
Groundbreaking Research on Filtration Technology Impacts Biotechnology and Medical Diagnostics
Groundbreaking Filtration Technology in Biotechnology
A team of researchers from Gel Coat Biomaterials, the University of Tokyo, and Daisen Membrane Systems has recently published groundbreaking findings in MRS Communications. Their work addresses a longstanding issue in biotechnology and medical diagnostics: the challenge of filter fouling during separation and purification processes. This remarkable achievement has the potential to redefine industry standards and present a decisive solution in the filtration and separation market, which exceeds $25 billion annually.
The Challenge of Filter Fouling
In the medical and pharmaceutical fields, the separation and purification of specific proteins and cells—such as vaccines and drug delivery systems—are vital. However, traditional hollow fiber membrane filters face significant challenges. Proteins adhere to the membrane surface and pores, leading to fouling that diminishes separation performance. This fouling results in decreased processing speed and reduced filter lifespan, necessitating frequent replacements and causing operational costs to rise.
The new paper develops a unique coating technology that effectively suppresses this fouling and provides robust proof of its efficacy.
Technological Advantages
The standout feature of this technology lies in its simultaneous achievement of two crucial properties: a resistance to protein adsorption and a strong adhesion stability to the membrane. The hydrogel coating employed in this research combines three types of molecules, each serving distinct functions:
1. Hydrophilic Units: These repel proteins, preventing their adsorption.
2. Hydrophobic Units: They cling to the membrane's surface, stabilizing the coating.
3. Interface-Bonding Units: They form a strong bond to the membrane, making it resistant to delamination.
In general, increasing coating thickness can help prevent fouling but may decrease water permeability. However, the hydrogel from Gel Coat Biomaterials maintains an exceptional balance:
- - High Permeability: It retains over 50% of water flux compared to uncoated membranes.
- - Outstanding Anti-Fouling Performance: It dramatically curbs fouling caused by large proteins like gamma globulin.
- - Uniform Coating: A thin and uniform coating of just 20 nanometers is successfully formed on the inside of the hollow fibers.
Research Outcomes
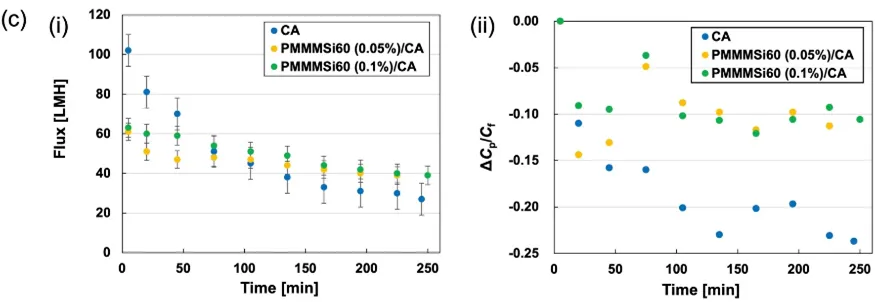
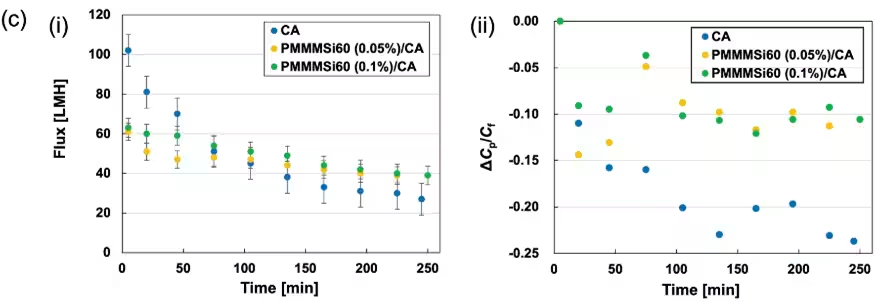
Graphs presented in the paper illustrate the significant advances achieved. One graph shows how the water flux changes over time:
- - Uncoated Cellulose Acetate Membrane: Initial high flux decreases significantly over time.
- - PMMMSi60 Modified Membrane: Displays a minor decline and ultimately exceeds the performance of the uncoated membrane.
This demonstrates the substantial advantage provided by the modified membrane in long-term manufacturing processes, confirming its reliability and effectiveness.
Future Applications and Market Impact
The implications of this technology extend broadly:
- - Cross-Platform Applicability: Originally demonstrated on cellulose acetate membranes, the principles can apply to medical polymers like silicone rubber and other plastics.
- - Customization: Adjusting the monomer's composition allows for tailored coatings for specific target proteins and operational environments.
The simplicity of the dip-coating method streamlines the manufacturing process, requiring no specialized equipment—only the circulation and heating of the solution for drying. This enables the production of high-quality products at reasonable costs.
Specific Use Cases
This technology offers high value in several critical sectors:
- - Vaccine and Pharmaceutical Filtration Market: Projected to reach $14.27 billion by 2026, with significant improvements in flow rates reducing protein adsorption.
- - Medical Devices and Hemodialysis Membranes: Market estimated at $10.31 billion, enhancing safety and lowering the frequency of consumable replacements.
- - Next-Gen Blood Diagnostics: Projected to grow to $450 million in 2026, improving speed and efficiency in cancer diagnostics via exosome recovery.
Overall, this technology offers a decisive solution to the fouling problem, providing substantial cost savings, consistent quality, and enhanced processing capabilities. Researchers interested in the hydrogel coatings or the details of the conducted study are encouraged to reach out to Gel Coat Biomaterials.
Conclusion
The research detailed in this paper represents a significant advance in the filtration technology field, with the potential to reshape industry standards. The hydrogel coating system developed by Gel Coat Biomaterials opens the door for vast improvements in the purification processes that are critical to both the pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries.
Topics Health)









【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.