

Exploring Work Engagement Factors Influencing Employee Retention in Japan
Analyzing Work Engagement of Employees at Risk of Leaving
Dreamhop Inc. has recently conducted an analysis of stress check data with the aim of understanding the varying levels of work engagement between current employees and those likely to leave within a year. This study showcases critical insights for organizations striving to enhance employee retention and wellbeing.
Background and Objectives of the Study
In a dynamic job market, retaining top talent is a pressing concern for many organizations. Dreamhop, led by President Mamoru Okaza and based in Chiyoda, Tokyo, has been dedicated to supporting businesses not only in compliance with stress check regulations but also in promoting healthier work environments. Through this analysis, the company sought to provide objective evidence and guidance that could help businesses in effective employee management, ultimately contributing to enhanced operational productivity.
Research Overview
Study Focus
The primary theme of the study was to compare stress factors influencing workplace retention among current employees and those who left within one year of taking a stress check.
Data Collection Period
The data was sourced from stress checks carried out between 2019 and 2022, employing the short occupational stress questionnaire.
Participants
The analysis involved results from Dreamhop’s stress check tool, ORIZIN, encompassing data from 105 companies with around 3,700 active employees and approximately 25,000 workers who left within a year.
Methodology
Using anonymized stress check responses, cross-tabulation and multivariate analysis were utilized to examine stress factors and engagement levels.
Sectors and Company Sizes
The study incorporated diverse sectors, including construction, services, manufacturing, and IT, with participating companies ranging from about 20 to 30,000 employees.
Key Findings
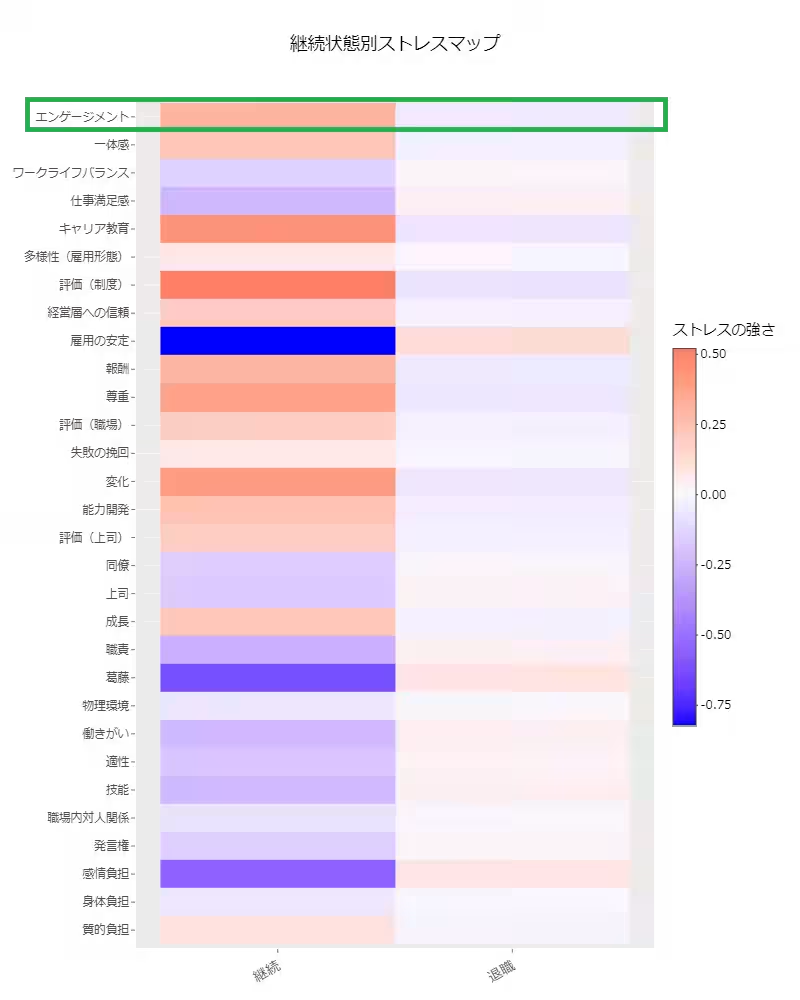
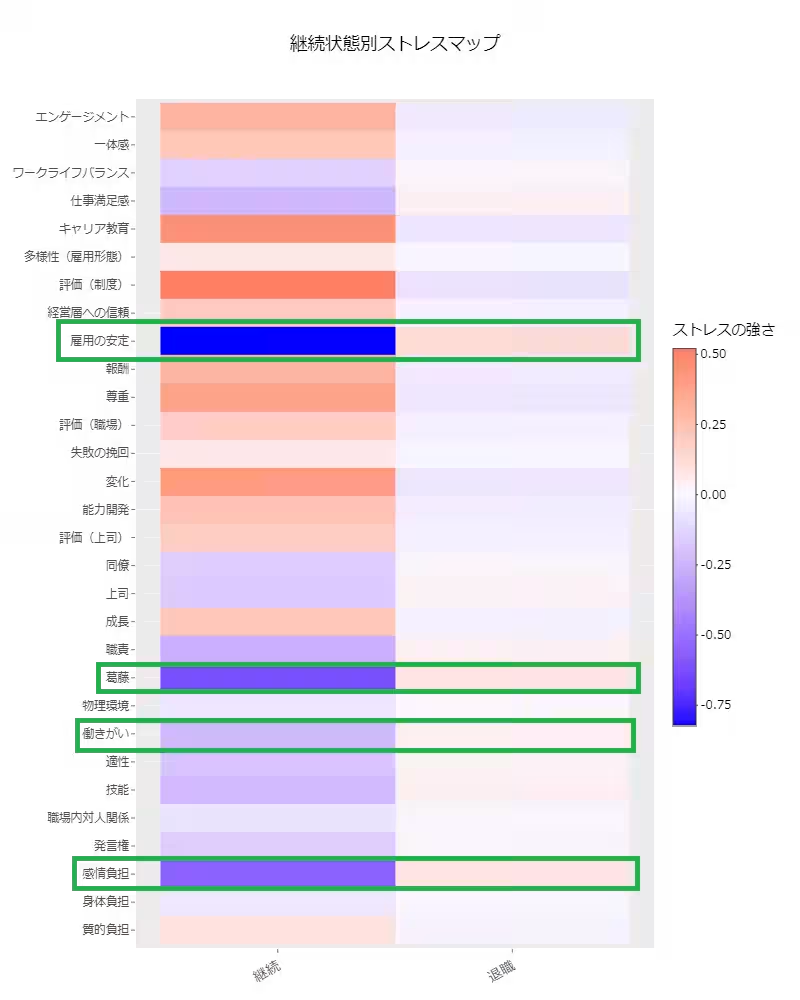
Lower Work Engagement Stress Among Leavers
Analysis distinguished between current employees and those who left within one year of the stress check. Results emphasized that employees at risk of leaving reported significantly lower stress levels regarding work engagement.
* Implication: In a surprising twist, it appears that employees contemplating departure might actually have higher work engagement levels.
The data suggested a contradicting notion within HR practices that high engagement reduces turnover risk; rather, an in-depth examination of the nature of engagement is necessary.
Factors Contributing to Turnover Risk
Stress factors such as job stability, internal conflict, lack of job satisfaction, and emotional burden were identified as potential risk factors for turnover. The findings indicate that workplace comfort and psychological burdens directly influence employee attachment and retention.
Insights and Recommendations
The study's outcomes shed light on the complex relationship between work engagement and employee retention. Understanding the nuances between different forms of engagement—namely, work engagement versus employee engagement—can guide companies in refining their management and development strategies.
As Dreamhop aims to propose actionable strategies to further ease employee retention, they will expand their offerings with new services aimed at tackling these challenges in corporate settings.
Services and Tools Offered by Dreamhop
In addition to the ORIZIN response tool, Dreamhop provides various services designed for continuous employee feedback and analysis, including:
- - Res-Q: A monthly pulse survey tool assessing performance and stress.
- - Psychological Correlation Diagram: A unique tool visualizing the relationship between stress check outcomes and workplace issues.
Conclusion
The insights drawn from this survey highlight the importance of work engagement in relation to employee retention and showcase the varying implications of different types of engagement. Moving forward, companies are encouraged to rethink their strategies surrounding employee management for enhanced stability and productivity.
For further detailed findings, an article explaining the results thoroughly will be published on April 22, 2025. The article can be accessed at Dreamhop's website.

Topics People & Culture)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.