

Tokyo University and UPDATER Develop Japan's First AI Model for Household Electricity Demand Data
Tokyo University and UPDATER: Pioneering AI for Household Electricity Simulation
In a remarkable collaboration that could reshape energy management in Japan, Tokyo University's Graduate School of Engineering, led by Kenji Tanaka's research group, and UPDATER, based in Setagaya, have co-developed Japan's first AI model designed to replicate household electricity usage patterns. This groundbreaking initiative promises to make household electricity demand data accessible through a web service, marking a significant advancement in energy research and management.
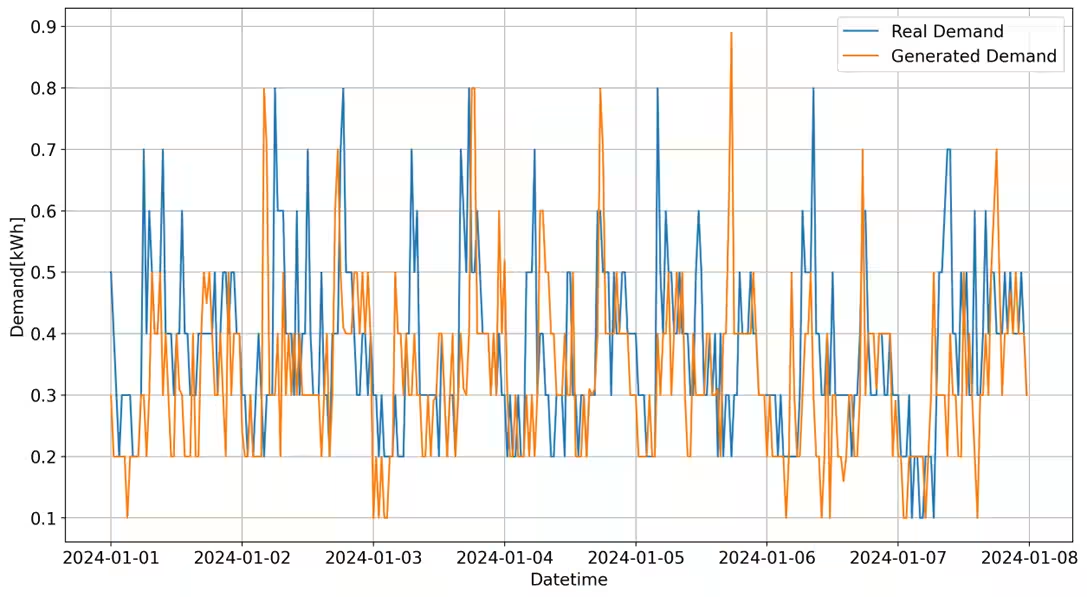
The innovative AI model serves as a key player in generating virtual demand data using a diffusion model, thus avoiding the use of actual household electricity data. The advantage of this approach lies in its ability to faithfully simulate real-world electricity usage patterns without exposing sensitive personal information. This development is expected to contribute significantly to the creation of next-generation energy-saving services while maintaining user privacy.
The research findings are scheduled to be presented at the upcoming 2025 Electric Power Society National Conference, which will take place from March 18th to 20th, further underscoring the importance of this breakthrough.
The Significance of Household Electricity Demand Data
Household electricity demand data plays a crucial role in numerous research fields, including energy management system optimization, demand forecasting, and smart grid planning. Leveraging this data has the potential to enable services that enhance energy efficiency, benefiting both household budgets and the environment.
The Future of Energy Management Services
1. Advanced Energy-Saving Services: With ongoing research and development, personalized electricity optimization services, such as alerts for upcoming surges in electricity bills or AI adjustments for heating and cooling, are becoming increasingly prevalent.
2. Integration with Renewable Energy: Optimizing self-consumption when paired with solar energy and storage systems will soon be more accessible, boosting energy independence and sustainability.
3. Stability of Power Systems: The widespread adoption of these services will contribute to the stabilization of electricity supply and demand balance across society, reducing the risks of blackouts and equalizing electricity costs.
Overcoming Privacy Challenges
While the potential benefits are immense, sharing actual household electricity data poses significant privacy concerns due to the sensitive nature of personal information it contains. Researchers have expressed the need for a robust solution that allows for thorough analysis and model verification without compromising privacy. This is where the newly developed AI model comes into play, acting as a breakthrough by generating realistic demand data without utilizing actual household information, thus facilitating research and development in the energy sector.
Key Features of the AI Model
1. High Precision Replication: Utilizing the diffusion model, this AI can generate hourly electricity usage patterns with remarkable accuracy, creating various pseudodata that reflect the characteristics of different households.
2. Privacy-Centric Design: By leveraging an AI model trained on household electricity data, it ensures that actual personal information remains confidential while still providing a realistic simulation of electricity usage patterns. This balances privacy protection with the advancement of energy sector research and development.
3. Adaptability to Varied Lifestyle Patterns: The model can generate data under specific conditions, such as temperature or holidays, making it versatile for analyzing and predicting electricity demand across diverse scenarios.
Availability of the AI Model
The AI model is now available via a web service for both individuals and organizations interested in developing or evaluating energy-related services and conducting research. This innovation allows for convenient access to a dataset that enables practical analysis while ensuring privacy protection.
Potential Use Cases
1. Researchers and Universities: Allows for validation and development of prediction models and energy management algorithms even when real data is scarce.
2. Startups and Companies: Facilitates rapid development and testing of algorithms related to electricity demand forecasting and household energy management systems (HEMS).
3. Educational Institutions and Students: The generated electricity data can be utilized as educational material for AI and data analysis courses.
Future Prospects
With the availability of this new model, the intricate analysis and simulation of household electricity usage will become feasible without privacy infringements. This shift could pave the way for innovative energy-saving services and more efficient methodologies for harnessing renewable energy. As developments continue, there is a hopeful outlook for establishing a smarter way of living that better utilizes technology for household energy management. By guiding the future of energy through these advancements, Tokyo University and UPDATER envision a world where consumers, society, and the planet can coexist harmoniously.
For more details or inquiries about utilizing the AI model, interested parties can contact the Kenji Tanaka research group at Tokyo University or the Strategy PR team at UPDATER.

Topics Consumer Technology)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.