
Innovative Technique Produces Biocompatible Microcapsules Without Oils or Surfactants
Innovative Method to Create Safe Microcapsules
In a significant advancement in microcapsule technology, a team led by Ken Hirano from the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) has successfully developed a novel technique to create microcapsules measuring less than 20 micrometers using only biocompatible materials, completely eliminating the need for oils or surfactants. Collaborating with distinguished professors from Doshisha University, including Kenichi Yoshikawa and Akihisa Shioi, the research focuses on creating consistent microdroplets that are essential for various applications in pharmaceuticals, regenerative medicine, cosmetics, and food industries.
Key Developments
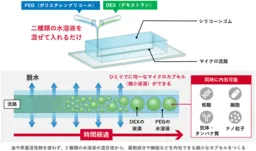
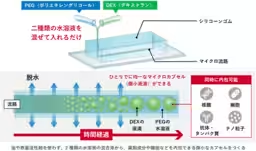
This newly introduced methodology utilizes silicone rubber (PDMS) to fabricate a microfluidic device. The techniques exploit a unique property of PDMS, which allows for dehydration-driven phase separation to develop uniformly sized microcapsules without sophisticated equipment or complex procedures. The system requires only the mixing of two low-concentration aqueous solutions, leading to the automatic formation of microcapsules as the liquid evaporates spontaneously.
This significant technological advancement addresses previous concerns related to safety and environmental impacts usually associated with existing methods that involve oils and surfactants. The new approach not only makes the process eco-friendlier but also fundamentally simplifies production, opening doors for innovative applications wherever microencapsulation is beneficial.
Benefits of Microcapsules
Microcapsules are widely used to encapsulate active ingredients and protect them from environmental factors, thereby preserving their efficacy. They contribute to the controlled release of drugs, enhance the freshness of cosmetic ingredients until application, and prolong the taste and nutritional value of food products. With increasingly stringent regulatory demands surrounding safety and transparency, the market has shown heightened interest in safer, more environmentally friendly encapsulation technologies.
Overcoming Challenges
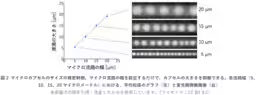
Historically, achieving uniform microcapsules that are both small and consistent in size has been challenging due to the inherent difficulties in using conventional methods involving oils and surfactants. These traditional methods often lead to residual substances within products, raising safety concerns for consumer products such as pharmaceuticals and cosmetics. Furthermore, producing microcapsules smaller than 20 micrometers has been particularly difficult, limiting their applications. The research team’s innovative focus on leveraging the dehydration property of PDMS has successfully cracked this issue.
Research Methodology
To implement this innovative approach, researchers have formulated a microfluidic device made of biocompatible PDMS that employs a micro-channel system. In the experiment, two types of aqueous solutions—polyethylene glycol (PEG) and dextran (DEX)—are mixed at low concentrations to prevent phase separation. When the mixed solution is introduced, water slowly permeates through the PDMS walls, thus increasing the concentration of the solutions, which eventually leads to phase separation and formation of microcapsules. This controlled phase separation results in the formation of microcapsules that are neatly aligned and uniformly sized, achieving sizes below 20 micrometers without complex apparatus.
Future Directions
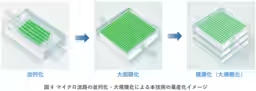
Moving forward, this technology holds promise for expanding its capabilities beyond PEG and DEX systems, allowing for various combinations of polymer materials to optimize specific functionalities tailored to different applications. Additionally, researchers aim to scale up this process by integrating numerous microchannels into a compact platform, enabling mass production of microcapsules. This can significantly enhance the efficiency of manufacturing for diverse industries, including pharmaceuticals, food, and cosmetics.
In conclusion, this groundbreaking technique not only paves the way for cleaner, safer production of microcapsules but also represents a notable advancement in biocompatible product development, offering a platform for versatility and innovation in numerous sectors.
Future publications focusing on this research are expected to address the detailed findings and implications for industry applications, slated for online release in the journal "Small Methods" on June 8, 2025.


Topics Consumer Products & Retail)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.