

Breakthrough Development of Plant-Insertable Multi-Enzyme Sensors for Real-Time Monitoring of Sugar Transport
Groundbreaking Advancement in Plant Sensor Technology
A pioneering scientific collaboration among Waseda University, Kitakyushu City University, and Okayama University has led to the creation of an innovative biosensor that can monitor the transport of sugars in plants in real-time. This significant achievement is set to revolutionize how we understand plant physiology and improve smart agricultural practices.
Key Features of the Multi-Enzyme Sensor
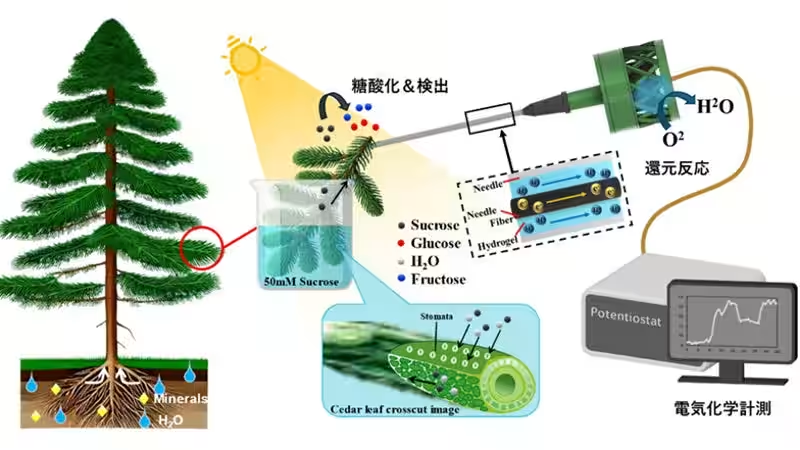
The new sensor, which integrates multiple enzymes like glucose oxidase, invertase, and mutarotase, is designed to be inserted into the stems and fruits of plants. It provides a unique capability to measure sucrose dynamics within these plant tissues continuously for 24 hours, offering a window into the essential processes of photosynthesis and growth in response to environmental changes.
Research Validation
To confirm the functionality of the sensor, researchers employed stable isotope-labeled water as a tracery tool. This verification demonstrated the ability of Japanese cedar leaves to absorb water and sucrose in a light-dependent manner, underscoring the sensor's effectiveness in real-world applications.
Importance of Real-Time Measurement
Real-time monitoring of sugar transport dynamics within plants is crucial for advancing our understanding of photosynthesis and growth. Previously, realizing a high-sensitivity sensor capable of long-term insertion into plant tissues had posed a significant challenge. However, this innovative bio-sensor operates based on self-generated electric signals through enzymatic reactions, enabling precise and continuous visualization of sugar transport.
Supporting Research Funding
The research was accomplished with the aid of funds from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) under the Strategic Creation Research Program's “Bioiontronics” initiative, further validating the project's scientific merit. The findings from this effort were published online on June 8, 2025, in the journal Biosensors and Bioelectronics.
Publication Details
- - Journal Name: Biosensors and Bioelectronics
- - Paper Title: A Plant-Insertable Multi-Enzyme Biosensor for the Real-Time Monitoring of Stomatal Sucrose Uptake
- - Authors: Shiqi Wu, Wakutaka Nakagawa, Yuki Mori, Saman Azhari, Gábor Méhes, Yuta Nishina, Tomonori Kawano, Takeo Miyake
- - Published Date: June 8, 2025
- - Access the Article Here
Anticipated Applications
The implications of this sensor technology extend beyond mere academic interest. Its potential applications in smart agriculture could lead to more sustainable farming strategies, optimized crop yield, and enhanced understanding of plant responses to climate variations. As researchers continue to explore the intricacies of plant biology, this innovative biosensor stands as a testament to the power of interdisciplinary collaboration in pushing the boundaries of what is possible.
The project was shared publicly on July 7, 2025, by Waseda University, Kitakyushu City University, and Okayama University, paving the way for a new chapter in plant research.





Topics Consumer Technology)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.