
Development of High-Conductivity Composite Electrolyte Films for Fuel Cells Using Functional Nanofiber Frameworks
Introduction
In March 2025, the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) unveiled a roadmap aimed at advancing fuel cell technology for heavy-duty vehicles (HDV). This initiative intends to enhance the driving range, operating time, and suitability of fuel cells for large commercial mobility solutions. To achieve these ambitious objectives by 2035, NEDO has initiated a funding application for joint research and development aimed at bolstering the foundations for hydrogen utilization.
Project Overview
Tokyo Metropolitan University has been selected as a key collaborator in this project, which is set to run from 2025 through 2027, with an overall budget of approximately 620 million yen. The primary goal is to develop high-conductivity and highly durable composite electrolyte films using a functional nanofiber framework, addressing the technical challenges outlined in the fuel cell roadmap.
Professor Hiroyoshi Kawakami and Associate Professor Masafumi Yamato, both from Tokyo Metropolitan University, will guide this pioneering research. The project also includes re-delegation to Iwate University and Akita University, ensuring a collaborative effort across multiple institutions.
Innovation in Electrolyte Development
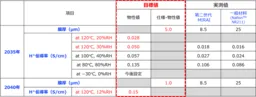
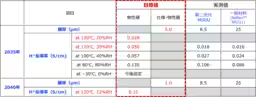
A critical factor in achieving the 2035 fuel cell roadmap goals is the enhancement of the proton conductivity and gas barrier properties of the electrolyte membranes. The project will focus on creating innovative composite electrolyte films that utilize a nanofiber framework to support proton conduction, improve chemical stability, and ensure mechanical stability even in ultra-thin membranes measuring less than 5 micrometers.
This development will leverage newly engineered non-fluorinated polymer materials and quenching agents designed to enhance durability by mitigating the production of reactive radicals that can compromise membrane integrity. To significantly expedite the development process, automation through robotics will be integrated, coupled with performance evaluation devices to create a fully automated experimental setup aimed at accelerating the progress of membrane development by over 100 times.
Research Challenges and Goals
Achieving the objectives set forth in NEDO's roadmap requires overcoming significant trade-offs inherent in the development of electrolyte membranes. For high-performance applications, the challenges include:
1. Balancing high proton conductivity with durability.
2. Achieving durability while maintaining ultra-thin membrane design.
3. Managing cost alongside the requirements for high proton conductivity.
Despite potential resolutions for each challenge individually, the intricate relationships necessitate innovative approaches to simultaneously meet all requirements—an endeavor that the current project seeks to tackle.
Historical Context and Importance
Japan has been at the forefront of fuel cell technology for years, successfully commercializing household units such as Enefarm and fuel cell vehicles (FCVs). As a result, Japan holds a leading position in the field with the highest number of patents globally. Focusing on heavy-duty vehicles presents a new frontier for fuel cell applications, given their specific needs for long range, extended operating time, low weight, and cost-effectiveness.
To stay competitive, this project aims not only to elevate the performance standards in fuel cell technology but to adapt existing innovations to meet market demands, ultimately leading to enhanced adoption of hydrogen-fueled solutions in larger commercial vehicles. The focus on DX technology will catalyze an accelerated pace of research, significantly enhancing Japan's competitive edge in the global fuel cell market.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the development of high-conductivity composite electrolyte films via functional nanofiber frameworks stands as a pivotal step towards achieving the future of hydrogen fuel cell technology. The collaboration between universities, pioneering research methods, and commitment to innovation promises to yield groundbreaking advancements that will not only meet but exceed the ambitious targets set by NEDO for the year 2035. By harnessing advanced manufacturing processes and material sciences, the project aims to establish a strong foundation for the widespread utilization of fuel cells in heavy-duty transport, ultimately benefiting industry sustainability and reducing carbon emissions.
References
- - NEDO: Research and Development Projects
- - Tokyo Metropolitan University Department: Kawakami Lab
Topics Consumer Technology)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.