
Exploring Japan's Robotics Adoption: Insights and Challenges Unveiled by QNX's New Research
Insights into Robotics Adoption in Japan
QNX, a division of BlackBerry Limited, has released its latest findings on robotics adoption, specifically focusing on the Japanese market. Conducted among 1,000 executives across healthcare, manufacturing, automotive, and heavy equipment sectors globally—100 of whom were from Japan—the survey highlighted distinct trends and challenges facing Japanese companies in their robotics implementation journey.
Key Findings on Robotics Adoption in Japan
The survey revealed that 54% of Japanese companies currently utilizing robots attribute their decision primarily to labor shortages, a striking figure compared to the global average of 27%. This underscores the acute labor challenges Japan faces due to its aging population and declining birth rate.
Additionally, 68% of Japanese executives indicated that the high initial costs represent the most significant barrier to implementation, compared to 47% globally. This cost-related concern significantly hampers the adoption of robotic solutions, compounded by burdens associated with long-term costs.
In terms of industry-specific statistics, the survey noted that robotic adoption rates are higher in manufacturing (79% vs. 71% global average) and the automotive sector (74% vs. 65% global average). However, the healthcare sector lags at just 23%, while logistics trails even further at 16%, both significantly below global averages of 40% and 48%, respectively.
Trust and Preparedness Deficiencies
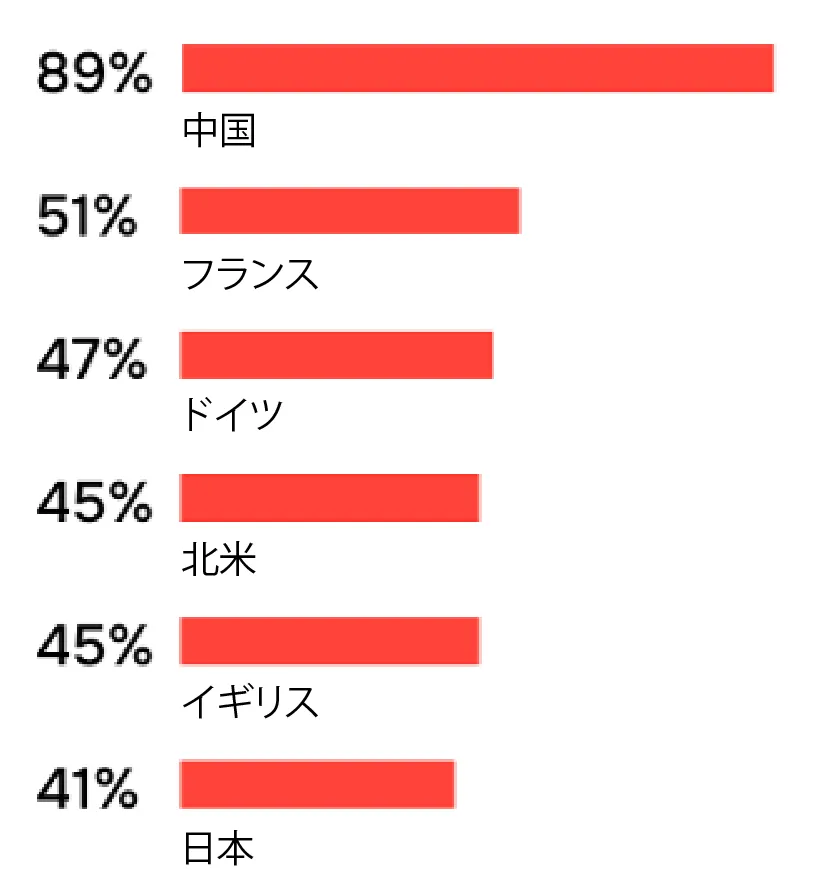
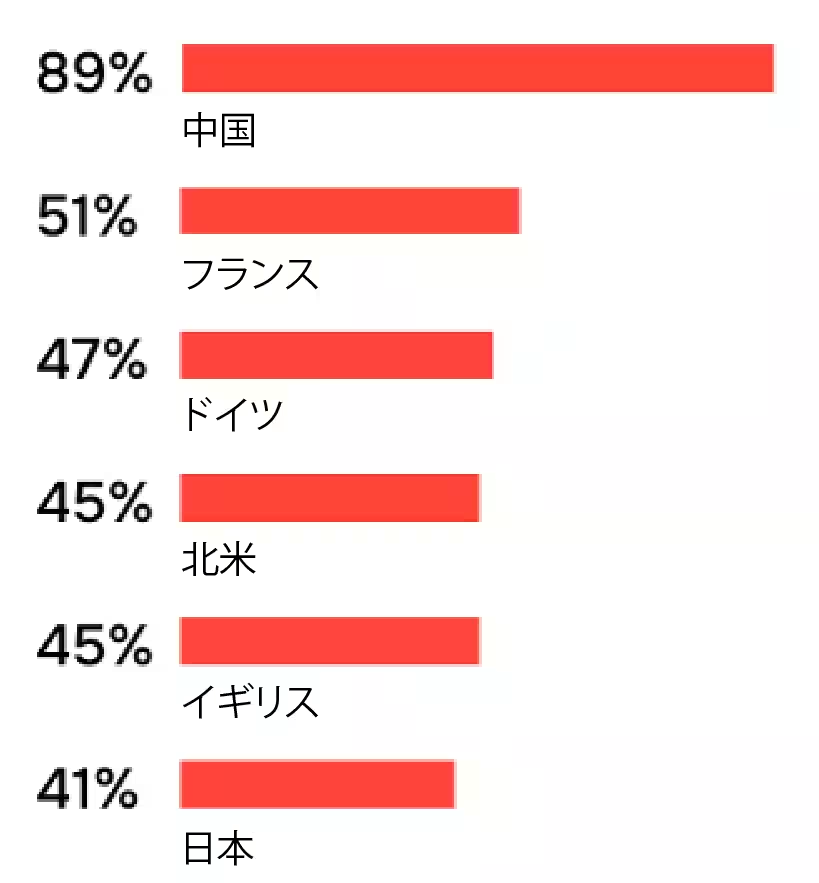
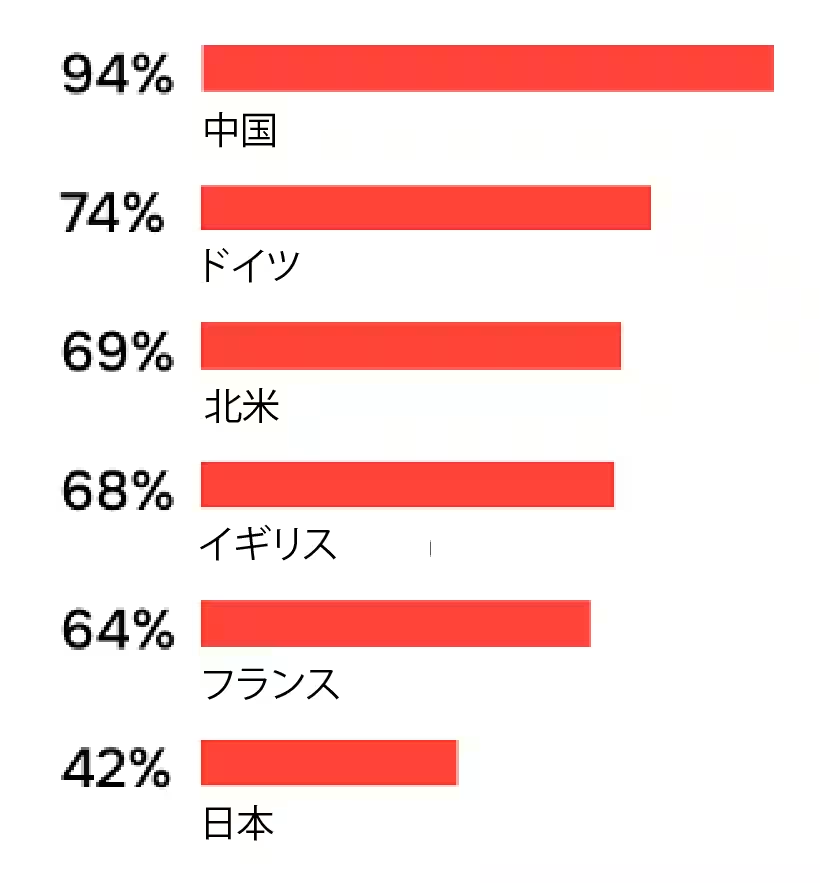
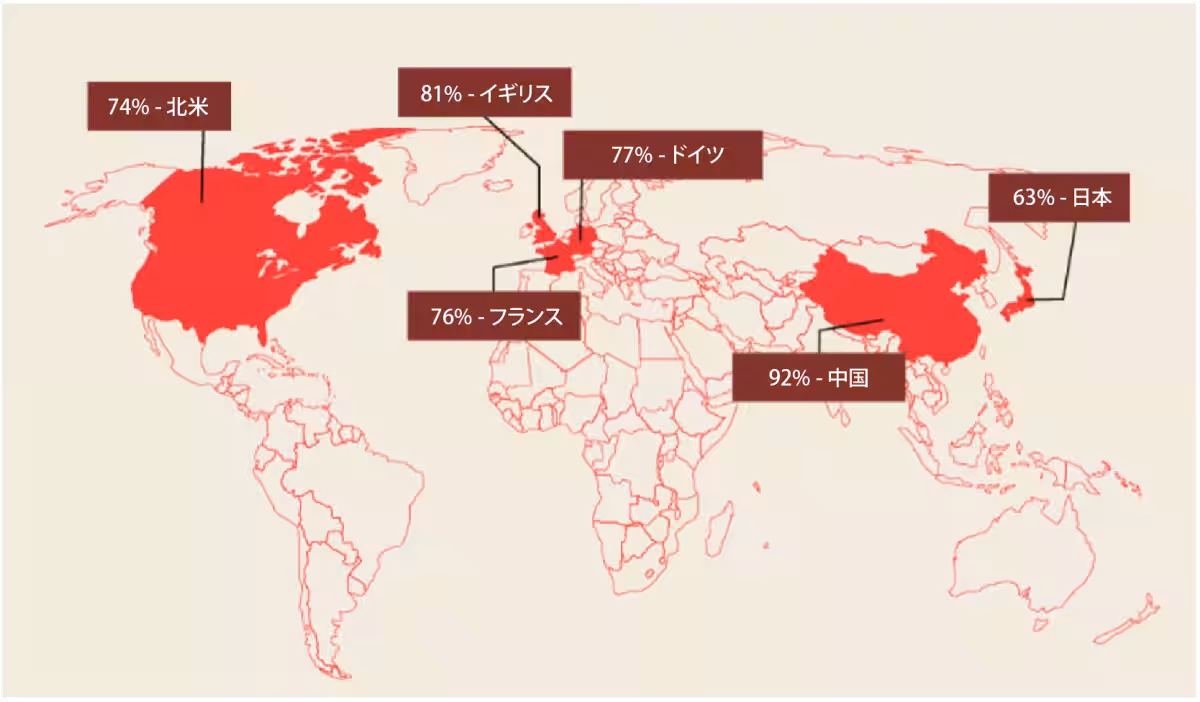
The research also pointed out a gap in preparedness among Japanese companies, revealing that only 42% feel they are ready to operate robots, compared to 69% internationally. This is the lowest among the nations surveyed, particularly stark when contrasted with 94% in China.
Furthermore, trust in robotic solutions appears lacking with only 10% of Japanese companies fully trusting their robots, compared to 13% globally, and 23% expressing total distrust. These disparities expose a broader hesitance towards full robotic integration, revealing that while acceptance is present, confidence in operational reliability remains low.
Japan anticipates that 19.7% of its workforce could be automated in the next decade, paralleling the global estimate of 19.9%, yet significantly lower than China's projected 32.1%. Interestingly, 65% of Japanese workers feel no resistance to collaborating with robots, which is slightly below the global average of 70% and starkly lower than 89% in China.
Industry Variance in Robotics Adoption
This disparity in robotics adoption rates reveals a striking polarization across different industries. While manufacturing and automobile sectors demonstrate robust uptake, the healthcare and logistics industries appear reticent. This variance suggests a critical need for enhancing safety and reliability in robotics, particularly within healthcare, where human interaction is vital.
According to Sachin Agarwal, Country Sales Director for QNX Japan, the findings highlight the unique challenge of labor shortages exacerbated by Japan’s demographic trends. He notes that not only is there significant disparity in robotics adoption between large and small companies, but also that industries like healthcare and logistics need focused encouragement to facilitate adoption—underscoring the necessity for dependable software solutions like those from QNX.
Global Trends and the Future of Robotics
Globally, the survey emphasized that 77% of technology leaders express trust in robotics for critical workplace functions, largely influenced by factors of safety and proven reliability. Approximately 20% of executives anticipate their workforce could be automated within a decade, mirroring overall trends where the robotics market is projected to grow significantly—from $51 billion in 2024 to over $163.9 billion by 2030.
Jim Hirsch, Vice President of EMEA and North America for QNX's embedded market, highlights that while acceptance of robotics technology has increased significantly, skepticism persists against the backdrop of lapses in performance, safety, and reliability that may arise from deploying inadequately supported robotic systems. He emphasizes that robots should prioritize the safety of human operators and the working environment to truly deliver on their potential.
Conclusion and Recommendations
To address the profound labor shortages anticipated in Japan, focusing on enhancing robotics adoption in sectors that lag remains crucial. QNX stands ready to support organizations in leveraging reliable, safe, and sophisticated robotic technologies that can positively impact workforce dynamics and operational efficiency.
For organizations looking to explore robotics further, QNX offers a reliable foundation in embedded systems, proven across various industries, ensuring alignment with existing infrastructures and enhancing overall system reliability.
To learn more about QNX's solutions, visit QNX.com and follow @QNX News on social media for updates.
Topics Consumer Technology)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.