
The Impact of Generative AI on Recruitment Activities: A Comprehensive Survey
Understanding the Role of Generative AI in Recruitment Activities
A recent survey conducted by HERP, a Tokyo-based company, explored the current state of generative AI in recruitment activities. This survey involved 181 executives, HR managers, and recruiters, and aimed to shed light on how companies are leveraging AI in their hiring processes.
Key Findings of the Survey
The study uncovered several significant insights:
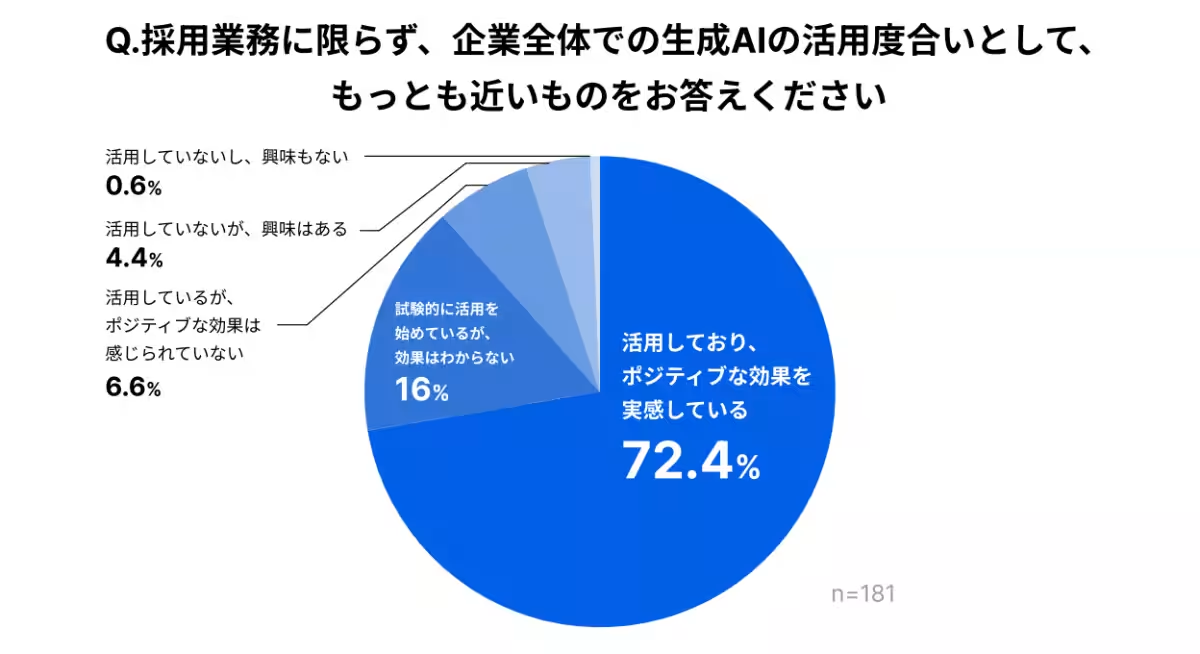
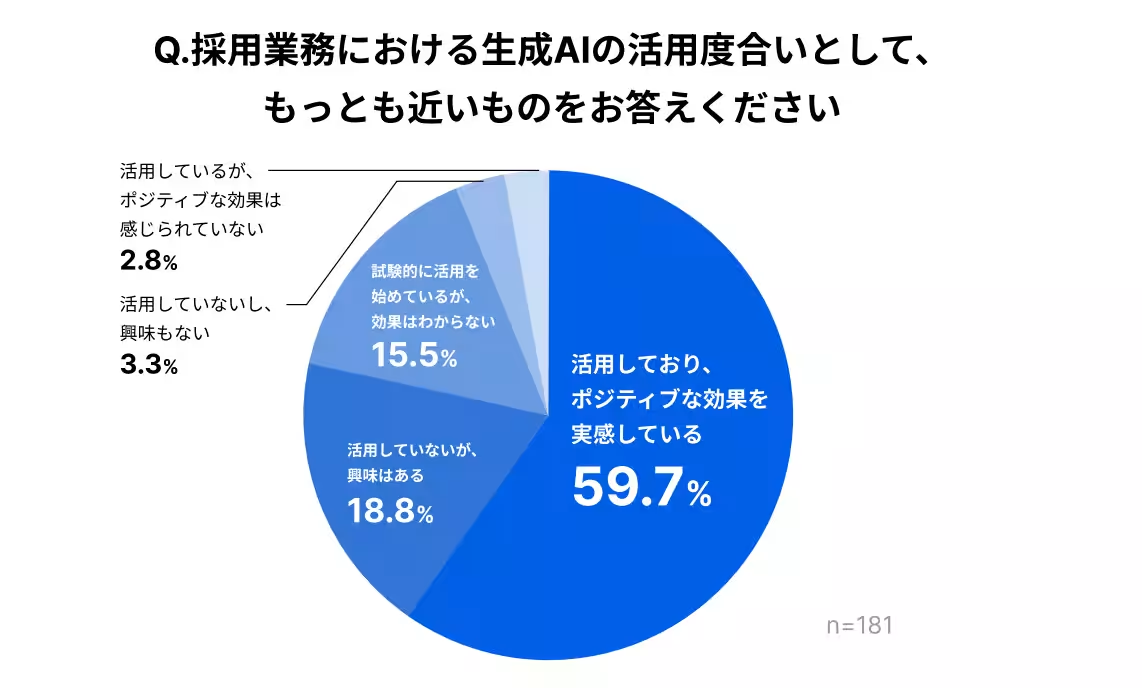
- - AI Utilization: An impressive 95% of companies reported using generative AI in various capacities, with 78% specifically utilizing it in recruitment processes. Among these, 76.6% of respondents acknowledged that they experienced positive impacts from its usage.
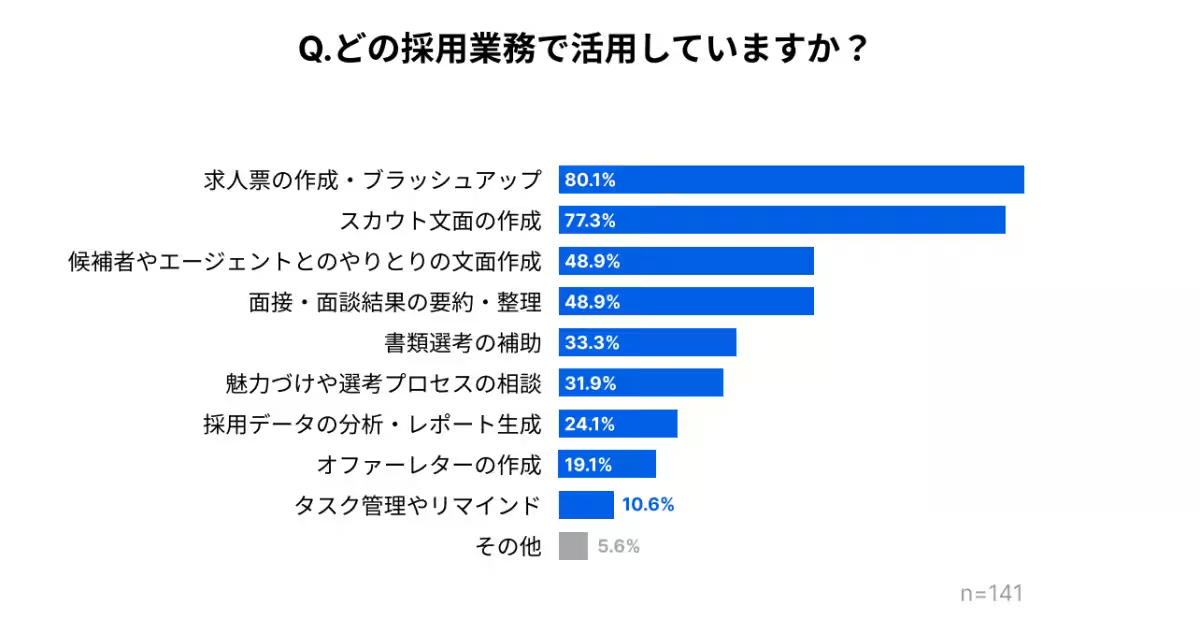
- - Common Applications: When asked about specific applications of AI in recruitment, the majority pointed to the creation and refinement of job postings, with 80.1% of respondents stating that this was a primary use case. Other notable applications included crafting scouting messages (77.3%) and preparing communication for candidates and agents (48.9%).
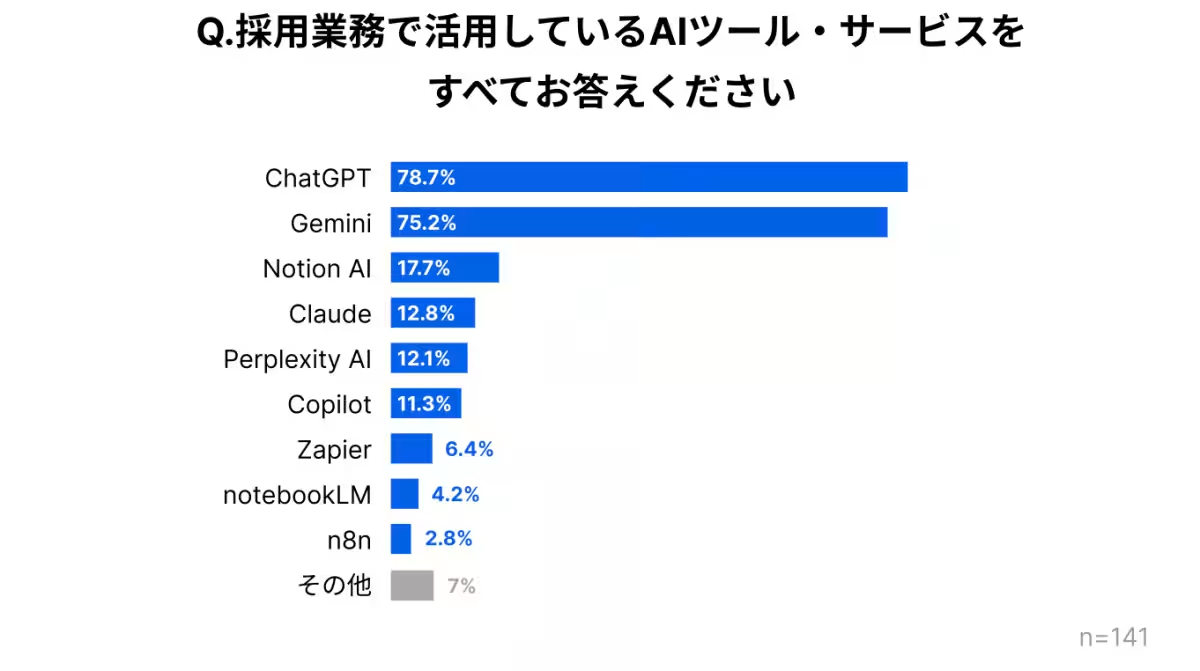
- - Popular Tools: The tools most frequently used in recruitment include ChatGPT (78.7%) and Gemini (75.2%), showcasing a trend towards widely adopted AI platforms that enhance efficiency in hiring processes. Other tools mentioned include Claude and Perplexity AI, along with workflow automation tools like Notion AI and Zapier.
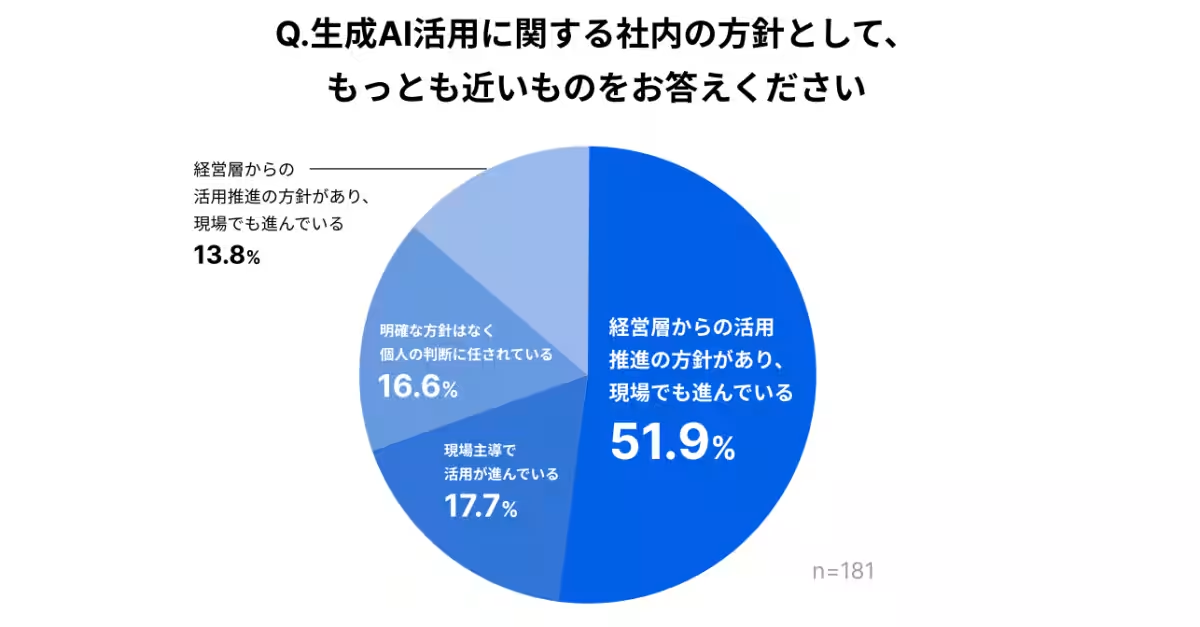
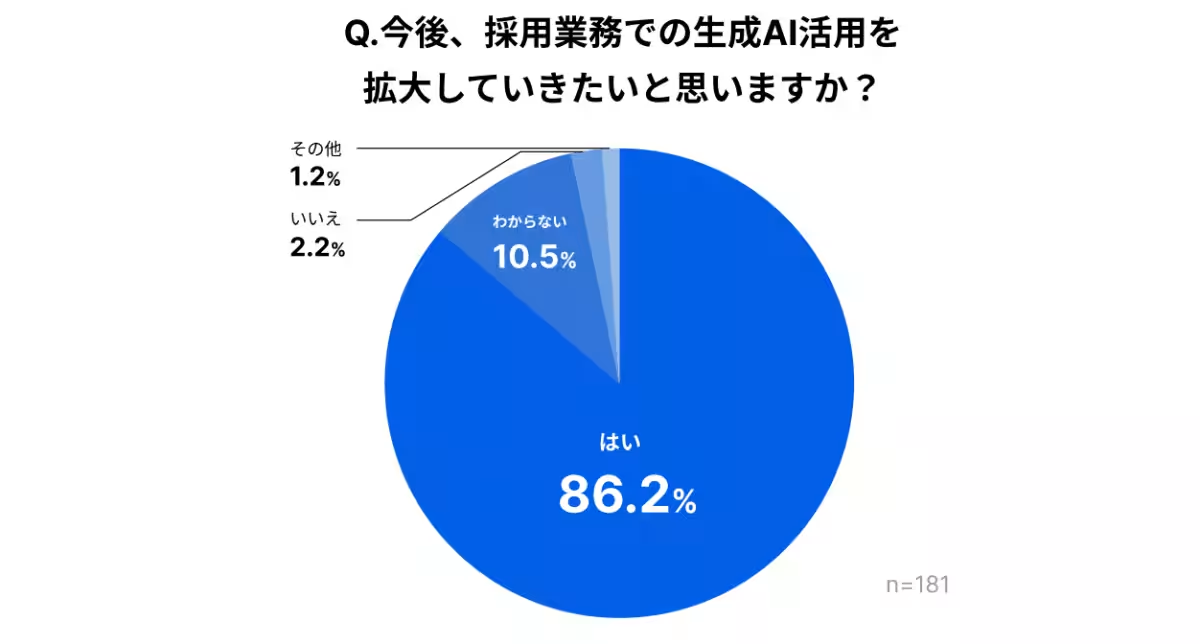
- - Executive Support: More than half of the respondents indicated that there is a strong push from executive management to embrace AI in recruitment, with a majority stating that this drive is evident at the operational level. Specifically, 86.2% expressed a desire to expand the use of AI within their hiring practices.
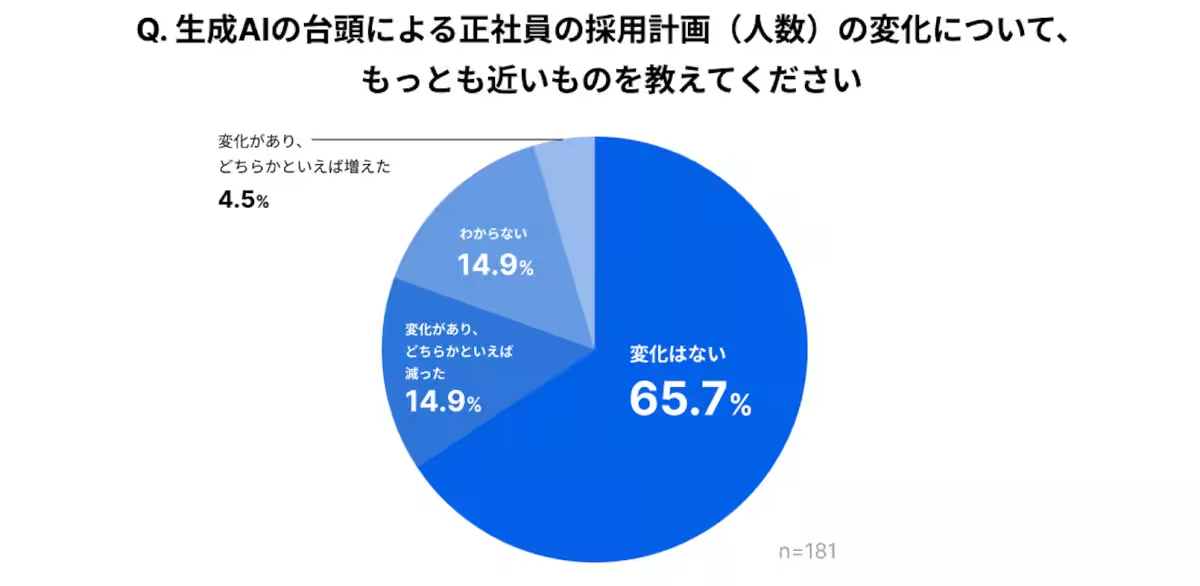
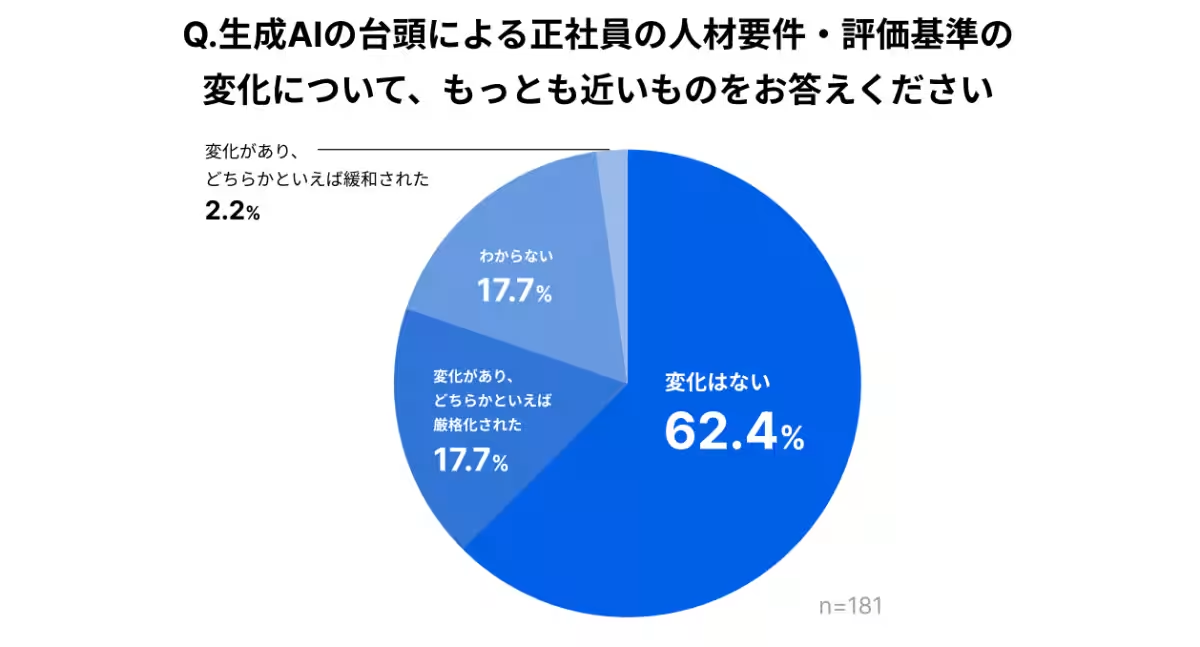
- - Limited Impact on Hiring Standards: Despite the heightened adoption of AI, many companies reported minimal changes to hiring numbers or evaluation criteria. About 65.7% of respondents believe there has been no change in recruitment numbers. Similarly, 62.4% stated that there hasn't been any modification in the criteria or standards for evaluating potential candidates.
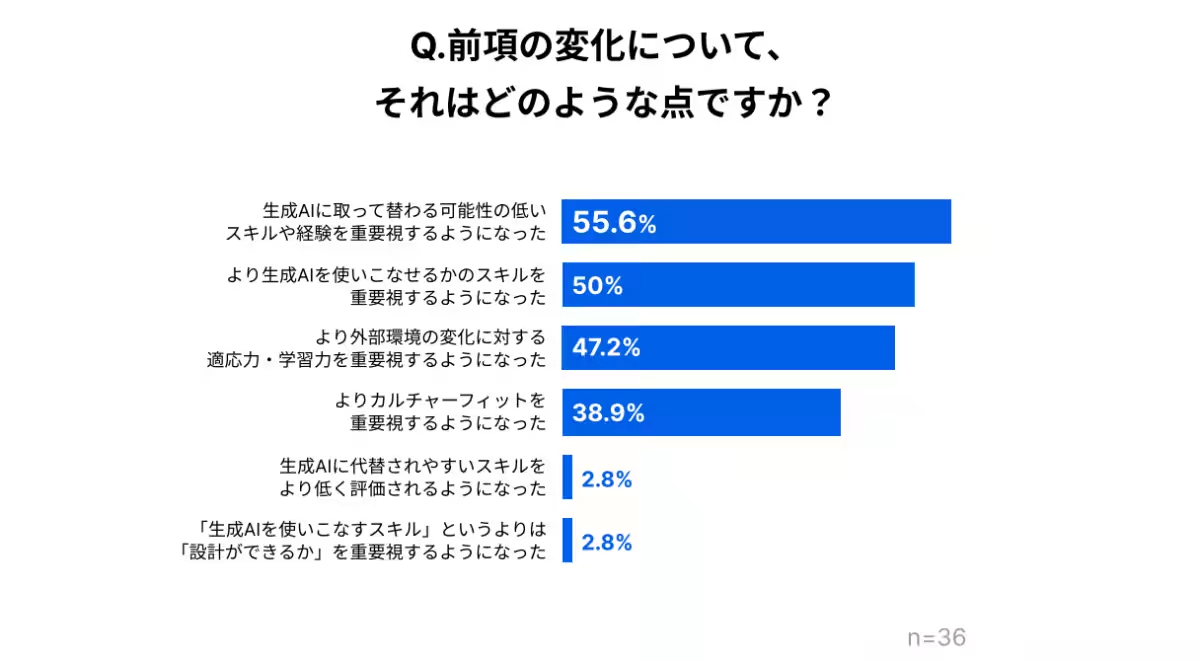
- - Focus on Skills: Among companies that acknowledged a change in their evaluation criteria, there was a noticeable shift towards valuing skills that are less likely to be automated by AI, alongside the ability to utilize AI effectively in their roles. Answers to open-ended questions revealed a heightened demand for experienced leadership that can manage teams and processes involving AI.
Real-World Applications in Hiring
Reflecting on the evolving landscape of recruitment, specific responses from companies highlighted the following:
- - Emphasis on Leadership: Companies are increasingly seeking higher-level candidates with management capabilities, as generative AI can handle routine tasks that entry-level roles typically perform.
- - Skill Evaluation: During technical assessments, companies are focusing on the approaches candidates take rather than simply grading them on the right or wrong answers. This shift implies a significant interest in how candidates apply AI tools in practical scenarios.
- - Enhanced Evaluation Criteria: Incorporating AI skills as a factor in performance assessments has lifted the standards for recruitment, necessitating a more thorough evaluation of potential hires.
Furthermore, HERP has announced an upcoming online seminar titled "Generative AI x Recruitment Activities: Insights from a Survey of 180 Companies," scheduled for September 3, 2025. This session will delve into real-world applications of AI in recruitment, featuring success stories from leading firms like UPSIDER.
Conclusion
The findings from HERP's survey underscore the transformative role of generative AI in modern recruitment practices. As companies continue to integrate these technologies, understanding the implications for both hiring processes and candidate evaluations will be crucial. For organizations struggling to navigate this landscape, leveraging AI adeptly can provide a competitive edge in attracting top talent. More details on the seminar and the survey can be found on the HERP website and associated links.
For more information, visit: HERP


Topics People & Culture)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.