

Revolutionary Autonomous Navigation System for Robots Using IR-UWB Technology
Introduction
In a remarkable advancement for autonomous technology, the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT) and Techno Ryuwa have unveiled a novel system that leverages Impulse Radio Ultra-Wideband (IR-UWB) technology. This system facilitates the autonomous operation of Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) without the need for prior mapping or coordinate setup, marking a significant step forward in the operational efficiency of robotic systems.
High-Precision Distance Measurement
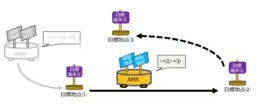
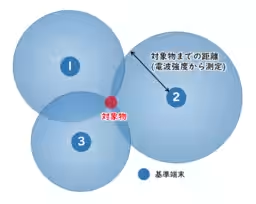
The newly developed autonomous navigation system employs IR-UWB, known for its capability to conduct high-precision distance measurements. This technology allows the placement of portable IR-UWB devices at target locations alongside one installed on the AMR. Through real-time distance measurement between these devices, the AMR can traverse a predetermined path autonomously.
Operational Benefits
One of the standout features of this innovative system is its ease of use. It eliminates traditional barriers in autonomous navigation, wherein previous systems required extensive mapping and prior setup. Users need only to position the portable IR-UWB terminals at various target points, with the AMR capable of consistently navigating to these points with a remarkable accuracy of 20 cm.
This capability is revolutionary for environments that require stringent cleanliness, such as cleanrooms. In such settings, measuring particulate matter while minimizing human presence is crucial as human activity inherently generates particles that could skew measurement results. Thus, the deployment of AMRs utilizing this IR-UWB-based navigation becomes invaluable.
Overcoming Key Challenges
In traditional cleanroom operations, methods like LiDAR and SLAM have been widely adopted. However, the presence of reflective surfaces in cleanrooms posed a significant challenge, causing erroneous readings when using laser technology. Additionally, laying magnetic or colored tape on the floor to guide autonomous systems compromises cleanliness—an inappropriate solution for sterile operational environments.
The introduction of the IR-UWB navigation system addresses these challenges directly. By leveraging the unique characteristics of distance measurement using IR-UWB, the development team effectively crafted a solution that supports autonomous navigation in clean environments.
Distinctive Features of the New System
Historically, IR-UWB-based positioning systems relied on a “three-point positioning” method, necessitating the arrangement of multiple reference terminals throughout a designated area and pre-configuration of their coordinates. This traditional requirement placed a strain on operational efficiency. In contrast, the newly developed system bypasses these cumbersome prerequisites. With just the placement of target terminals, the AMR can initiate autonomous operations seamlessly.
The new navigation system integrates two crucial components: a target location estimation unit, developed by NICT, which estimates distances and directional angles based on the distances recorded between the moving and target terminals, and a drive control unit by Techno Ryuwa. The coordination of these systems enables real-time updates in navigation data, allowing the AMR to adjust its direction continuously.
Usage in Cleanroom Environments
When applied within a cleanroom, this autonomous navigation system transforms the measurement process entirely. By simply placing the target device at the desired measurement point, robots can automatically conduct tests, thereby allowing measurement tasks to be scheduled during off-hours, including night and weekends. This practice frees up work hours for other important tasks, effectively optimizing resource allocation in these sensitive environments. Furthermore, robotic systems produce less particulate matter compared to stationary humans, enhancing the precision of cleanliness measurements and contributing significantly to increased operational efficiency.
Future Prospects
Looking ahead, the potential to merge the target estimation and drive control systems into a unified CPU system will result in increased compaction and enhanced control efficiency of the overall mechanism. The applications for this autonomous navigation system are promising, with potential uses extending into various fields such as measurement technology, logistics, and construction.
The system will be showcased at the forthcoming NICT Open House 2025 event, scheduled to take place on June 20-21, marking an opportunity for experts and stakeholders to witness firsthand the future of autonomous navigation technology based on IR-UWB.
Related Press Releases
- - August 10, 2015: Major efficiency enhancements in logistics, leveraging UWB positioning systems. Read More
- - May 26, 2014: Development of a high-precision indoor positioning system utilizing UWB technology. Read More
Reference Video
- - Research and development of Ultra-Wideband (UWB). Watch Video

Topics Consumer Technology)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.