
Comprehensive Security Assessment of the Decentralized SNS Protocol Nostr Unveiled
Comprehensive Security Assessment of Nostr
In a rapidly evolving digital landscape, decentralized social networking services (SNS) are gaining traction as alternatives to traditional, centralized platforms. Among these innovations, Nostr stands out, boasting a user base of approximately 1.1 million. A collaborative research team, comprising the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT), Osaka University, NEC Corporation, and Hyogo Prefectural University, has conducted the world's first comprehensive security evaluation of the Nostr protocol.
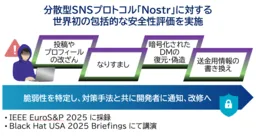
This evaluation, employing methods such as specification analysis, implementation investigation, and proof of concept, identified critical security vulnerabilities associated with the protocol. Issues like post tampering, impersonation, and the potential for restoring encrypted direct messages were among the top concerns. The team proactively designed eight specific attack scenarios and validated their efficacy through Python-based test codes, thereby unveiling significant risks present within the protocol.
The results of this security assessment were reported to various application developers in June 2023 and January 2024, highlighting important countermeasures to mitigate these vulnerabilities. The response to these findings has been overwhelmingly positive, with developers initiating phased patch deployments and feature modifications across major client applications.
Background
Historically, SNS platforms like X (formerly Twitter) operated under centralized models, forcing users to relinquish control over their data and privacy. However, increasing discontent with algorithmic biases and the potential misuse of user information has prompted a shift toward decentralized models—a movement where users can choose trusted operators across multiple servers for enhanced data privacy and security.
Despite the growing adoption of decentralized applications utilizing the Nostr protocol, the complexity of its specifications and implementations often leaves them inadequately scrutinized for security flaws. This gap has created opportunities for malicious hacking attempts, necessitating urgent corrective measures.
Results of the Evaluation
The research team’s comprehensive analysis revealed various structural flaws within the Nostr protocol, leading to grave vulnerabilities such as:
- - Tampering with posts and profiles
- - Impersonation threats
- - Forgery or restoration of encrypted messages
- - Modification of information related to financial transactions
Following the identification of these vulnerabilities, the team systematically designed plausible attack scenarios ahead of the hackers. The attack scenarios were carefully crafted, tested, and their effectiveness confirmed, creating a robust framework for future defenses.
Future Prospects
This pioneering work not only leads to immediate improvements in the safety of the Nostr protocol but also sets the stage for assessing other decentralized SNS applications in the future. Continuous evaluation and enhancement efforts will contribute to the security evolution required to forge a safer environment for the next generation of social networking.
Academic Contributions
The research findings have been formally recognized, with a paper titled Not in The Prophecies: Practical Attacks on Nostr accepted for presentation at the upcoming IEEE EuroS&P 2025 conference. Furthermore, prominent participation in the highly regarded Black Hat USA 2025 briefings signifies the academic and industrial acclaim surrounding this work.
Speaker Information:
- - Speaker: Hayato Kimura
- - Co-Authors: Ryoma Ito, Kazuhiko Minematsu, Shogo Shiraki, Takanori Isobe
- - Presentation Title: Not Sealed: Practical Attacks on Nostr, a Decentralized Censorship-Resistant Protocol
- - Conference: Black Hat USA 2025 Briefings
This groundbreaking research is supported by JST, AIP Accelerated Program, JPMJCR24U1, and JSPS Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (JP24H00696).
Topics Consumer Technology)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.