

Exploring the Mechanism Behind Amorphous Materials' Hardness Through Topology
Exploring the Mechanism Behind Amorphous Materials' Hardness Through Topology
A groundbreaking study led by esteemed researchers from Osaka University, the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, Okayama University, and the University of Tokyo has unveiled the elusive structural factors influencing the mechanical behavior of amorphous materials, specifically their hardness. The findings, published in the prestigious journal Nature Communications, utilize advanced topological data analysis techniques to shed light on this complex subject.
While the mechanical properties of amorphous materials such as glass have long posed challenges for researchers, understanding how these characteristics emerge from atomic arrangements remains critical. Unlike crystalline materials, amorphous structures are characterized by their disordered atomic organization, which manifests distinctively in their electrical and mechanical properties. To date, probing the relationship between local structural features and the mechanical responses of these materials has proven notoriously difficult due to the intricacies of the atomic networks involved.
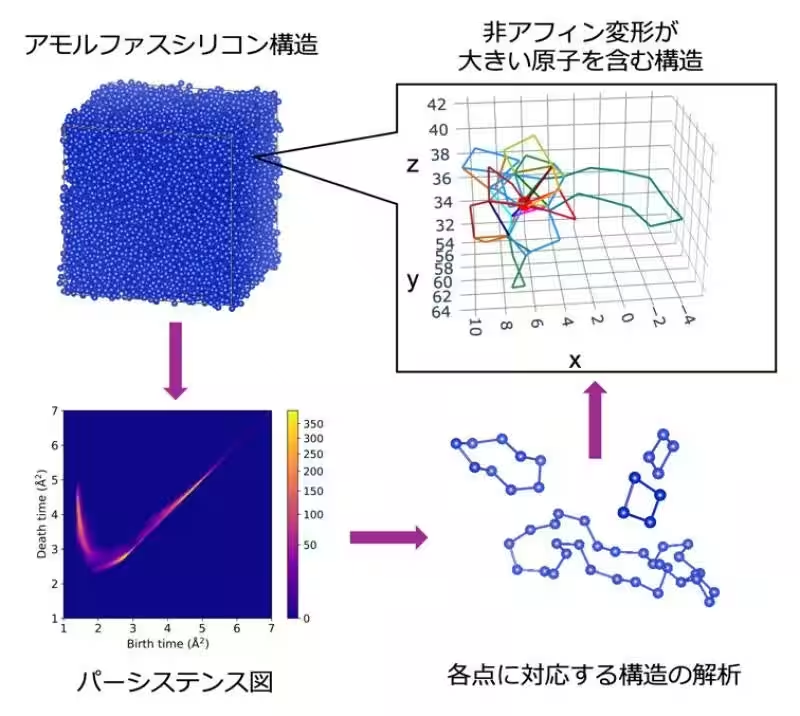
This new research employs a topological method known as persistent homology to investigate the atomic arrangements within amorphous materials. Persistent homology allows researchers to maintain a robust analysis of mid-range order in the arrangement of atoms, capturing key structural elements that influence how these materials deform. The findings reveal that regions prone to non-affine deformation—areas that easily yield to stress—possess a unique hierarchical structure characterized by larger loops that enclose smaller, irregular loops. This duality of order and disorder underscores the material's mechanical properties and provides insights into the atomic configurations that facilitate deformation.
Professor Emi Minamitani from Osaka University, one of the leading voices in this collaborative research initiative, expressed intrigue at the study’s broader implications. She likened the structural constraints that enable significant movement in materials to certain dynamics found in human activities, presenting the potential for applications beyond materials science.
The implications of these findings are significant, as they pave the way for innovative approaches in the design of more durable and resilient amorphous materials. The prospect of creating stronger, impact-resistant glass and other such materials could revolutionize various applications, from construction to electronics, where resilience is paramount.
The research team, including prominent figures like Takunobu Nakamura and Ippei Obayashi, emphasized the applicability of their findings across various materials. Their collaborative efforts have not only unveiled knowledge hidden within amorphous materials but have also initiated a dialogue on how these insights can foster advancements in materials engineering, potentially leading to breakthroughs in technology and sustainability efforts.
As the scientific community continues to explore the fundamental properties of amorphous materials through the lens of topology, it becomes increasingly evident that these findings may redefine our understanding of material science and its multifaceted applications. This study marks a critical milestone in the ongoing quest to harness the full potential of amorphous structures. Moving forward, researchers will expand these insights into multicomponent glass systems and other material types, potentially offering a wide-ranging influence on future scientific inquiry and industrial applications.
In conclusion, the research underscores the efficacy of employing mathematical concepts in deciphering material properties, merging the fields of mathematics and materials science in unprecedented ways. With this new understanding, industries focusing on durable consumer products, energy solutions, and technological innovations are likely to experience significant advancements driven by the recent breakthroughs in amorphous material design and analysis.





Topics Consumer Products & Retail)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.