

Transforming Salt Reduction Standards: A Collaboration Between Toy Medical and Greenhouse
Transforming Salt Reduction Standards: A Collaboration Between Toy Medical and Greenhouse
The importance of salt reduction in diets has never been more crucial, especially in Japan, where salt intake consistently surpasses healthy levels. Japan, along with Kanagawa Prefecture, reports average salt consumption exceeding the recommended limit by 2-3 grams, leading to significant health complications such as hypertension and cardiovascular diseases. With healthcare costs for hypertension reaching a staggering ¥1.7 trillion nationwide, the need for effective solutions becomes self-evident.
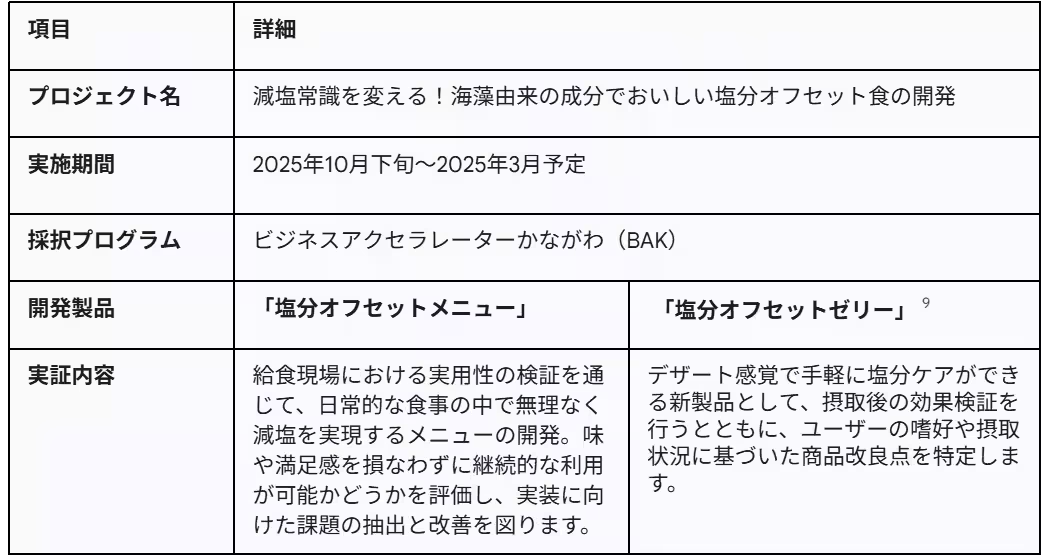
Recognizing these pressing issues, Toy Medical Co., a wellness and health food manufacturer based in Kumamoto, has teamed up with Greenhouse Co., a food service provider in Shinjuku, Tokyo, under the Kanagawa Prefecture's Business Accelerator Kanagawa (BAK) collaboration program. Their joint project aims to create a new category of cuisine—salt-offset foods—designed to maintain flavor and satisfaction while significantly reducing salt intake.
Understanding the Problem: The Role of Excess Salt Intake
Excessive salt consumption is linked to various health problems, including elevated blood pressure and increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. Traditional salt reduction methods often face criticism for compromising flavor, leading to decreased enjoyment of meals. This factor poses a dual challenge for both consumers and food service providers striving to address health concerns without sacrificing palatability.
Introducing Salt-Offset Technology
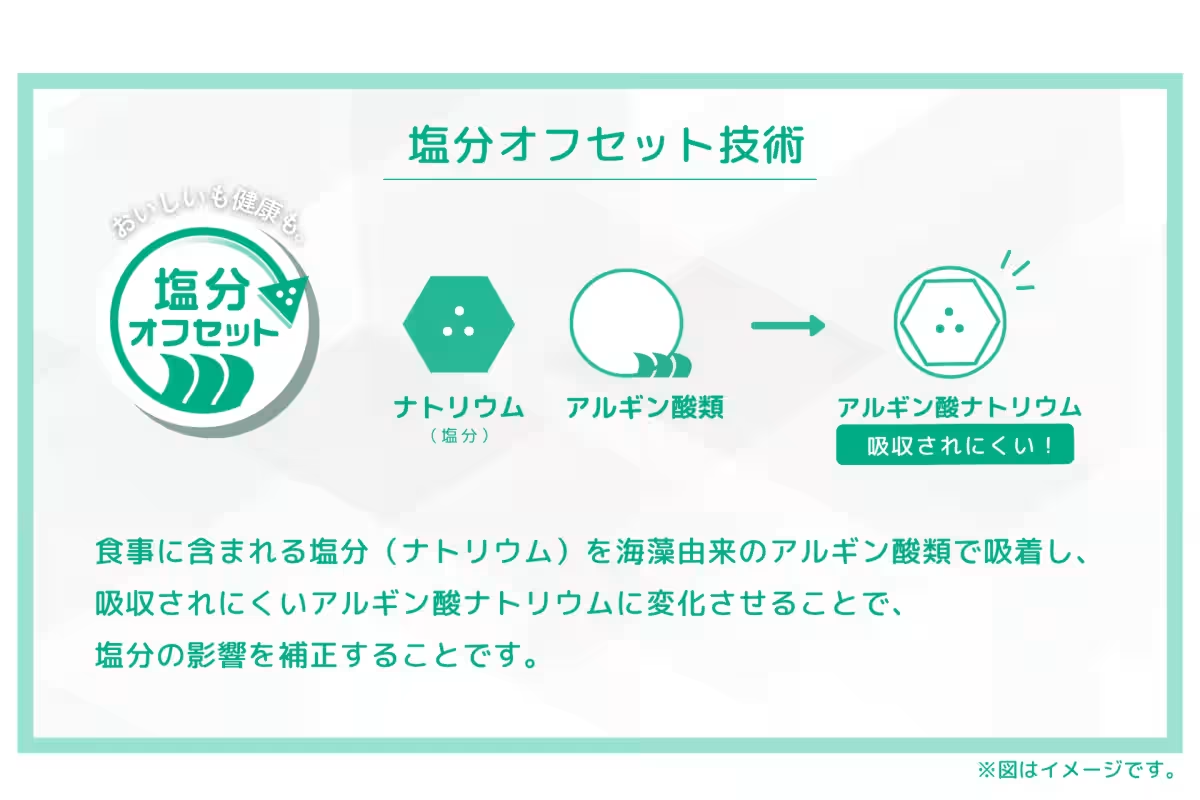
The innovative Salt Offset Technology developed by Toy Medical utilizes alginate, a dietary fiber derived from seaweed. This technology works by capturing sodium in food while altering it into a form that the body can expel without absorption, thereby effectively achieving a reduction in salt intake without affecting flavor. This method makes it suitable even for individuals on potassium-restricted diets, ensuring wider accessibility.
Currently, this technology is deployed in various products including supplements, seasonings, and snacks. The collaboration within the BAK program aims to broaden its application, making healthy eating more accessible to the wider public.
Significance of the Collaboration
The partnership between Toy Medical and Greenhouse seeks to create a healthier food ecosystem that does not compromise the sensory qualities of meals. By promoting dishes that align with salt-offset principles, they aim to address public health issues while enhancing the enjoyment of food. This initiative is aligned with Kanagawa's broader goals of contributing to preventive healthcare and extending health spans for its citizens.
About the Kanagawa BAK Program
The BAK program fosters collaboration between large enterprises and startups, providing a platform for open innovation among companies, research institutions, and support organizations. The project’s outcomes are scheduled for presentation in late March 2024, showcasing the fruits of this innovative partnership.
Company Backgrounds
Toy Medical Co. focuses on developing medical products, health foods, and seasonings for discerning consumers driven by the pursuit of wellness. Their dedicated approach targets the growing trend of salt reduction without sacrificing taste.
Greenhouse Co. operates extensively in contract food services across various sectors, including government agencies, schools, and hospitals. They aim to further enhance their culinary offerings by integrating these innovative health-focused products.
With their combined expertise, Toy Medical and Greenhouse are not just participating in a community initiative; they are leading a crucial shift in how we think about salt in our diets. By focusing on enjoyable, healthy food options, they are paving the way for a generation of healthier eating habits.





Topics Consumer Products & Retail)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.