
Innovative Nucleic Acid Drugs Targeting Brain Diseases Revealed
Unveiling Chol-HDO: New Frontiers in Nucleic Acid Medicines
In a groundbreaking study conducted by researchers from the Tokyo University of Science, a new nucleic acid medicine, Cholesterol-Conjugated Heteroduplex Oligonucleotides (Chol-HDO), demonstrates the potential to effectively target and treat challenging brain diseases such as Alzheimer's.
This innovative therapy uses a unique delivery mechanism, ensuring that Chol-HDO remains in the bloodstream for extended periods, allowing it to penetrate the brain tissue efficiently. The findings establish a promising avenue for treating previously hard-to-cure neurological disorders, showcasing how next-generation medicinal approaches can significantly impact patient outcomes.
Research Overview
The collaborative effort involved experts from various fields, including Yukitake Yoshioka, a recent graduate from the School of Pharmaceutical Sciences at Tokyo University of Science, and Professor Motoya Nishikawa. They, alongside professionals from Takeda Pharmaceutical Company, explored the pharmacokinetics of Chol-HDO using experimental models with mice and rats. Their experiments confirmed that this drug exhibits an impressive ability to be delivered into the brain, opening doors to potential treatments for high unmet medical needs in cerebral disorders.
Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASOs) have emerged as a forefront therapy option, effectively regulating gene expression by suppressing specific proteins responsible for diseases. Recent advancements underscore the growing recognition of nucleic acid drugs as viable solutions for treating previously intractable conditions.
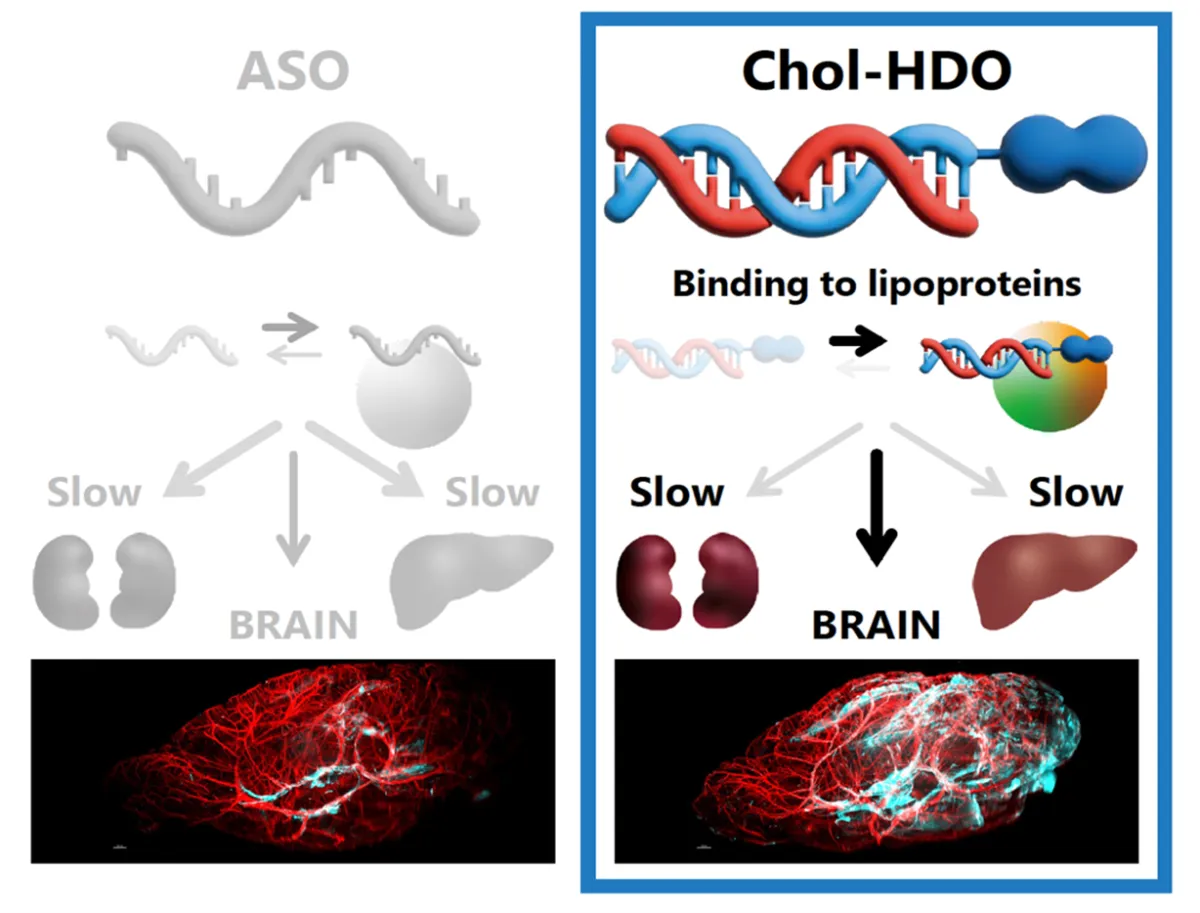
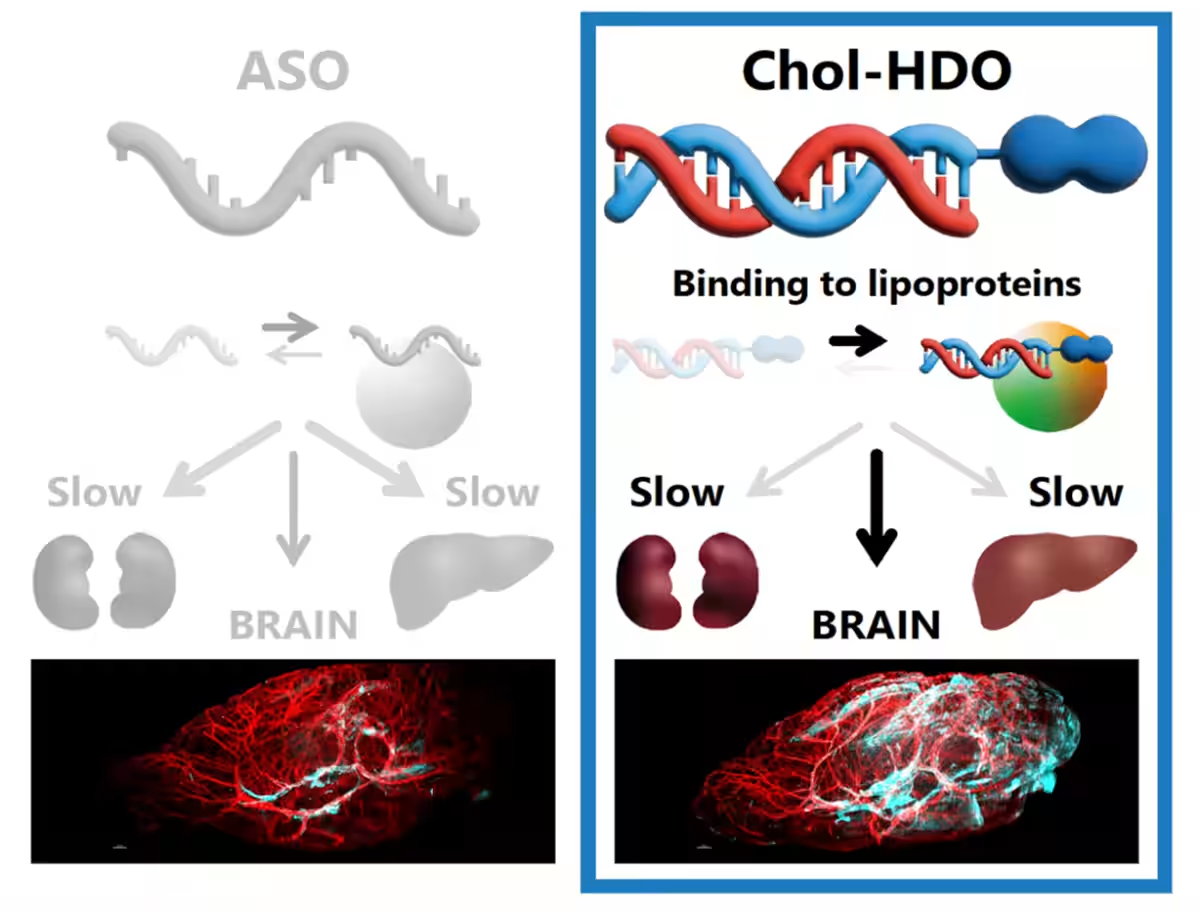
Heteroduplex Oligonucleotides (HDO), composed of an ASO and its complementary RNA, represents a novel category within nucleic acid therapeutics. The research indicates that Chol-HDO can effectively inhibit the expression of target genes across various tissues, including the brain. However, there has been limited information on the pharmacokinetics of Chol-HDO, which is crucial for its future applications.
The Importance of Delivery Mechanisms
A crucial hurdle in the development of nucleic acid medicines lies in their effective delivery to the specified organs or tissues. Understanding how a drug behaves in the body and how it distributes to target sites is essential. This study successfully analyzed the pharmacokinetics of Chol-HDO and its derivatives, affirming that their body dynamics can be precisely controlled.
This research's key finding reveals that Chol-HDO significantly suppresses gene expression within brain tissues, unveiling a promising pathway for efficiently targeting various nucleic acid drugs in therapeutic applications. Professor Nishikawa emphasizes this point: “If we can elucidate the brain-targeting mechanism of Chol-HDO, it may revolutionize the delivery of many nucleic acid medicines.”
Background of the Research
Despite advances in medicine, numerous diseases currently lack effective treatments. In response to this, continuous research and development are being pursued to address unmet medical needs. Nucleic acid medicines, targeting DNA and RNA within cells, offer a fresh approach to disease management by controlling gene functionality.
ASOs and siRNA act on mRNA to inhibit the production of harmful proteins associated with various diseases. The rapid increase in clinical approvals of ASO-based therapeutics reflects the growing confidence in this field. Yet, a significant challenge persists: effectively distributing ASOs to specific tissues or organs.
To tackle this, the novel approach of binding ASOs with complementary RNA to form a “duplex” was developed, enabling ASOs to effectively reach their target mRNA while being released intracellularly. Chol-HDO, a cholesterol-conjugated variant of HDO, has shown promising antisense activity, particularly in the brain—a site traditionally challenging for drug delivery.
Detailed Research Results
In their experiments, the team administered ASOs, HDOs, and Chol-HDOs through intravenous injections in the animal models to study their behavior within the body. Results revealed that while ASOs and HDOs diminish rapidly from the bloodstream, Chol-HDO remained in circulation for much longer.
Evaluation of the liver and kidney distribution indicated that Chol-HDO demonstrated a unique behavioral pattern compared to ASOs and HDOs, highlighting its ability to migrate into brain tissue effectively.
The comparative analysis of protein binding rates showcased that HDOs bond more weakly with proteins than ASOs, while Chol-HDO exhibited a significantly stronger attachment. These insights suggest that Chol-HDO's bonding characteristics, especially with lipoproteins, play a critical role in the drug's tissue distribution and penetration into the brain.
The differing binding rates further hint at the possibility of developing a controlled delivery system for ASOs that effectively targets the brain, reinforcing the significance of these findings in advancing nucleic acid therapeutics.
Future Outlook
To develop more effective nucleic acid medicines, understanding their mechanisms of action is vital. The ability to successfully deliver these drugs to target sites, as exemplified by the promising results with Chol-HDO, positions the field of nucleic acid therapeutics at the precipice of transformative strategies.
Continued research into the drug delivery mechanism of nucleic acid medicines is crucial for unveiling new treatments for neurological conditions traditionally lacking effective interventions. The prospects for Chol-HDO and similar innovations promise a brighter future for patients facing challenging brain diseases.
This research received funding from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) under grant numbers 21K1269 and 24K15755.
Terminology
- - mRNA (messenger RNA): A single-stranded RNA that serves as a template for protein synthesis by transcribing DNA information in the cell nucleus.
Published Paper Information
- - Journal: Journal of Controlled Release
- - Title: Pharmacokinetics and protein binding of cholesterol-conjugated heteroduplex oligonucleotide
- - Authors: Yukitake Yoshioka, Syunsuke Yamamoto, Kosuke Kusamori, and others
- - DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2025.02.025
Topics Health)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.