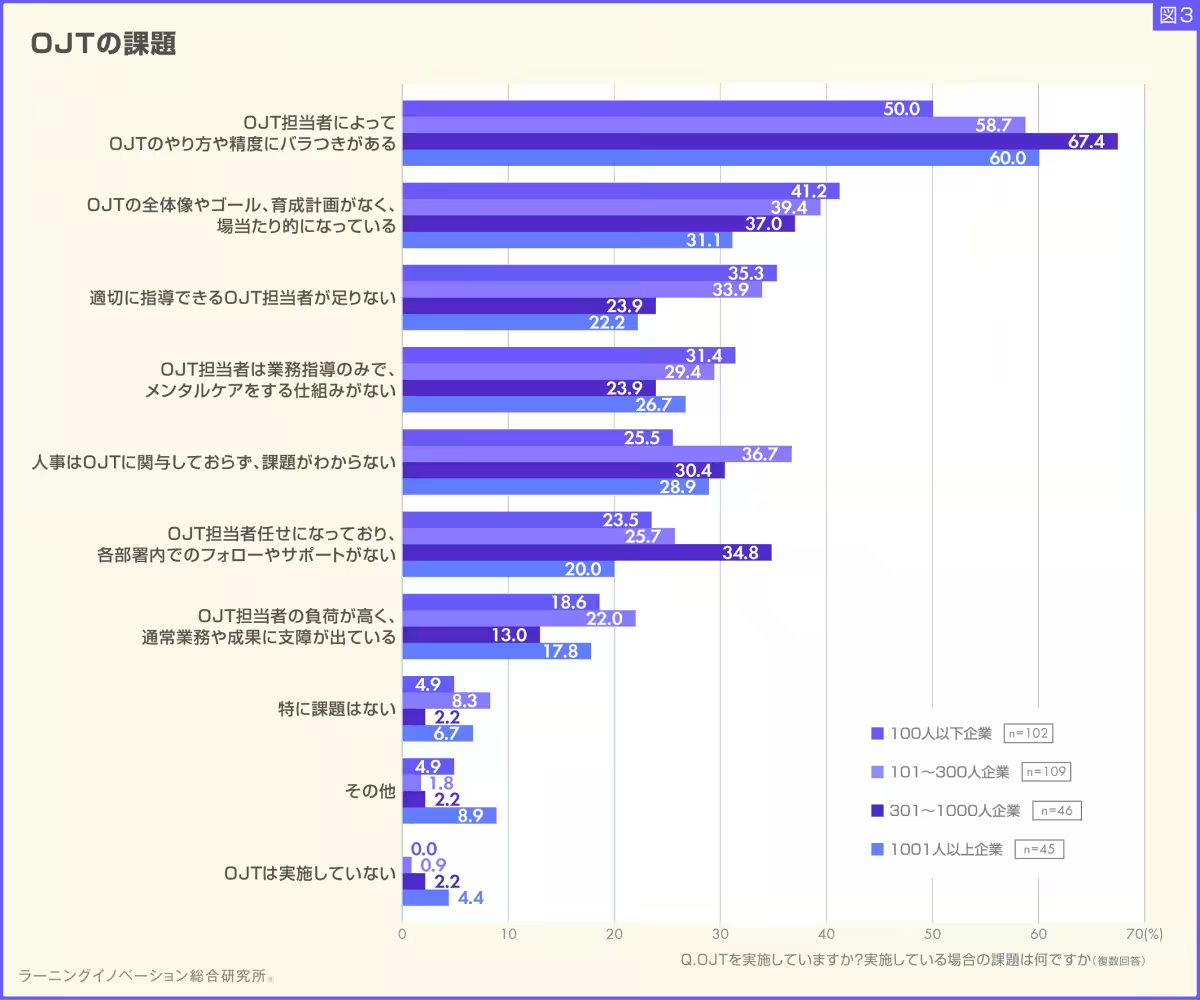
According to the survey, which engaged 302 HR personnel between October 2024 and February 2025, the most pressing challenge cited was the lack of initiative and proactivity among new hires. OJT practices faced criticism due to inconsistencies in execution and effectiveness, primarily attributed to varying approaches by different OJT instructors. In fact, more than 90% of companies actively engage in OJT yet struggle with the quality and uniformity of training.
Analysis of OJT Execution and Variability
A closer examination showed that the inconsistency in training was recognized uniformly across different-sized organizations, highlighting a fundamental need for structured guidelines in OJT processes. Respondents identified a lack of clear objectives, comprehensive training frameworks, and adequate training associated with OJT supervisors. Notably, businesses with smaller workforces (under 100 employees) tended to report a more acute shortage of qualified trainers capable of delivering effective OJT.
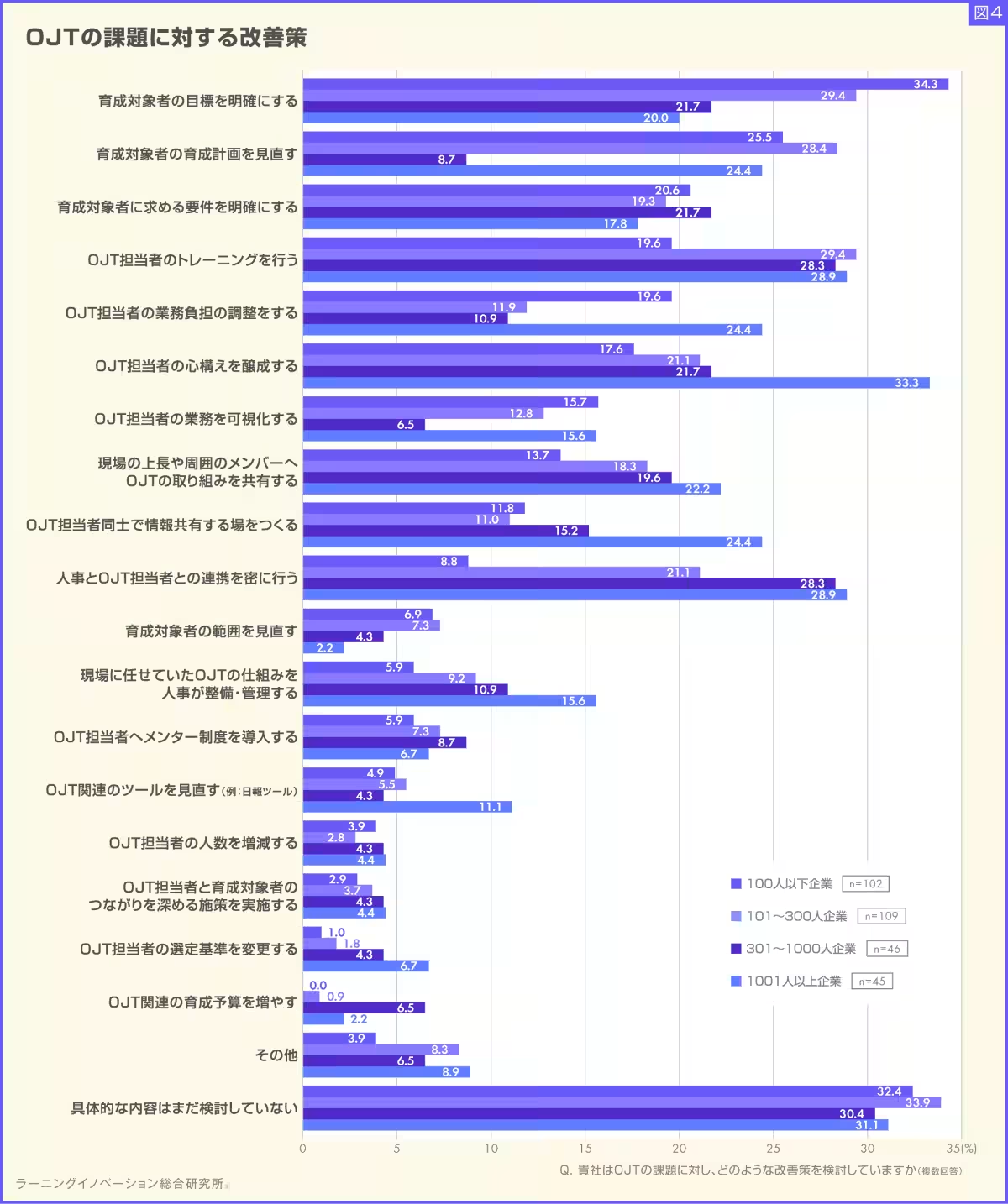
Engagement with Improvement Strategies
Interestingly, when asked about potential solutions to these challenges, over 30% of respondents admitted that they had yet to formulate specific improvement strategies. For companies with fewer than 100 employees, defining clear goals for newly trained staff emerged as a key focus area. Meanwhile, larger organizations prioritized professional development for OJT supervisors to ensure consistency and effectiveness.
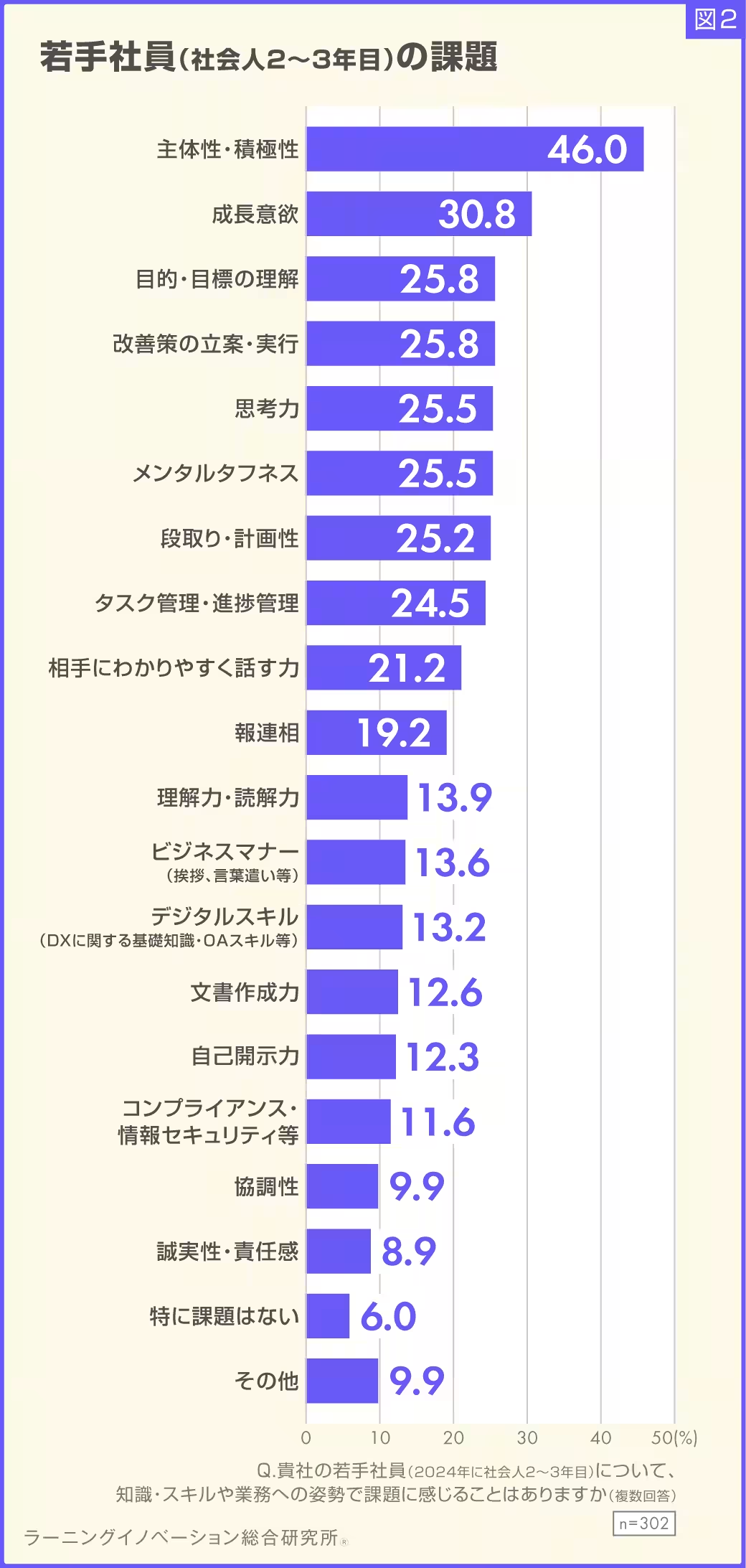
The Role of Proactivity and Initiative in Employee Development
The overarching theme deduced from this research is the critical importance of fostering a sense of proactivity and initiative among young employees. While there are calls for staff to display these qualities in their work conduct, many young workers find the expectations vague and challenging to interpret in practical terms.
Creating a successful OJT program necessitates that HR professionals not only articulate these attributes clearly but also integrate them into structured training plans. Establishing attainable short-term goals such as independent task execution or offering constructive feedback can empower young employees to take charge of their responsibilities.
Practical Steps for Effective OJT Implementation
1. Intentional Approach: Set OJT goals that include not only achieving competency in specific tasks but also nurturing initiative and participation.
2. Systematic Plan: Introduce gradual engagement where initial training focuses on mastering tasks, progress to encouraging proactive input, and eventually aim for independent execution in decision-making situations.
3. Ongoing Support: Continuously monitor employee development and provide constructive feedback, recognizing both achievements and areas for improvement to motivate young workers.
Conclusion
The findings of the survey conducted highlight that HR professionals are acutely aware of the challenges presented in nurturing a proactive workforce through OJT. With many organizations successfully implementing OJT, it remains crucial to consistently evaluate and improve training practices so that young employees can not only meet expectations but exceed them. This structured training approach may ultimately prove instrumental in reducing turnover rates and cultivating the next generation of committed and empowered workers.
About the Authors: Keisuke Nakanishi, a Senior Consultant at ALL DIFFERENT, has extensive experience in organizational training. He leads initiatives in planning and developing training programs, ensuring effective onboarding processes tailored to enhance productivity.
For full survey details and further insights, you can follow the links provided by the Learning Innovation Institute.



Topics People & Culture)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.