
Introducing Groundbreaking ADU Technology for Selective AI Memory Control
Introduction to Novel AI Technology
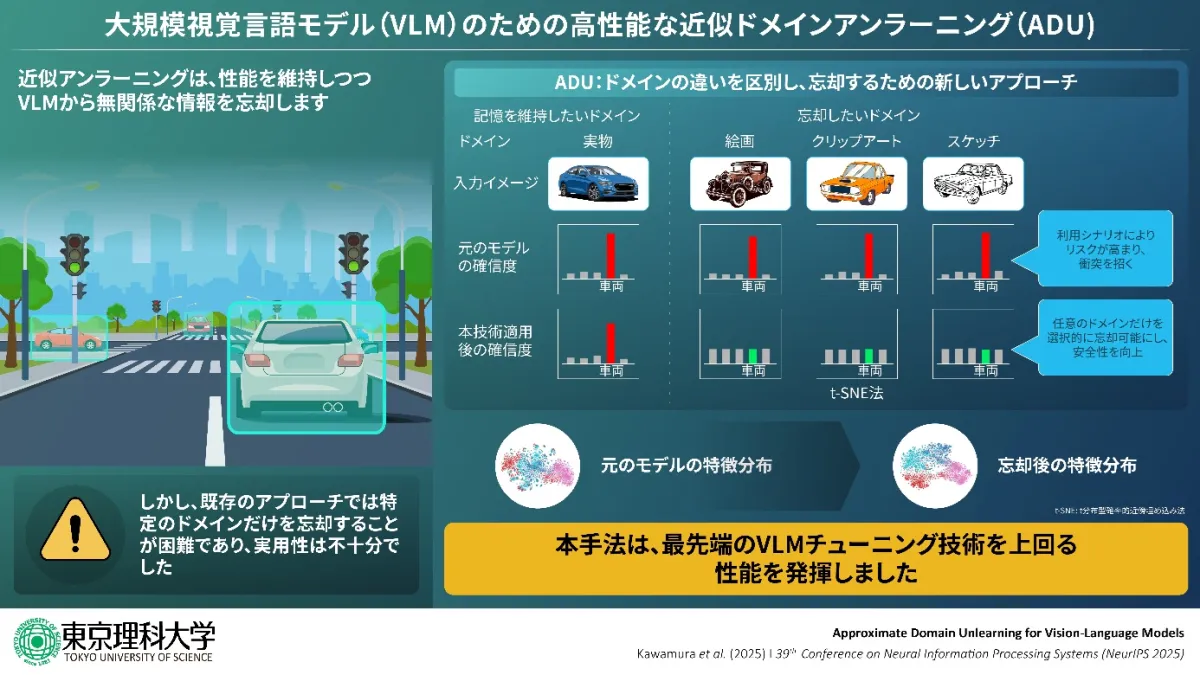
In a remarkable advancement within the realm of artificial intelligence, researchers at the Tokyo University of Science have unveiled a groundbreaking technology known as Approximate Domain Unlearning (ADU). This pioneering technique allows for the selective forgetting of knowledge based on specific domains in pre-trained Vision-Language Models (VLM). As AI becomes increasingly integrated into daily operations, the ability to manage its knowledge effectively is crucial for ensuring accuracy and reliability across applications.
The Need for Selective Forgetting
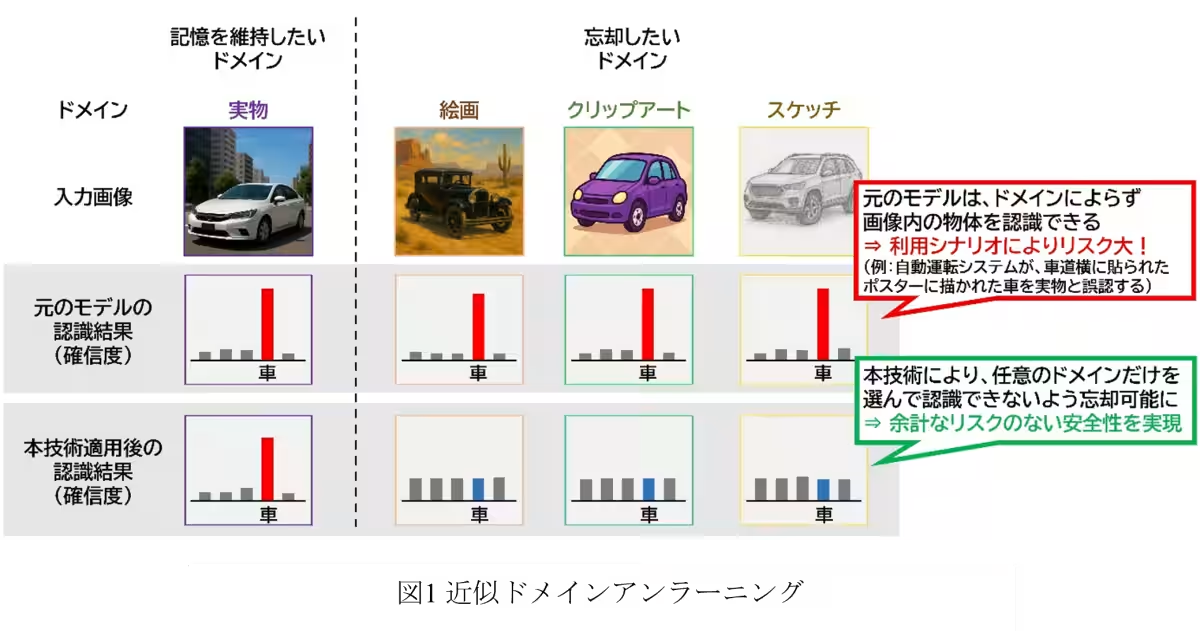
AI models, particularly VLMs, are celebrated for their robust capability to recognize various objects across multiple domains. However, this versatility can lead to potential misidentifications. For instance, a traffic monitoring system might confuse a displayed illustration of a vehicle with a real one—a mistake that could result in erroneous analysis. The introduction of ADU addresses this concern by enabling AI to forget specific domain knowledge while retaining its general understanding, thus enhancing trust and security in its operations.
Key Innovations: DDL and InstaPG
The dual-invention of Domain Disentangling Loss (DDL) and Instance-wise Prompt Generator (InstaPG) are central to the ADU framework. DDL works to segregate differing domain characteristics within the model’s feature space. It fundamentally alters AI behavior by ensuring distinct domain information is processed separately, allowing selective forgetting to be implemented effectively. InstaPG complements this by adapting AI responses to the unique characteristics of each image, recognizing that visual representations can significantly vary even within the same category.
Performance Benchmarks
In rigorous testing across four standardized image recognition datasets, the ADU technique demonstrated an impressive performance enhancement of approximately 1.6 times compared to traditional approaches. In scenarios that posed the greatest challenges to recognition, an astounding improvement of nearly 1.7 times was observed. This significant increase not only showcases the efficacy of ADU but also reinforces the importance of adaptable AI in varied contexts.
Future Implications
The implications are vast. By promoting the selective retention of valuable AI knowledge while diminishing unnecessary data, ADU could pave the way for safer and more manageable AI systems. This paradigm shift represents a strategic approach to designing AI that aligns closely with specific tasks or environments, thereby improving operational efficiency and user trust.
Presentation at NeurIPS 2025
The research group's findings will be showcased as a spotlight paper at the esteemed Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2025) conference, held from November 30 to December 7, 2025, in San Diego, USA, and Mexico City, Mexico. This opportunity underscores the significance of their contributions to the field of machine learning and AI.
Conclusion
As AI technology progresses, the need for flexible and context-aware systems grows ever more critical. The emergence of ADU technology is a significant step towards achieving better control over AI memory use and functionality. As Go Irie, a key researcher from Tokyo University of Science states, understanding how to control AI capabilities situationally is vital for successful long-term deployment. The innovations spurred by ADU and its application potential could catalyze a new era in the responsible use of artificial intelligence.

Topics Consumer Technology)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.