
Rising Summer Heat and Awareness of Natural Disasters Highlight Solar Power and Battery System Adoption in Japan
Rising Summer Heat and Awareness of Natural Disasters Highlight Solar Power and Battery System Adoption in Japan
With the intensifying summer heat and increasing awareness about natural disasters, there has been a notable surge in interest among homeowners in Japan regarding the adoption of solar power generation systems and batteries. This trend, however, faces obstacles primarily due to initial cost concerns and a lack of awareness about subsidy programs. A recent research conducted by ECODA, a specialized solar power and battery system provider, sheds light on homeowners' motivations, expectations, and apprehensions when considering these energy solutions.
Overview of the Research
On May 23, 2025, ECODA conducted a survey entitled "Intent and Determining Factors for the Adoption of Solar Power and Battery Systems." Targeting homeowners interested in solar power and battery systems, the survey involved 1,021 participants and aimed to understand their motivations, information sources, and decision-making criteria. The findings reveal that rising electricity costs and frequent natural disasters influence households to consider energy self-sufficiency and emergency preparedness more seriously than ever before.
Long-Term Interest in Solar Energy
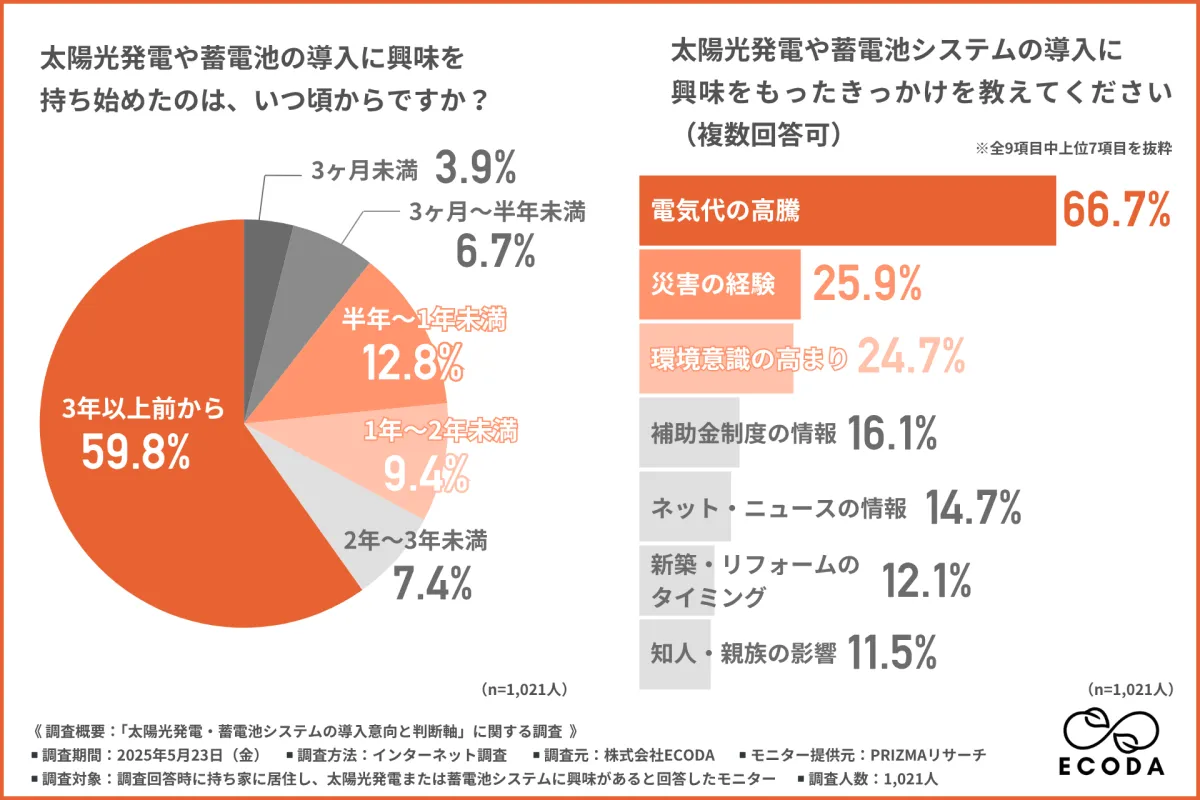
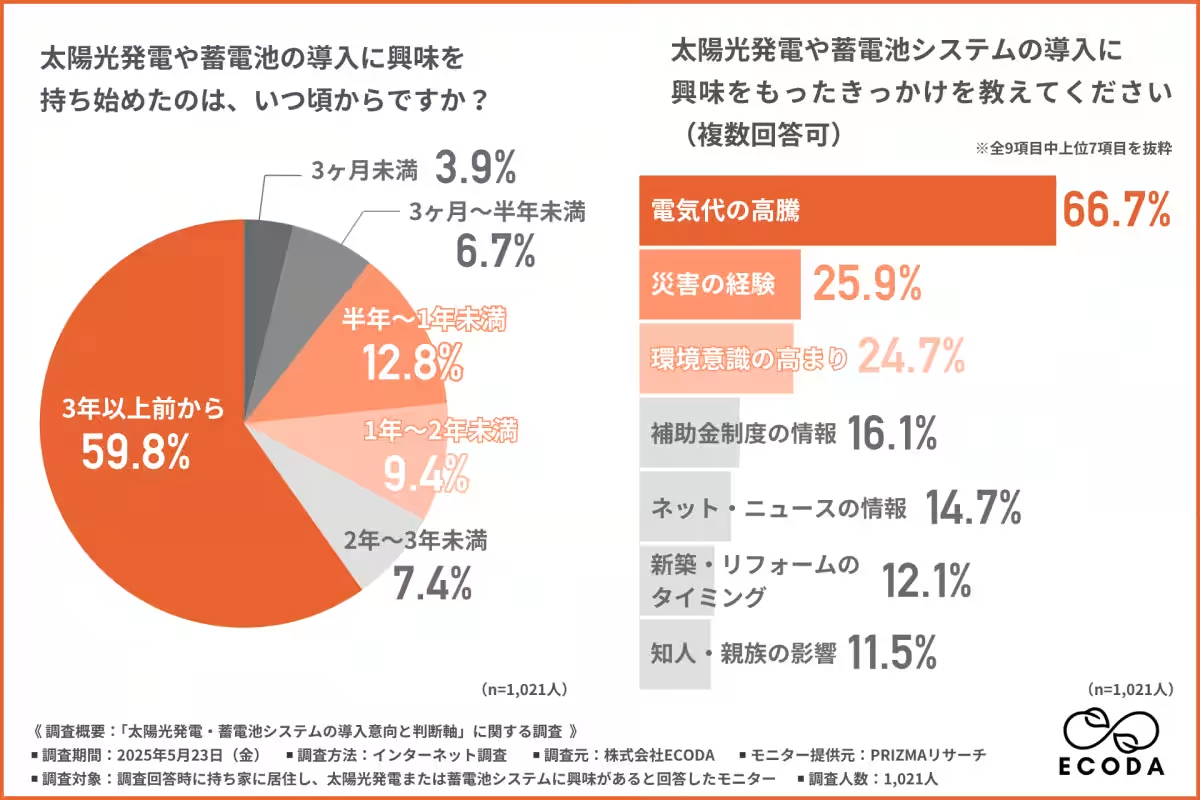
The initial question of the survey asked participants when they first became interested in solar power or battery systems. Surprisingly, nearly 60% of respondents expressed that their interest emerged over three years ago. In contrast, only smaller percentages indicated interest within the last three months to two years. The data suggests a persistent and growing curiosity among homeowners.
Triggers for Interest
When asked what stimulated their interest in adopting solar power or battery systems, the predominant reason was the increase in electricity prices (66.7%). Other significant factors included personal experiences with disasters (25.9%) and a heightened awareness of environmental issues (24.7%). The urgency stemming from energy concerns and climate-related events clearly plays a vital role in convincing households to consider renewable energy solutions.
Expectations from Adoption
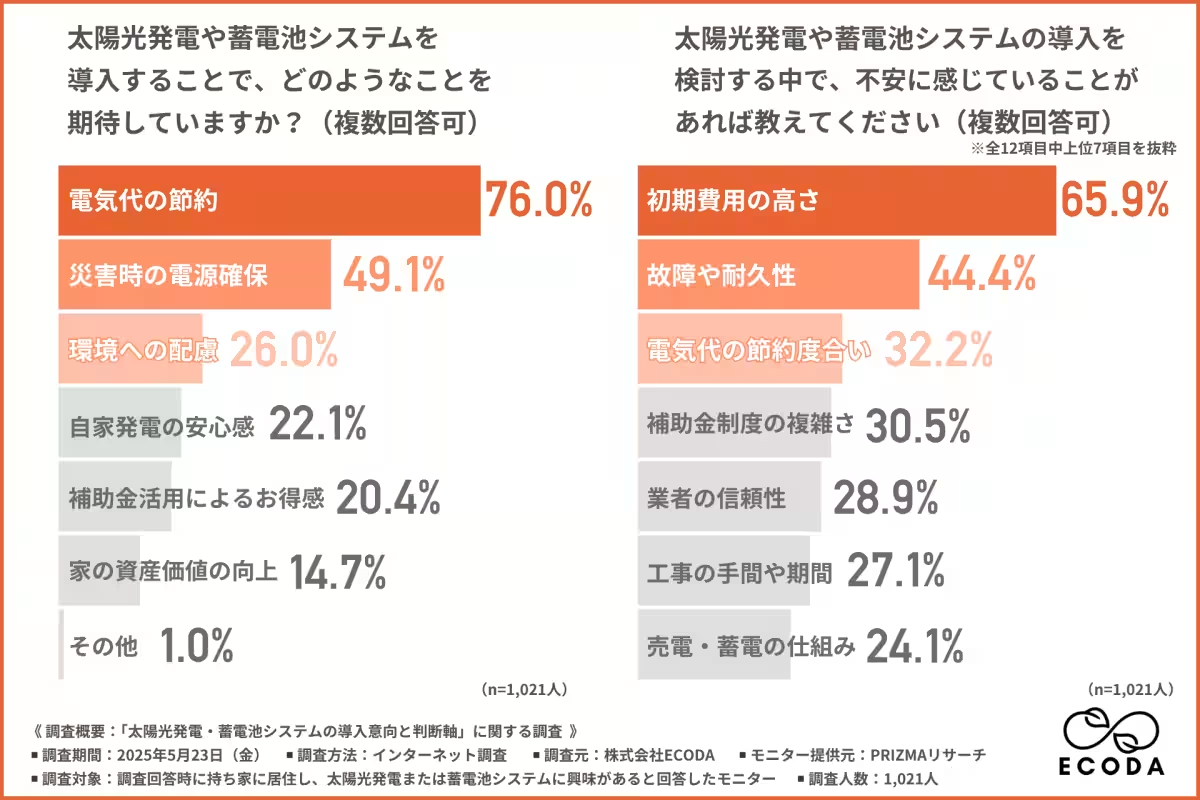
Respondents were also asked about their expectations associated with implementing these systems. Notably, 76% anticipated saving on electricity costs, while nearly half (49.1%) sought reliable power sources during emergencies and 26% expressed concern over environmental impacts. These motivations underline the practical benefits that homeowners aim to achieve through solar energy adoption.
Concerns Hindering Adoption
Despite increasing interest, many potential adopters also voiced concerns. The primary apprehension cited by 65.9% of respondents was the high initial costs associated with solar energy setup. Other significant worries included system reliability (44.4%) and an unclear picture of potential savings on electricity bills (32.2%). The substantial upfront investment appears to be a critical factor influencing homeowners' decisions.
Furthermore, when they were prompted about realistic budget expectations for installing these systems, a significant number believed that a budget of around 1 million yen ($7,500) was reasonable, highlighting a gap between their perceived costs and market prices.
Savings Expectations
In the context of expected savings, close to 45.5% of homeowners anticipated a reduction of between 3,000 to 5,000 yen ($22 to $37) per month on electricity bills. This expectation aligns with an overall trend where families are looking for tangible evidence that adopting solar energy will effectively lower their living expenses.
The Role of Subsidies
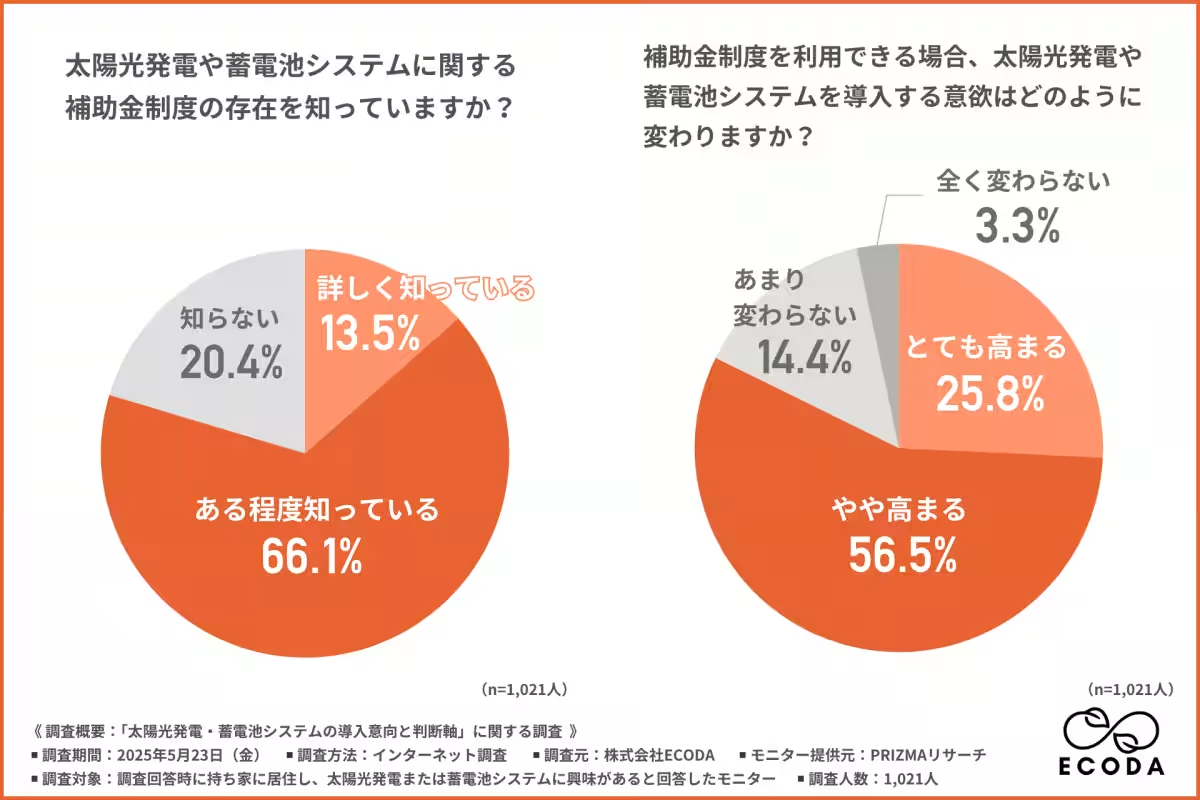
The survey further explored awareness of subsidy programs aimed at facilitating the adoption of solar power and battery systems. While over 60% of respondents claimed to have some awareness about these programs, only 13.5% were familiar with them in detail. Yet, a striking 81% stated that their willingness to adopt these systems would increase significantly if subsidies were made available.
The most critical factors when utilizing subsidies included the percentage covered (44%), the simplicity of the application process (25.6%), and the speed of receiving funds (15%). This places an emphasis on the necessity for clarity, accessibility, and expediency in subsidy programs to drive adoption.
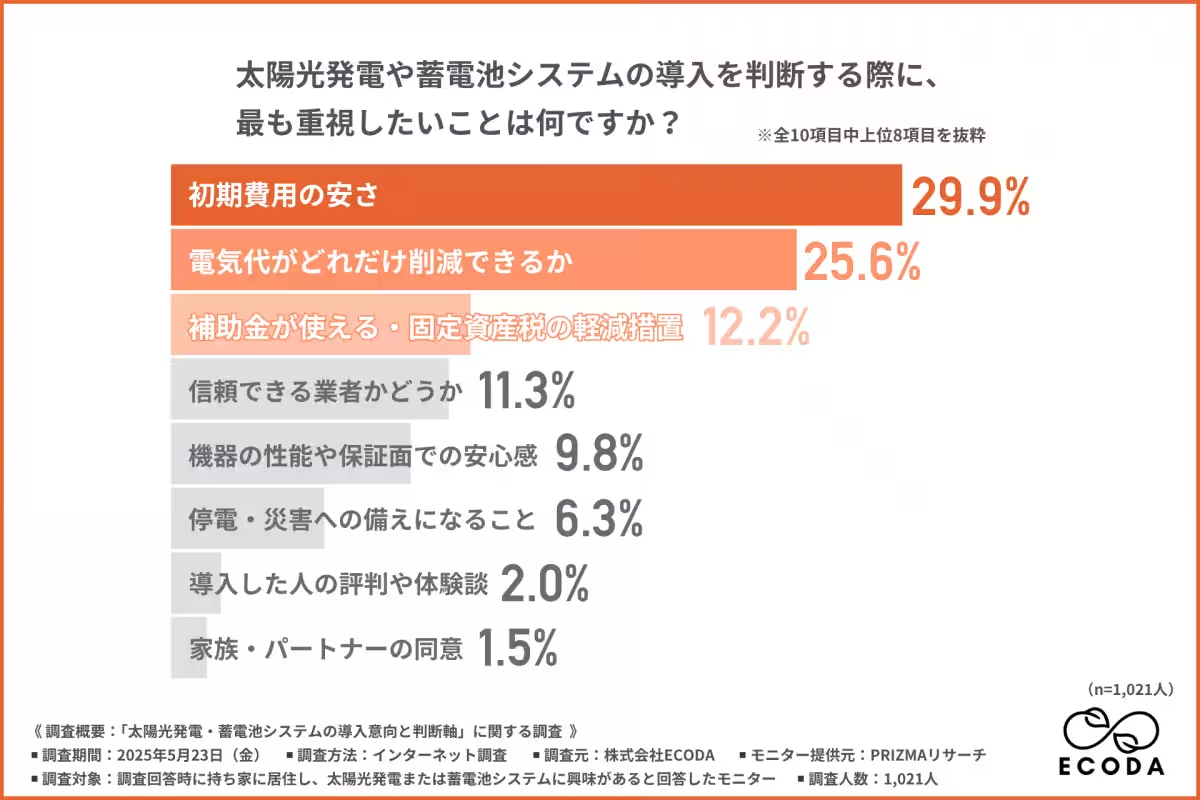
Key Decision Factors
When examining what homeowners prioritize in their decision-making, the results indicated that the primary considerations were the affordability of initial costs (29.9%), quantifiable savings on utilities (25.6%), and the availability of subsidy options (12.2%). This underscores an essential viewpoint where families regard the adoption of solar power and battery systems as an investment linked directly to their economic circumstances.
Conclusion
The recent survey results illustrate that interest in solar power and battery systems persists long-term among homeowners. Factors such as rising electricity bills and disaster preparedness serve as potential catalysts for adoption. Although significant expectations exist regarding cost savings and reliable power, there are notable apprehensions surrounding initial costs and system durability.
As subsidy programs can significantly elevate willingness to adopt, more transparency and accessibility in these initiatives will be crucial. Ultimately, homeowners are looking for a balance of initial affordability and long-term savings as they navigate the decision to invest in solar energy for their homes. ECODA, a company dedicated to providing reliable solutions, offers comprehensive services from pre-installation consultations to aftercare, ensuring families can embrace renewable energy confidently. For further information, please visit ECODA's official site.

Topics Consumer Products & Retail)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.