

Understanding CIRCIA: New Cybersecurity Regulations Impacting Critical Infrastructure in the U.S.
Understanding the CIRCIA Regulation and Its Impact
In recent years, cybersecurity has emerged as a top priority for governments and industries alike. One of the most substantial developments in this arena is the introduction of the CIRCIA (Cyber Incident Reporting for Critical Infrastructure Act of 2022) in the United States. This significant regulation mandates that operators of critical infrastructure report any cyber incidents within 72 hours. The introduction of CIRCIA aims to enhance the resilience of the nation's infrastructure against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats, as evidenced by high-profile incidents such as the SolarWinds hack and the Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack.
What is CIRCIA?
CIRCIA represents a pivotal shift in how the U.S. government expects industries to respond to cyber threats. By requiring timely reporting of incidents, the law not only aims to improve the cybersecurity stance of critical infrastructure sectors but also serves as a preventative measure against larger scale disasters. Non-compliance with these directives can lead to severe penalties, including substantial fines and the potential suspension of federal contracts, emphasizing the seriousness with which this regulation is viewed.
The Dual Focus: Prevention and Incident Response
CIRCIA is not the only legislative move in the U.S. aimed at bolstering cybersecurity. Alongside CIRCIA, President Biden issued Executive Order 14028, which directs federal agencies to adopt 'security by design' principles in procurement practices. The national standards set forth by the NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) further contribute to this comprehensive strategy. The Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) and various SP800 series guidelines offer technical guidance that complements CIRCIA, while the CMMC (Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification) ensures compliance with these standards through a structured certification process. This multi-layered approach is designed to create a robust cybersecurity framework across industries.
Global Implications: Japanese Manufacturing Industries
The impacts of CIRCIA extend beyond U.S. borders, particularly affecting Japanese manufacturing sectors. The law applies to critical infrastructure defined under the U.S. presidential directive PDD-21, which encompasses 16 sectors, including semiconductor manufacturing, machine tools, and marine equipment—fields where Japan excels. For Japanese suppliers that provide components to U.S. critical infrastructure sectors, adherence to the reporting requirement is crucial, creating a domino effect. This means that supply chain partners must implement rapid detection and communication mechanisms to ensure compliance within the mandated 72-hour window.
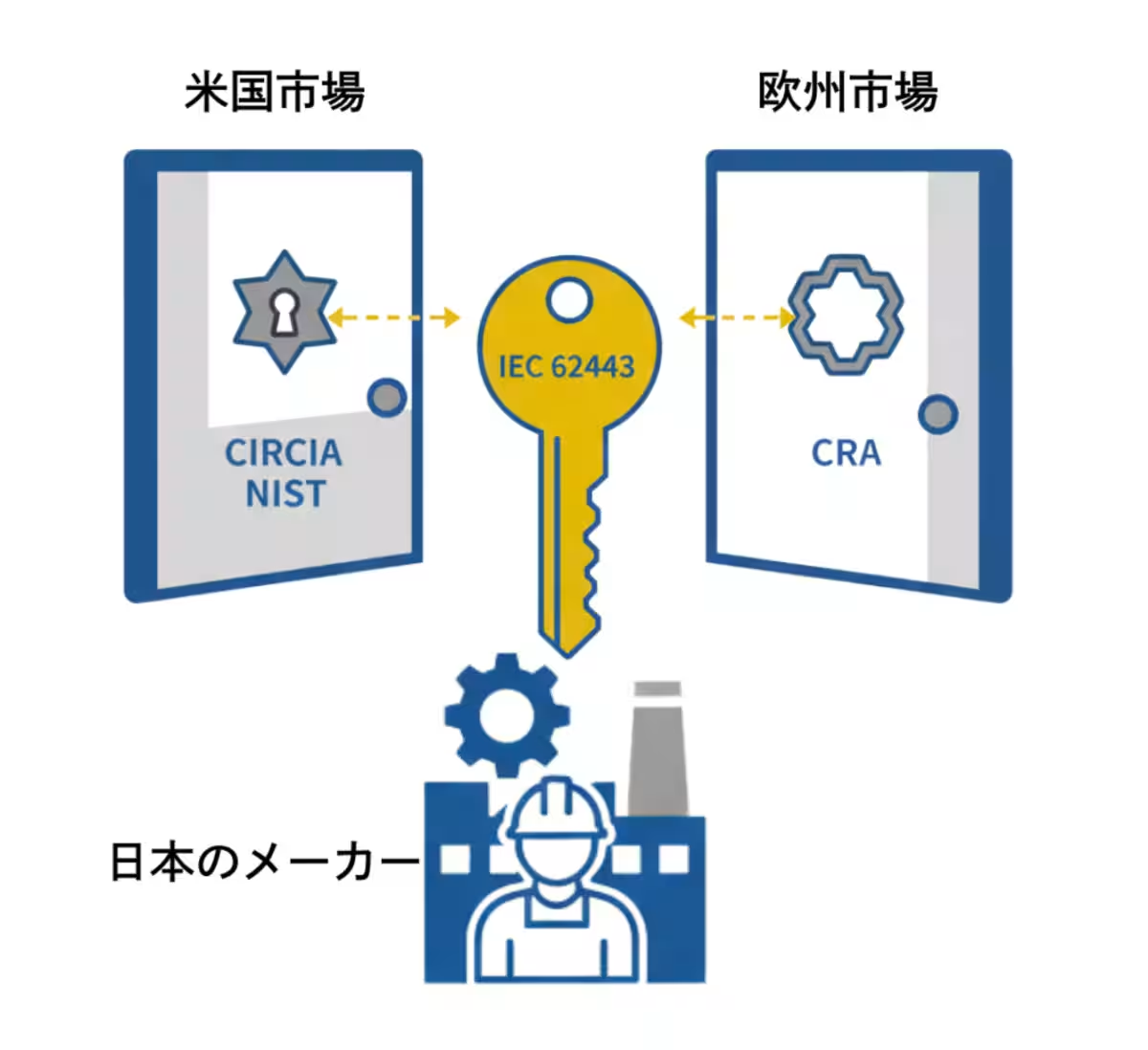
The Common Language of IEC 62443
In addressing the complexities of international and regional regulations, such as CIRCIA and the European Cyber Resilience Act (CRA), the ICS Laboratory proposes a unified framework based on the international standard IEC 62443. This standard offers a common language that manufacturers can adopt to bridge the varying demands of different markets. By applying IEC 62443 as a central pivot, companies can efficiently address compliance across the U.S., Europe, and Asia, reducing inefficiencies created by disparate regulations.
A Shift Towards Proactive Security
As global cybersecurity regulations increasingly influence manufacturing processes and design elements, organizations must shift their mindset from being passive recipients of security measures to becoming proactive defenders of their systems. The ICS Laboratory aims to empower employees on the front lines of manufacturing by providing accessible information that helps them make informed security decisions.
The transition from a defensive position to one of active protection is crucial for establishing a sustainable industrial security landscape. As part of its ongoing commitment to safeguarding the future of manufacturing, the ICS Laboratory continues to share insights and guidance in navigating the evolving cybersecurity landscape.
Upcoming Series on CIRCIA
A series of articles titled "Understanding CIRCIA" will explore the various facets of the regulation and its implications in depth:
1. The New Normal in the U.S. Market: CIRCIA and Cybersecurity Executive Orders
2. Analyzing the NIST SP800 Series: Technical Standards for Manufacturing Compliance
3. The Common Language of Regulations: An Integrated Approach Using IEC 62443
4. The 72-Hour Challenge: Practical Processes for Incident Reporting under CIRCIA
5. Implementing Cyber Resilience: Incorporating Resilience Design into Supply Chains
6. Industry Sectors Focus (1): Key Implementation Points in Semiconductor and Machine Tool Manufacturing
7. Industry Sectors Focus (2): Key Implementation Points in Marine and Shipbuilding Industries
8. The Final Chapter on Proactive Compliance: How Third-Party Certification Can Drive Business Forward
Stay tuned for these articles, which will be published on the ICS Laboratory’s dedicated CIRCIA feature page. Through these discussions, ICS Laboratory seeks to advocate for the interpretation of international regulatory changes as opportunities for growth and innovation within the manufacturing sector.
About ICS Laboratory
Founded in 2015, ICS Laboratory specializes in consultancy for control system security and support for obtaining IEC 62443 certification. They also offer e-learning services and skill assessments in control system security. Based in Tokyo, Japan, ICS Laboratory is committed to leading discussions around the future of manufacturing security.
For more information, visit ICS Laboratory.

Topics Business Technology)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.