
Survey Reveals Trends in Financial Education for Children in Households
Introduction
Sony Bank, headquartered in Tokyo, has recently conducted a comprehensive survey on household financial education aimed at children. With the increasing importance of financial literacy in today's economy, this research sheds light on how parents are currently approaching the subject with their children from elementary to high school.
Survey Overview
The survey was conducted with 2,709 customers holding accounts at Sony Bank during July 2025. The insights gained are crucial for understanding current family dynamics surrounding money education in Japan.
Key Findings
Financial Education Implementation at Home
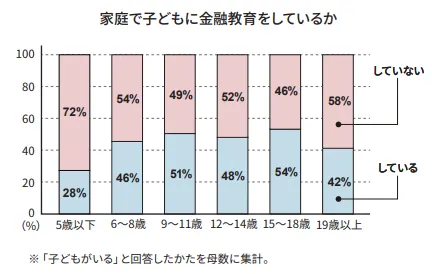
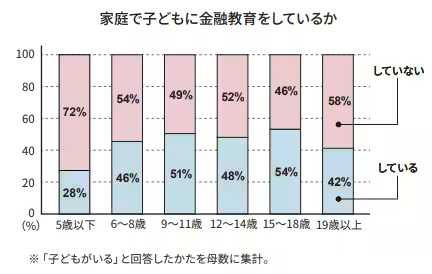
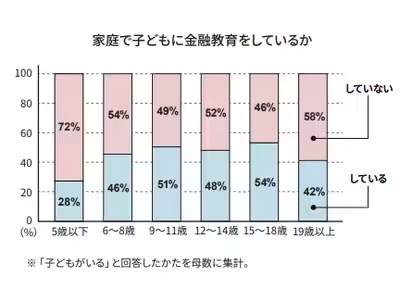
The survey reveals that nearly half of the families are engaged in providing financial education to their children. Specifically, 40% of the 2,110 respondents with children at home reported conducting some form of financial education. Among them, the trend is notable that formal education typically begins when children reach elementary school age (around six years old), correlating with an increased allowance or pocket money being given. The statistics indicate that 28% of families educate their children under five and this increases to 46% for children aged six to eight, showcasing the transition into a more conducive understanding of financial matters as children grow older.
Priorities in Teaching Financial Literacy
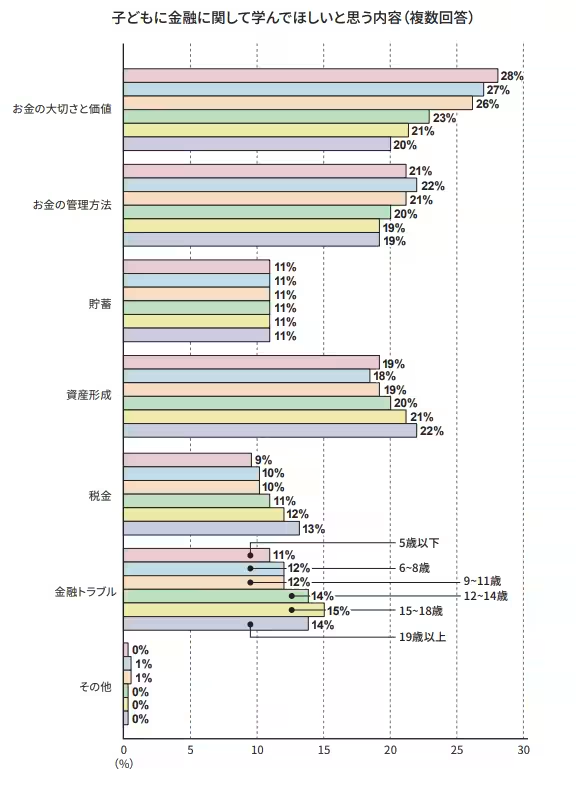
When examining the content of what parents want their children to learn, the emphasis is overwhelmingly on understanding the importance and value of money, along with effective money management techniques. For younger children (under the age of 14), foundational lessons focus on the value of money, with parents expressing a desire for their children to grasp the fundamentals early on. Interestingly, with older children, there is a noticeable shift towards wanting them to learn about asset formation, taxation, and understanding financial troubles as they prepare for adulthood. This indicates a clear evolution in the complexity of financial education as children mature.
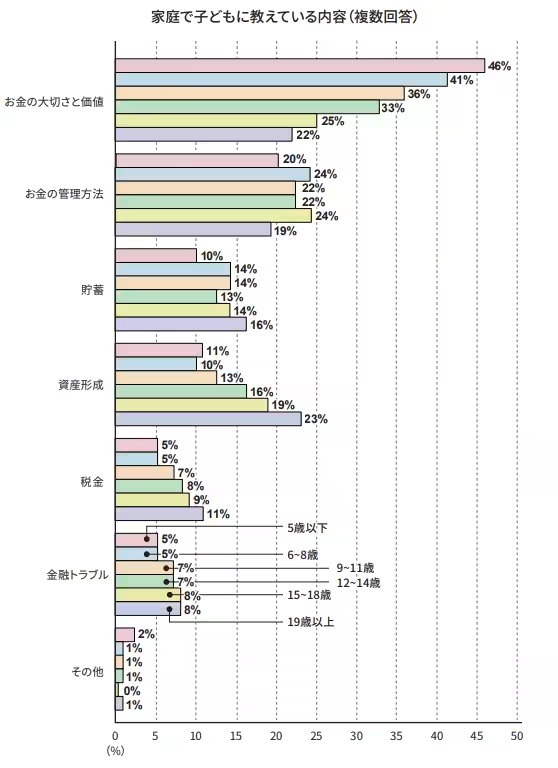
Family Dynamics and Educational Content
The statistics further reveal that the prevailing topics taught include the value and management of money, where families with high school-aged children (up to 18 years) show a strong tendency to educate about these essentials. This was noted as being particularly strong among families teaching children aged six to eight, where over 20% of parents reported discussing money management practices. Conversely, while the teaching of asset formation and management of tax seems crucial, fewer families feel equipped to impart these lessons, indicating a gap in resources or comfort levels among parents on more advanced topics.
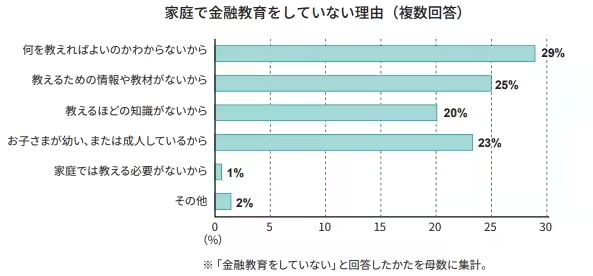
Barriers to Financial Education
Despite the willingness to educate, nearly 30% of the surveyed parents cited a lack of knowledge on what specific topics to teach as a barrier to providing financial education. Furthermore, 25% expressed that there are no sufficient resources or materials available for teaching these concepts. As a solution, many parents recognize the necessity of emphasizing not only the value of money but also broader life skills such as communication and interpersonal relationships, signaling a well-rounded approach towards raising financially savvy children.
The Role of Technology in Financial Learning
An interesting development in the survey is the potential use of technology in financial education through Sony Bank WALLET. Families can access family debit cards starting from age 12, promoting practical financial skills from an early age. Parents can monitor their spending through the app, creating a real-time learning scenario for children about money management.
Conclusion
As financial education effectively evolves, the value of addressing its components early on cannot be overstated. Sony Bank's survey underscores the importance of initiating conversations about money in families, dispelling uncertainties, and paving the way for the next generation to navigate their financial futures wisely. Overall, equipping children with the right tools and knowledge can form a formidable foundation for their financial literacy journey.
Topics Financial Services & Investing)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.