
Ipsa Unveils Discovery on Moisture Dynamics in Skin's Epidermal Layer
Introduction
Ipsa, a renowned skincare brand, has dedicated over 20 years to researching skin hydration, evolving with unique compound ingredients that hydrate and maintain moisture. Recent advancements allowed them to measure internal skin moisture precisely and visualize water distribution in the stratum corneum. In their latest study, they turned their focus toward the deeper epidermal cell layer, analyzing the mobility of water molecules, leading to a new perspective in skin hydration research.
Research Details
Using confocal Raman spectroscopy, Ipsa assessed water molecules at varying depths. They discovered that skin with high moisture content and strong barrier functions exhibited greater increases in the mobility of water molecules in the epidermal cell layer. Notably, they confirmed that the extract from lemon balm enhances the mobility of these molecules. This paves the way for new moisturizing technologies that not only provide hydration but also improve the internal dynamics of skin moisture.
Background of the Research
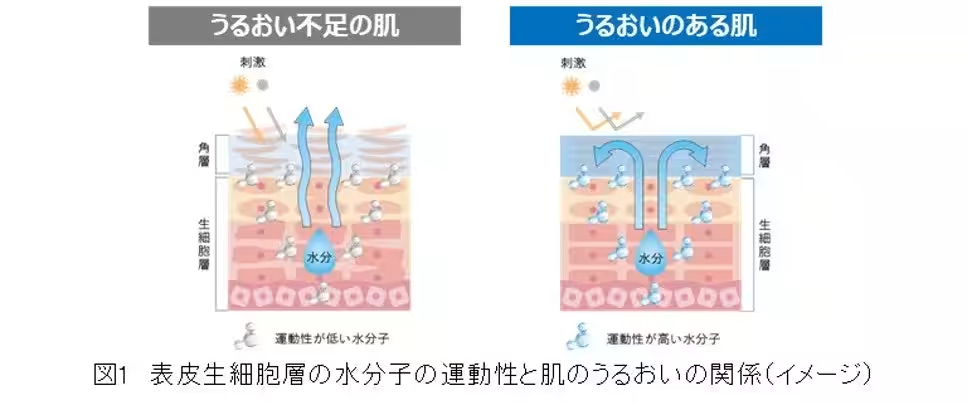
Through observing many individuals' skin conditions, Ipsa noticed discrepancies in perceived hydration and skin states, even with similar moisture levels. This observation sparked the need to address skin issues that traditional methods could not solve, prompting research focusing on one pivotal property of water: mobility. Water, made up of H2O molecules, is constantly in motion, and measuring the mobility at a molecular level revealed crucial insights. High mobility among water molecules typically leads to enhanced enzyme reactions and biological activities. However, much remained unknown about the mobility of water in the epidermal cell layer compared to the stratum corneum. Thus, a study aimed at uncovering the connection between the mobility of water molecules in the epidermal layer and skin condition was initiated.
Analytical Techniques and Findings
Observing water deeply within the skin without invasive methods is challenging, limiting available measurement techniques. The researchers applied confocal Raman spectroscopy to non-invasively measure the mobility of water molecules in the epidermal cell layers.
Key Findings #1
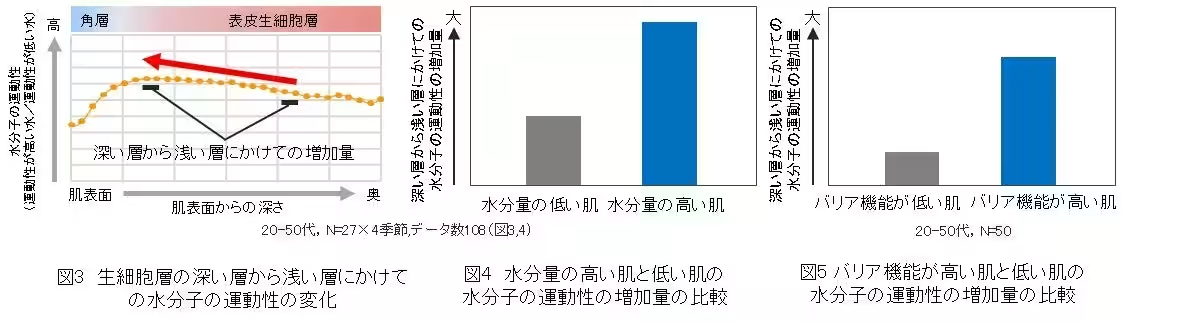
The study determined that skin with high moisture levels and robust barrier functions exhibited significant increases in the mobility of water molecules across various skin depths. The analysis demonstrated a strong correlation between the water content in the stratum corneum and the mobility of water molecules within the epidermis. Specifically, high moisture content directly corresponded to increased mobility from deeper to shallower layers.
Key Findings #2
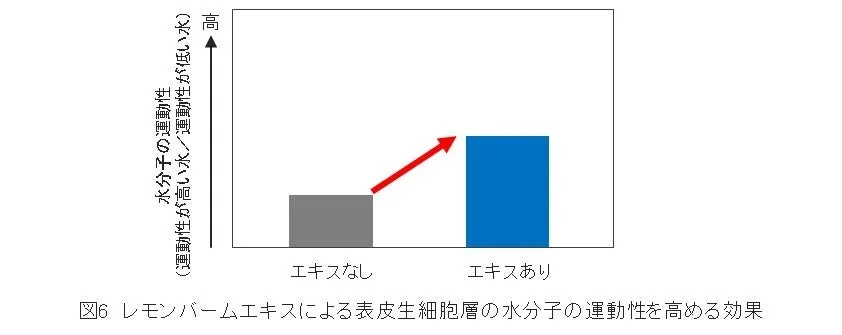
From screening around 200 plant-based ingredients, the study identified that the extract from lemon balm leaves boosts the mobility of water molecules in the epidermal cell layer, enhancing hydration significantly. This discovery is currently under patent application.
Conclusion and Future Prospects
This research has shown that skin with high moisture content and effective barrier functions correlates to increased mobility of water molecules in the epidermal layer. Furthermore, the positive effects of lemon balm extract on this mobility open new avenues for moisturizing approaches. Ipsa aims to harness these insights to deliver new hydration solutions that emphasize inner skin vitality and a radiant complexion.
Ipsa remains committed to its philosophy of "Fullness of skin and mind," focusing on vital elements like water, oxygen, and energy. They will continue to evolve their research to draw out the skin’s inherent beauty power and enhance product experiences with various scientific methodologies.
Ipsa is a brand of Ipsa, Inc., a subsidiary of Shiseido Co., Ltd.
Contact Information
For inquiries, please contact:
Ipsa PR Department: [email protected]
Address: 7-1-16 Akasaka, Minato-ku, Tokyo, 107-0052, Japan
Phone: 03-3405-2432
Website: www.ipsa.co.jp

Topics Consumer Products & Retail)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.