
The Rise of Qilin: Japan's Most Active Ransomware Group in 2025
The Rise of Ransomware in 2025: Spotlight on Qilin
Check Point Software Technologies (Check Point) unveiled its quarterly ransomware report for Q3 2025, revealing alarming trends in cyber threats. Despite law enforcement efforts leading to multiple arrests earlier in the year, ransomware attacks have reached unprecedented levels. This report covers not just statistical data but also insights into the shift in attacker methodologies and the emergence of new groups.
Overview of Ransomware Attacks
The latest findings indicate that ransomware incidents initiated by 85 different extortion groups soared to 1,592 new attacks, marking a staggering 25% increase from the previous year. One notable player this year has been the Qilin group, whose recent attention-grabbing attacks include one targeting Asahi Group Holdings, a major Japanese beverage company. Qilin has significantly ramped up its activities, averaging 75 attacks per month in the third quarter alone, nearly doubling their operational volume since the start of the year.
Although well-known groups such as RansomHub and 8Base have disappeared, the landscape is seeing a rapid rise of smaller, emergent teams, contributing to a fragmented Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) market. Interestingly, while the top ten active groups accounted for 56% of total attacks, this is a decrease from 71% at the beginning of the year, showcasing how widespread and decentralized the ransomware ecosystem has become.
The Impact of Qilin
Qilin first emerged around July 2022 but has quickly ascended to become the most active ransomware group in 2025. Its recent activities emphasize not only technical skills but also strategic targeting across industries and regions, particularly in Japan. In September, Qilin publicized its claim of responsibility for the attack on Asahi Group, prominently displaying the names of various Japanese companies on their leak site, raising concerns over future threats to the nation.
Furthermore, Qilin has executed a series of 30 attacks on the South Korean financial sector from August to September. Their affiliate sharing model, boasting up to an 85% revenue-sharing rate, makes it one of the most appealing programs in the RaaS market today.
Marketing Innovations in Cybercrime
In addition to Qilin, the emerging group DragonForce is distinguishing itself by focusing on branding rather than technology. They have publicly allied with infamous groups like LockBit and Qilin, providing services such as data audit to identify high-value files for affiliates, effectively rebranding cyber extortion as a legitimate business practice. DragonForce has also reported 56 incidents in the past quarter, mainly targeting high-revenue sectors in Germany.
Ransomware Target Areas and Perpetrators
Ransomware threats are pervasive across numerous regions. The United States alone accounts for nearly 50% of global ransomware incidents, with Qilin's campaigns pushing South Korea into the top ten for the first time, particularly targeting its financial sector. European nations such as Germany, the UK, and Canada are increasingly becoming hotspots for ransomware actors like INC Ransom, Safepay, and DragonForce.
Industries most affected include manufacturing and business services, each representing about 10% of all attacks. The healthcare sector, while less frequently targeted due to regulatory scrutiny, remains vulnerable to cyber threats, albeit at a slightly reduced rate of 8%.
The Resilience of Ransomware Groups
Despite numerous crackdowns by law enforcement agencies, the monthly ransomware attack count remains stable, fluctuating between 520 to 540 incidents. This persistence raises questions about the effectiveness of current strategies against these cybercriminals. Affiliates swiftly transition to new groups or form new clusters, maintaining an overall steady attack volume despite the temporary collapse of specific factions.
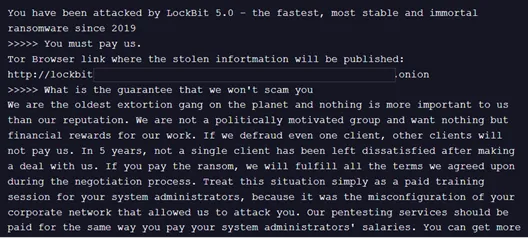
Notably, LockBit, which was thought to be defunct, has made a comeback as LockBit 5.0, introducing advanced features such as multi-platform support and enhanced evasion capabilities. This resurgence reflects the need among affiliates for reliable RaaS platforms.
Future Outlook and Recommendations
Looking towards the latter half of 2025, experts predict an ongoing trend of diversification among smaller groups alongside the consolidation of historically prominent brands. Organizations are advised to enhance endpoint and network defense, maintain immutable backups offline, educate employees on phishing risks, and actively monitor emerging RaaS infrastructures.
Conclusion
Ransomware continues to be one of the most adaptive and lucrative forms of cybercrime well into 2025. The ongoing battle of decentralization and subsequent re-consolidation will shape the threat landscape for the coming years. As the ransomware ecosystem evolves, preparedness and robust cybersecurity measures will be essential for organizations to mitigate risks.
Topics Other)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.