
Introducing iComBat: A New Method for Correcting Batch Effects in DNA Methylation Array Data
iComBat: A Transformative Dataset Correction Method in DNA Methylation Analysis
Overview of the Research
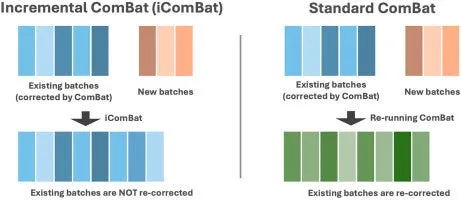
Recently published in the Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal (CSBJ), researchers from Rhelixa have unveiled a groundbreaking method called iComBat. This innovative approach is designed to address a persistent challenge in DNA methylation array analysis known as batch effects. Batch effects can manifest due to variability in measurement devices, reagent lots, or the timing of measurements, leading to systematic distortions in the data. Traditional methods to correct these discrepancies have often forced researchers to reanalyze already adjusted data whenever new datasets are integrated. This can distort earlier results and complicate longitudinal studies.
iComBat innovatively focuses solely on correcting newly added data without altering previously adjusted data. This feature is especially beneficial in intervention studies or cohort studies that require continuous data collection, as it allows for the maintenance of reliability and consistency over time.
Key Features of iComBat
As a modification of the widely used ComBat technique, iComBat ensures that while new batches undergo correction, the integrity of pre-existing corrected data remains intact. By doing so, it addresses the significant shortcoming of reprocessing previously corrected results. This flexibility not only streamlines the data analysis process but also enhances the accuracy of assessing intervention effects over time.
Simulations and benchmarking against public datasets have demonstrated that iComBat maintains comparable precision to traditional batch correction methods while offering the advantage of focusing solely on newly added datasets. This significant improvement is expected to have widespread application in fields where gradual data accumulation is standard, particularly in studies analyzing changes in epigenetic clocks before and after interventions.
Future Applications and Impact
The implications of iComBat are profound for long-term research endeavors that rely on accumulating data over time. Rhelixa plans to leverage this new methodology to enhance the precision of its proprietary service, the Epigenetic Clock® Test, which continuously measures changes in epigenetic markers.
Furthermore, the methodology is poised to benefit various longitudinal studies that probe the effects of lifestyle changes—such as diet, exercise, and environmental factors—on health outcomes. It is also anticipated to facilitate collaborative research involving clinical interventions, such as those assessing the impact of dietary supplements on health outcomes.
Research Outcomes
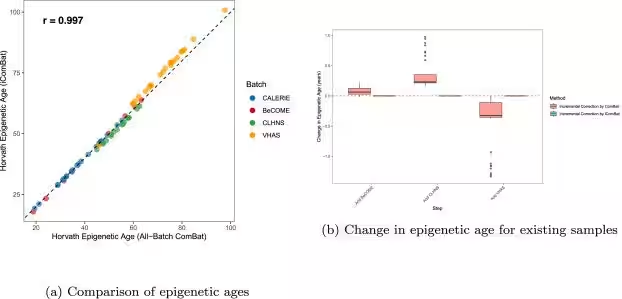
The introduction of iComBat marks a significant step forward in the realm of batch effect correction for DNA methylation array data. Through extension of existing methodologies, specifically the ComBat method, iComBat (short for incremental ComBat) allows researchers to advance their analysis without losing previously established corrections. Test results from multiple datasets across diverse research cohorts—including those from the United States and the Philippines—have illustrated that while adding new batches, iComBat successfully protects the epigenetic age calculations of existing samples, thus providing continuity in data integrity.
Diagram Description:
- - Part (a) features a scatter plot comparing epigenetic ages calculated from datasets corrected with traditional ComBat against those corrected with iComBat, showcasing a high correlation coefficient.
- - Part (b) presents a box plot demonstrating the variance in epigenetic age among existing samples when new batches are introduced. In contrast to the fluctuations seen with ComBat, iComBat maintains static results for previously corrected samples.
Conclusion
Conclusively, iComBat offers a promising new avenue for accurate and reliable batch effect correction in DNA methylation studies, enhancing the potential for longitudinal intervention assessments and making it a pivotal tool for biological and medical research sectors. The research paper detailing these findings, titled "iComBat: An incremental framework for batch effect correction in DNA methylation array data" by authors Togo Yui and Nagaki Ryu, is set to play an essential role in shaping future studies in this dynamic field.
For inquiries, contact: Rhelixa Corporation at [email protected].
About Rhelixa: Rhelixa is committed to leveraging advanced genomic and epigenomic analysis techniques, developing essential research tools and solutions in the realms of biology, medicine, and pharmacology.
Topics Consumer Technology)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.