

Revolutionary Discoveries on the Protective Mechanism of Thylakoid Membranes in Photosynthesis
Groundbreaking Research on Thylakoid Membrane Stability
Recent collaborative research involving Okayama University, Osaka University, RIKEN, and Kyoto Sangyo University has unveiled significant insights into the mechanisms sustaining the thylakoid membrane, vital for photosynthesis. Professor Wataru Sakamoto of Okayama University and his team elucidated the role of a protein named VIPP1, which is critical in maintaining the structure and function of thylakoid membranes under varying temperature conditions.
The Thylakoid Membrane: A Crucial Component
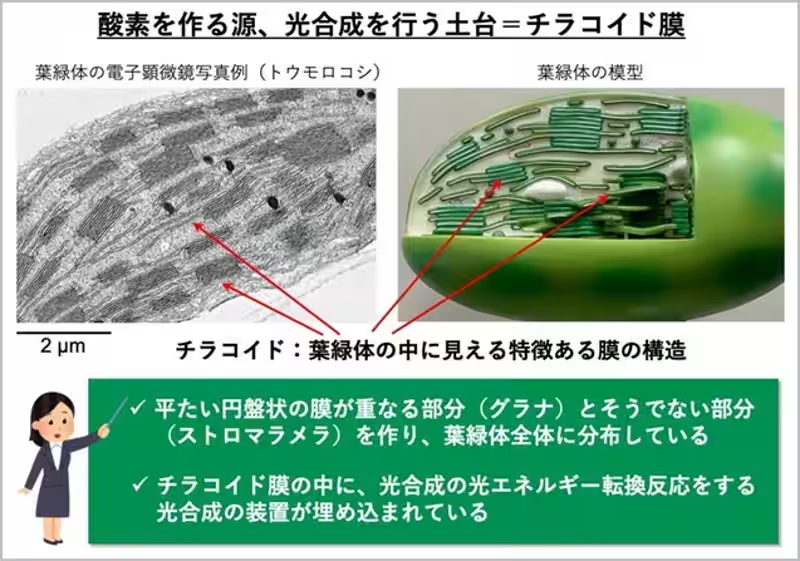
Photosynthesis, the process that transforms light energy into chemical energy, occurs at the thylakoid membranes in chloroplasts. These membranes are often likened to solar panels, capturing sunlight and converting it into energy-rich compounds. For years, the precise mechanisms underlying the stability and integrity of thylakoid membranes have remained largely mysterious; however, this research sheds light on this essential aspect of plant biology.
Focusing on the VIPP1 protein, researchers have discovered that it exists as long filamentous structures that form bundles adjacent to the thylakoid membranes. Notably, these structures can change shape in response to environmental stressors such as high temperatures. By manipulating the expression of VIPP1 in tobacco plants, the research team successfully demonstrated that elevated levels of this protein conferred increased heat resistance, suggesting a path forward for engineering climate-resilient crops.
Enhancing Photosynthesis Efficiency
The findings from this study are particularly significant as they hold the potential to improve photosynthetic efficiency and agricultural productivity. As global temperatures continue to rise, developing crops that can thrive under heat stress becomes increasingly critical. This research not only enhances our understanding of the fundamental processes of life but may also contribute to advancements in sustainable agriculture.
Professor Sakamoto expressed his enthusiasm about the implications of their findings, stating that the ability of plants to utilize light energy efficiently is a marvel that impacts all life on Earth. He envisions a future where the mysteries of photosynthesis can be further unraveled and potentially manipulated for improved agricultural outcomes.
Publication and Recognition
The findings of this groundbreaking research were published in the esteemed journal Plant Physiology on April 8, 2025. This recognition marks a significant milestone for the research teams involved and underscores the importance of collaborative scientific efforts in tackling global challenges related to food security and environmental sustainability.
Researchers note that the funding and support from various scientific entities, including the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science and the Okayama University International Photosynthesis Program, have been instrumental in driving forward this pioneering work.
Moving forward, the scientific community looks toward the practical applications of these findings, particularly in developing resistant crop varieties to ensure food security in the face of climate change. As we advance into an era where understanding plant biology holds the key to sustainable practices, studies like these will continue to play a pivotal role in shaping our agricultural landscape for generations to come.
For detailed information on the research, the full publication can be accessed here. Discover more about Okayama University's innovative approaches in plant science by visiting their official website.








Topics Health)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.