

Scientific Validation of ZEH Renovation in Rental Apartments for Comfort Enhancement
Exploring the Impact of ZEH Renovations on Comfort in Rental Housing
In an innovative initiative, Tokyo Tatemono Co., Ltd., YKK AP Corporation, and Keio University have launched a joint experiment aimed at scientifically verifying the effects of ZEH (Net Zero Energy House) renovations on residents' comfort and health. The project is set in a 20-year-old large-scale rental apartment, Brillia ist Shinonome Canal Court, located in Koto City, Tokyo.
The Objective of the Experiment
This collaborative experiment aims to understand how upgraded ZEH standards influence residents' living conditions. Participants will stay in units that have undergone significant renovations and those with standard improvements, allowing for a comprehensive comparison of various metrics related to their comfort and well-being. By leveraging internal environmental measurements and vital data comparisons, the project seeks to validate the perceived benefits of ZEH modifications.
Importance of ZEH Housing
As Japan aims for carbon neutrality by 2050, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism, and the Ministry of the Environment have united in their efforts to promote energy-efficient housing. The ZEH initiative represents a pivotal part of this strategy. Beyond just energy savings, ZEH compliance is anticipated to enhance living comfort and mitigate health issues stemming from temperature fluctuations, such as heat shock.
The Experimental Details
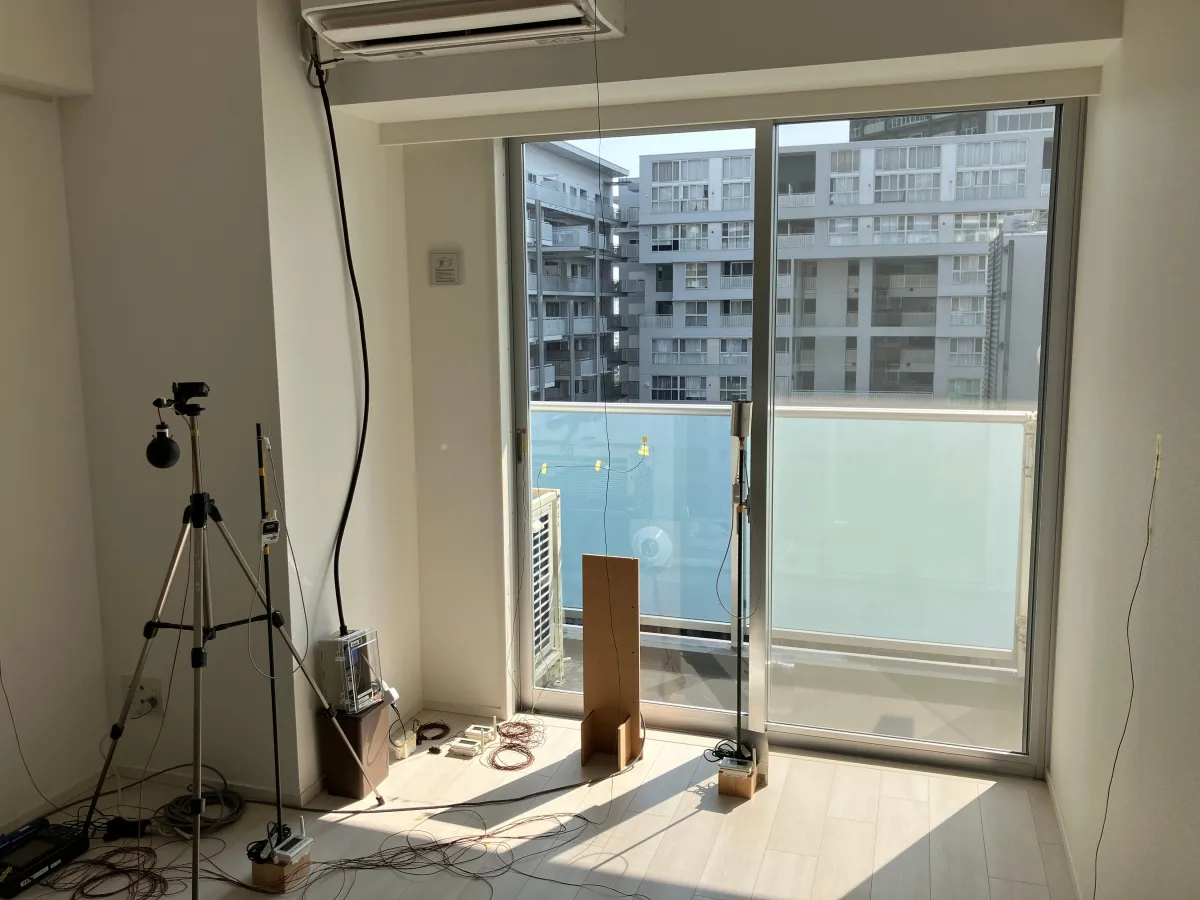
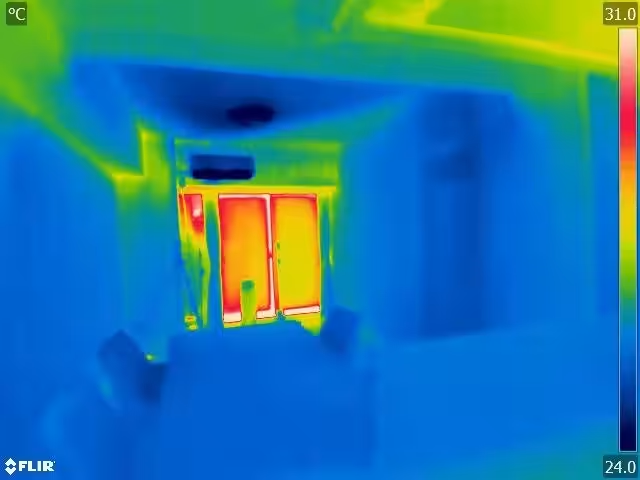
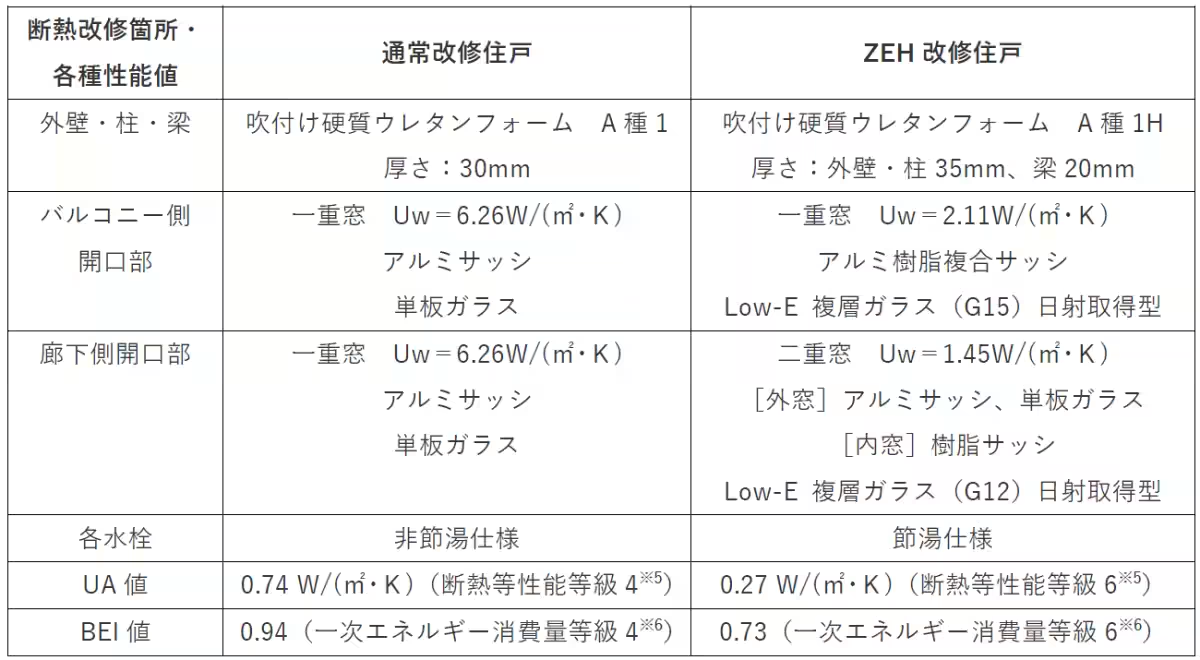
In the experiment, two types of units are being analyzed: one that has been upgraded to meet ZEH standards through high-performance insulation and windows, and another that has undergone typical renovations without improving insulation. The experiment entails two phases: during each season—summer and winter—internal parameters such as temperature, humidity, and surface temperatures from thermographic imagery will be captured.
Vital Data Monitoring
Participants, who are primarily students, will reside in each type of unit interchangeably, gathering important vital statistics such as blood pressure and heart rate to evaluate the impact of ZEH housing on health and comfort. The crucial idea is to provide a clear scientific narrative to back the advantages of ZEH renovations, going beyond subjective homeowner surveys.
Summer Schedule
- - Measurement Period: August 18 - 23, 2025
- - Participants' Stay: August 25 - September 6, 2025
Throughout this period, data collection will encompass indoor environmental variables like solar radiation, temperature and humidity levels, and electricity consumption, alongside monitoring participants’ health metrics. The aim of this multifaceted analysis is to draw a connection between ZEH improvements and increased resident satisfaction and health.
Unique Aspects of the Experiment
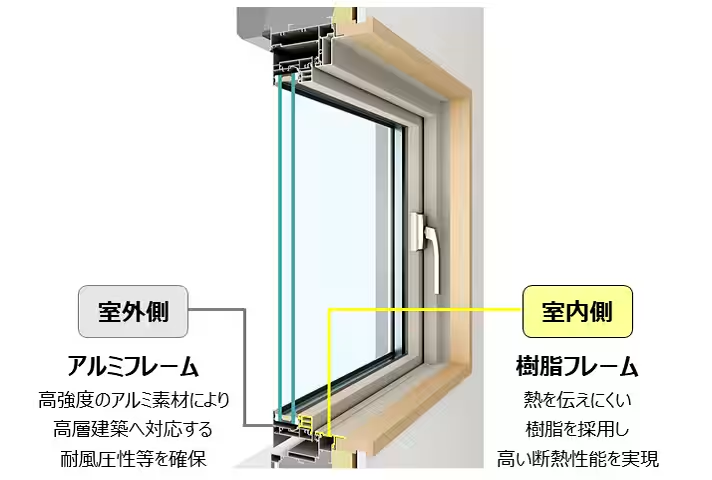
This study emphasizes the necessity of ZEH renovations in existing housing, addressing obstacles related to awareness and understanding of its benefits. The choice of units and the provision of high-thermal performance windows, particularly the EXIMA 55 model from YKK AP, showcases how advanced technology can redefine residential comfort.
Anticipated Outcomes
As the experiment progresses, both summer and winter data will be compared to analyze the tangible benefits of living in ZEH designed environments. This systematic approach aims to validate the health-perception relationship associated with energy-efficient homes and reduce cognitive barriers that might hinder the adoption of ZEH renovations.
Expert Insights
Professor Toshiyuki Kawakubo from Keio University emphasizes that while ZEH contributes to energy reduction and carbon neutrality, it also holds the potential to elevate residents' comfort and overall well-being. Transparent data from such studies affirm the value of ZEH renovations, enabling wider acceptance and implementation across the housing sector.
Conclusion
This joint effort by Tokyo Tatemono, YKK AP, and Keio University not only holds promise for improved living conditions but also serves as an essential step towards inspiring future housing developments in Japan. By anchoring ZEH standards in scientific research and tangible outcomes, the project represents a hopeful direction for energy-efficient living that prioritizes health and comfort.



Topics Consumer Products & Retail)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.