
The Impact of 360-Degree VR on Neurosurgery Education Explored in Cureus Journal
Groundbreaking Research on VR in Neurosurgery Education
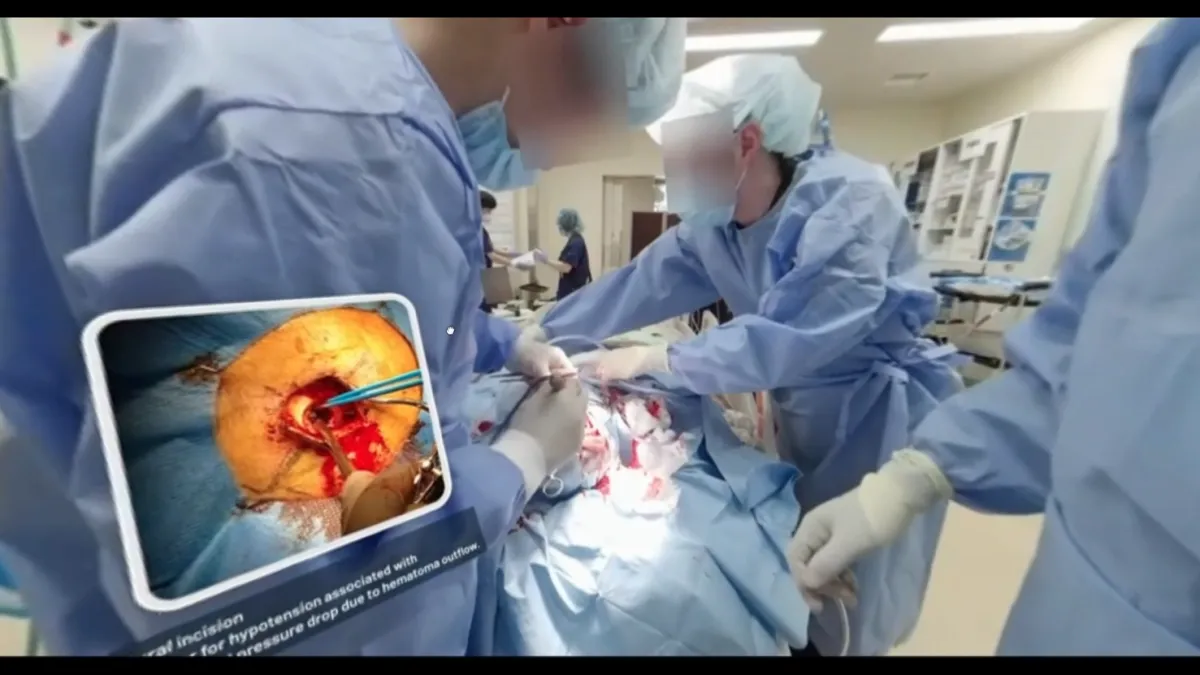
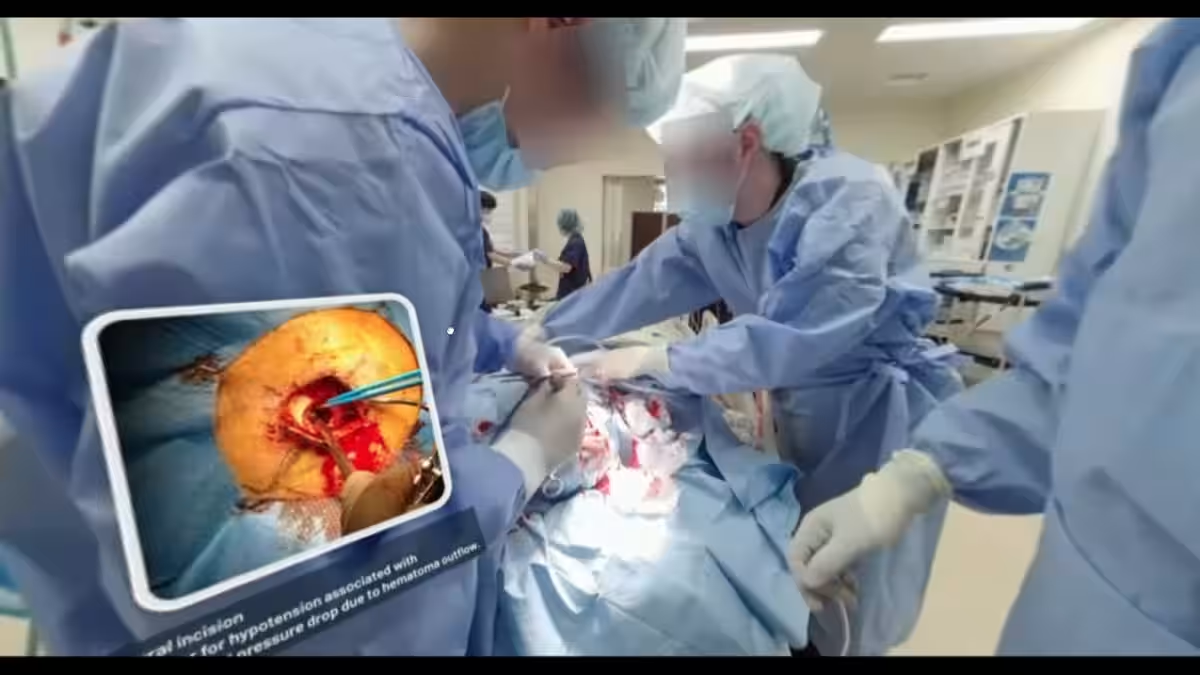
In a significant academic milestone, a paper titled "Seeing Is Believing: Real-Life 360-Degree Virtual Reality as a Catalyst for Neurosurgical Interest" has been published in the international open-access medical journal Cureus. This study, spearheaded by Dr. Tatsuya Tanaka and his team from Narita Hospital at International University of Health and Welfare, explores the transformative role of 360-degree virtual reality (VR) in neurosurgery education.
Purpose of the Study
The primary aim of this research was to assess the impact of immersive VR experiences on medical students' interest in pursuing a career in neurosurgery. The study involved 85 fifth-year medical students who participated in hands-on VR training designed to simulate real-life emergency procedures, surgeries, and angiography.
Methodology
The research utilized a pre- and post-study questionnaire method to evaluate changes in the students' perceptions regarding neurosurgery. Following the VR lectures, the number of students expressing an interest in neurosurgery saw a remarkable increase—from 22 students before the sessions to 52 afterward. The results were statistically significant (t=6.77; df=84; p<0.0001), demonstrating a compelling correlation between VR exposure and a heightened interest in the field.
Key Findings
One of the standout findings from the study was the overwhelmingly positive feedback regarding the VR experience itself. Over 90% of the participants rated the immersion level, ease of use, content comprehension, and overall enjoyment as high. This feedback indicates that VR not only provides an engaging educational experience but also serves as an effective learning tool in the post-COVID era, where traditional teaching methods have faced challenges.
Collaborations Enhancing VR Education
The development of the 360-degree VR educational material was made possible through collaboration with Jolly Good Co., Ltd., a creative technology company specializing in high-precision VR solutions and AI-driven services for the medical sector. Their involvement highlights the merging of advanced technology with educational frameworks, paving the way for innovative teaching methods in various industries facing workforce and training shortages.
Implications for Future Education
This research highlights the potential for VR technology to fundamentally reshape medical education. Beyond medical schools, the implications extend into other fields such as manufacturing, construction, logistics, retail, and food service. Jolly Good is actively seeking partnerships with businesses across different sectors who are exploring the integration of digital transformation, AI, and extended reality technologies.
In summary, the paper published in Cureus has set a precedent for the utilization of 360-degree virtual reality in medical training, particularly in neurosurgery, reinforcing the idea that seeing truly is believing. For more details on the study, you can read the full article here.
Topics Health)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.