
Unraveling and Controlling Combustion Oscillations using Network Science Insights
Understanding Combustion Oscillations through Network Science
Combustion oscillations, technical disturbances that can lead to significant damage within combustion devices, are a crucial area of study in engineering. Recent collaborative research led by Professor Hiroshi Gotoda and Assistant Professor Yusuke Nabae from the Tokyo University of Science has provided profound insights into the behavior and suppression of these destructive phenomena using network science principles.
The Essence of Combustion Instability
Combustion oscillations arise from the interactions between pressure fluctuations, heat release rates from flames, and velocity variations. Such phenomena can endanger the structural integrity of combustion systems, leading to unexpected failures and shortened lifecycles. The research team, which includes Kenta Kato from the graduate program, delved into these phenomena specifically concerning spray combustion invigorated by liquid fuels.
In conventional gas combustion scenarios, understanding oscillation behavior is already complex, but the introduction of liquid droplet dynamics introduces additional layers of intricacy. Together with researchers from Kyoto University, specifically Professor Ryoichi Kurose, they have been examining detailed mechanisms and behavioral patterns of spray combustion oscillations.
Key Findings: Network Behavior and Oscillation Dynamics
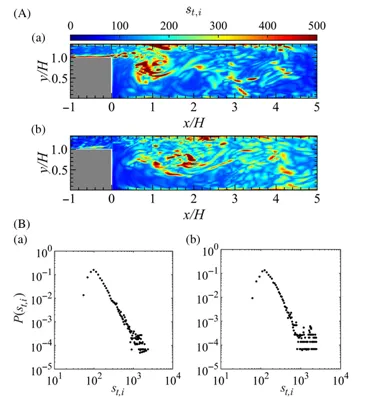
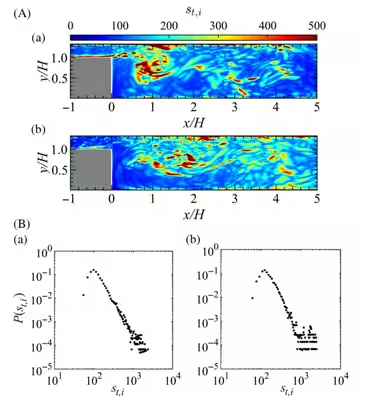
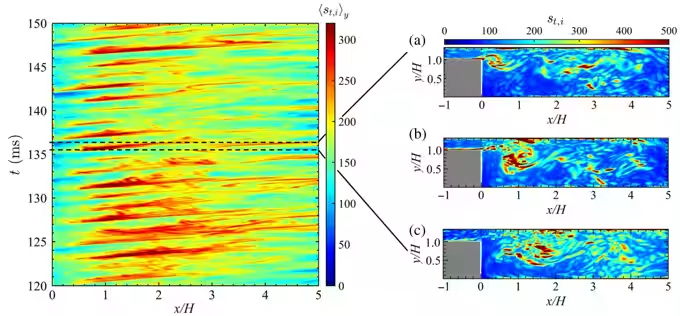
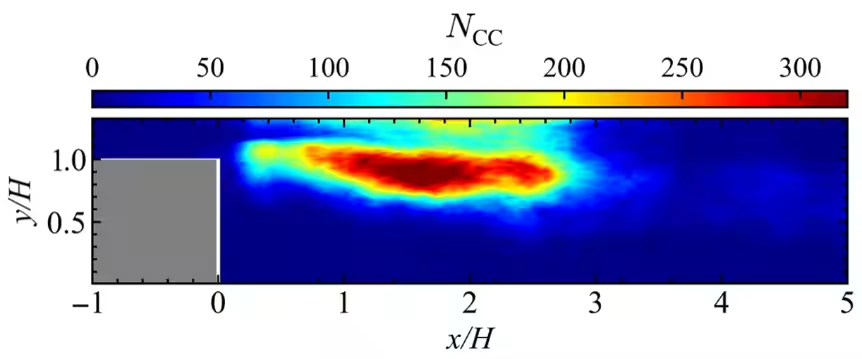
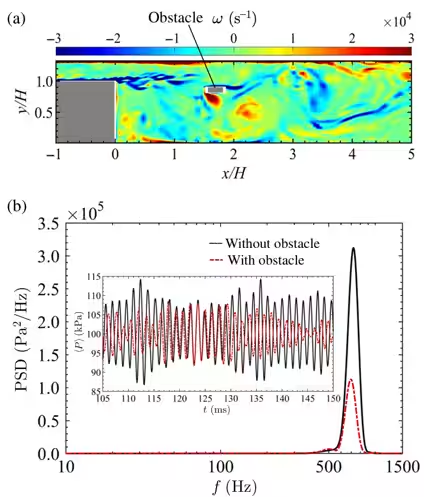
Through their research, the team identified that these oscillations exhibit 'scale-free' characteristics within turbulent networks, indicating a fixed correlation between large-scale organized eddy structures and pressure dynamics during combustion. Their investigations showed that significant hubs form within the turbulent network, representing zones of high node strength, which correspond to major oscillation occurrences.
This research highlights three primary findings:
1. The presence of scale-free characteristics in turbulent networks associated with combustion oscillations.
2. The emergence of key hubs that can dictate the dynamics of combustion oscillation behaviors.
3. The potential for disturbance suppression by strategically placing obstacles in identified high-connectivity regions within the turbulent networks.
Implementation of Suppression Techniques
The researchers proposed a novel concept of integrating small rectangular obstacles into the combustion chamber based on their findings from the connector community of the turbulent networks. These obstacles were placed in regions where significant oscillation patterns were identified, evaluated through high node strength and community density.
Experimental observations revealed that the introduction of these obstacles resulted in a marked reduction in pressure fluctuations and power spectral density peak values, effectively suppressing the oscillation behaviors in spray combustion systems. This demonstrates a potentially effective method to enhance the stability and performance of combustion chambers.
Conclusion: Future Directions and Implications
This research, published on July 2, 2025, in the journal 'Physical Review Applied,' underscores the importance of using innovative approaches in understanding and combating issues like combustion instability. As the dynamics of spray combustion reveal intricate behaviors influenced by network structures, this study lays the groundwork for developing more robust and efficient combustion systems.
The future of combustion technology may hinge on further exploring the intersections between network science and combustion instability, paving the way for safer and more efficient energy systems globally.
For those interested in detailed methodologies and further technicalities, the full paper titled "Network Dynamics and Suppression of Spray Combustion Instability in a Backward-Facing Step Combustor" is available in the journal, featuring comprehensive analyses and findings.
Topics Energy)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.