

Innovative Methanol Bunkering at Yokohama Port: A Maritime First
Innovative Methanol Bunkering at Yokohama Port
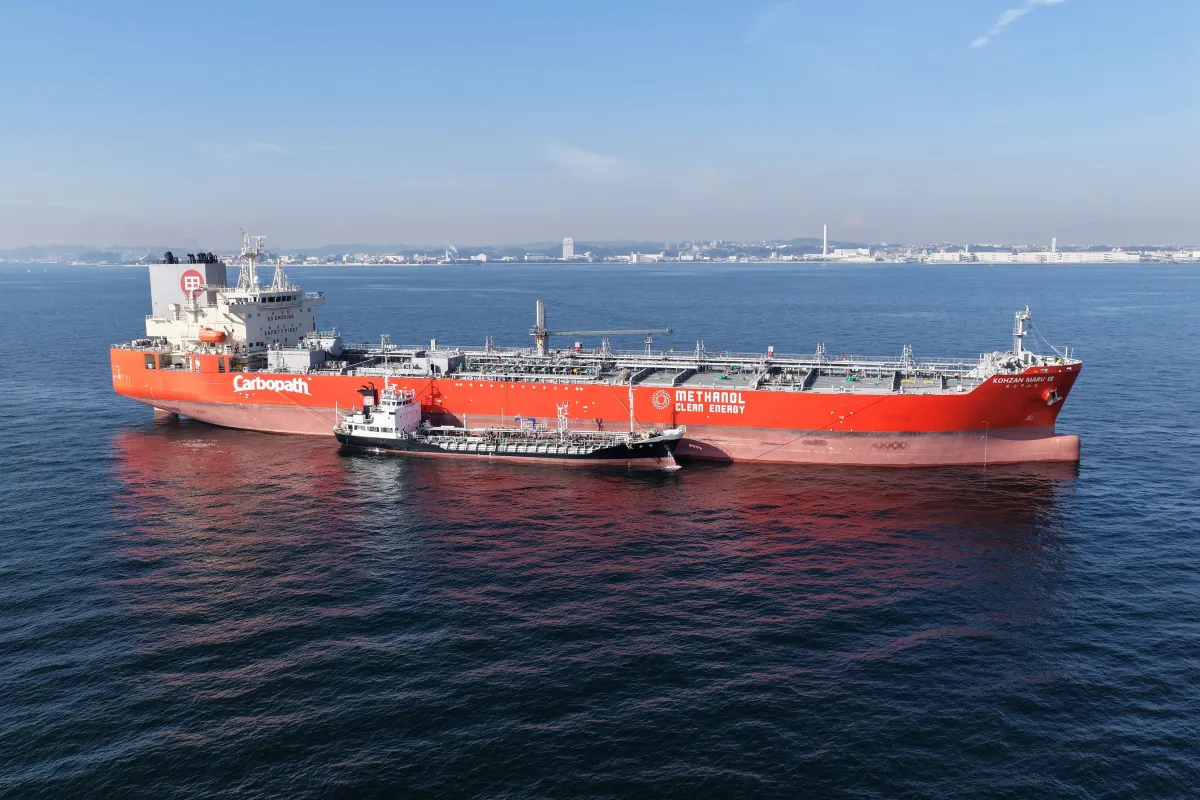
On February 6, 2026, a groundbreaking methanol bunkering operation was successfully executed at the anchorage of Yokohama Port, marking a significant milestone in Japan's maritime fuel industry. This innovative project saw the participation of Mitsui O.S.K. Lines, Kunika Sangyo, Idemitsu Kosan, and Mitsubishi Gas Chemical, collectively known as the five stakeholders involved.
The operation utilized the methanol dual-fuel ocean-going vessel, the "Dai-nana Koyama Maru," which is operated by Mitsui O.S.K. Lines, and the methanol transport coastal chemical tanker, the "Eika Maru," operated by Kunika Sangyo. This first-ever ship-to-ship (STS) methanol bunkering occurred in Japan in an anchorage setting, setting the stage for future developments in this area.
Overview of the Operation
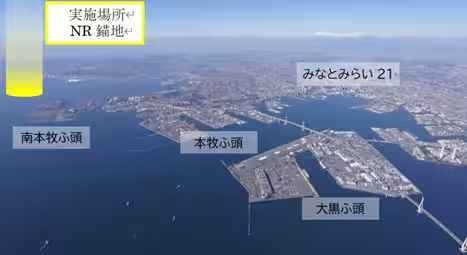
- - Date: February 6, 2026
- - Location: NR anchorage at Yokohama Port
The two ships involved in this historical operation have notable specifications:
| Ship Name | Dai-nana Koyama Maru | Eika Maru |
|---|---|---|
| ----- | ---- | ------- |
| Gross Tonnage | 29,969 tons | 498 tons |
| Deadweight Tonnage | 47,960 tons | 1,259 tons |
| Operator | Mitsui O.S.K. Lines | Kunika Sangyo |
Methanol, a vital chemical intermediate, is widely utilized across various industries and recognized as a clean fuel source due to its significantly lower emissions of CO2 and other pollutants compared to traditional bunkering fuels like heavy oil. The maritime industry is increasingly looking to alternative fuels to meet greenhouse gas (GHG) reduction goals, and methanol is gaining traction due to its compatibility with existing infrastructures and its potential for significant emissions reductions.
Furthermore, during this operation, domestically produced bio-methanol from Mitsubishi Gas Chemical's Niigata plant was supplied, intended for use on the "Dai-nana Koyama Maru" during its operations.
Regulatory Framework
The procedure and safety measures related to methanol bunkering were delineated in a committee organized by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT) from 2024 to 2025. This operation's successful execution was made possible through the collaborative efforts of stakeholders, including simulations conducted in September 2024 to gather insights into safe and efficient methanol bunkering practices.
This anchorage-based bunkering not only serves as a practical solution already in use for traditional marine fuels but positions methanol bunkering as a favored method due to its projected increase in demand.
This project sets a new precedent for domestic methanol bunkering practices and contributes significantly to the establishment of a robust methanol bunkering infrastructure in Japan. Continuous collaboration among stakeholders will ensure the ongoing development of methodologies that can extend to various vessel types and regions within Japan.
Future Directions
Since launching the world's first dual-fuel vessel in 2016, Mitsui O.S.K. Lines has expanded its fleet to include eight methanol dual-fuel vessels, making it one of the largest operators of methanol tankers worldwide. Under its Environmental Vision 2.2, the company aims to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050 while introducing clean energy solutions as part of this initiative. The target is to deploy 90 LNG/methanol fuel ocean-going vessels by 2030.
Company Spotlights
1. Idemitsu Kosan: Engaged in the development, manufacturing, and sale of diverse energy sources and materials, with a focus on carbon neutrality by 2050.
2. Kunika Sangyo: A maritime company that has expanded into the domestic and international market since its founding in 1947, focused on safe operations and stringent quality management.
3. Mitsubishi Gas Chemical: Driving the agenda of environmental circular economy with its initiatives focused on the recycling of CO2 and waste into methanol for diverse applications.
4. Yokohama City: Aiming to develop a carbon-neutral port by 2050, promoting energy transition through collaboration with national and private sector partners.
This initial operation paves the way for more widespread adoption of methanol bunkering, reinforcing Japan's commitment to innovation and sustainability in maritime fuel technology.


Topics Energy)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.