

Asahi Kasei Initiates Search for Global Partners for Biogas Purification Technology
Asahi Kasei's Biogas Purification System: A Step Towards a Sustainable Future
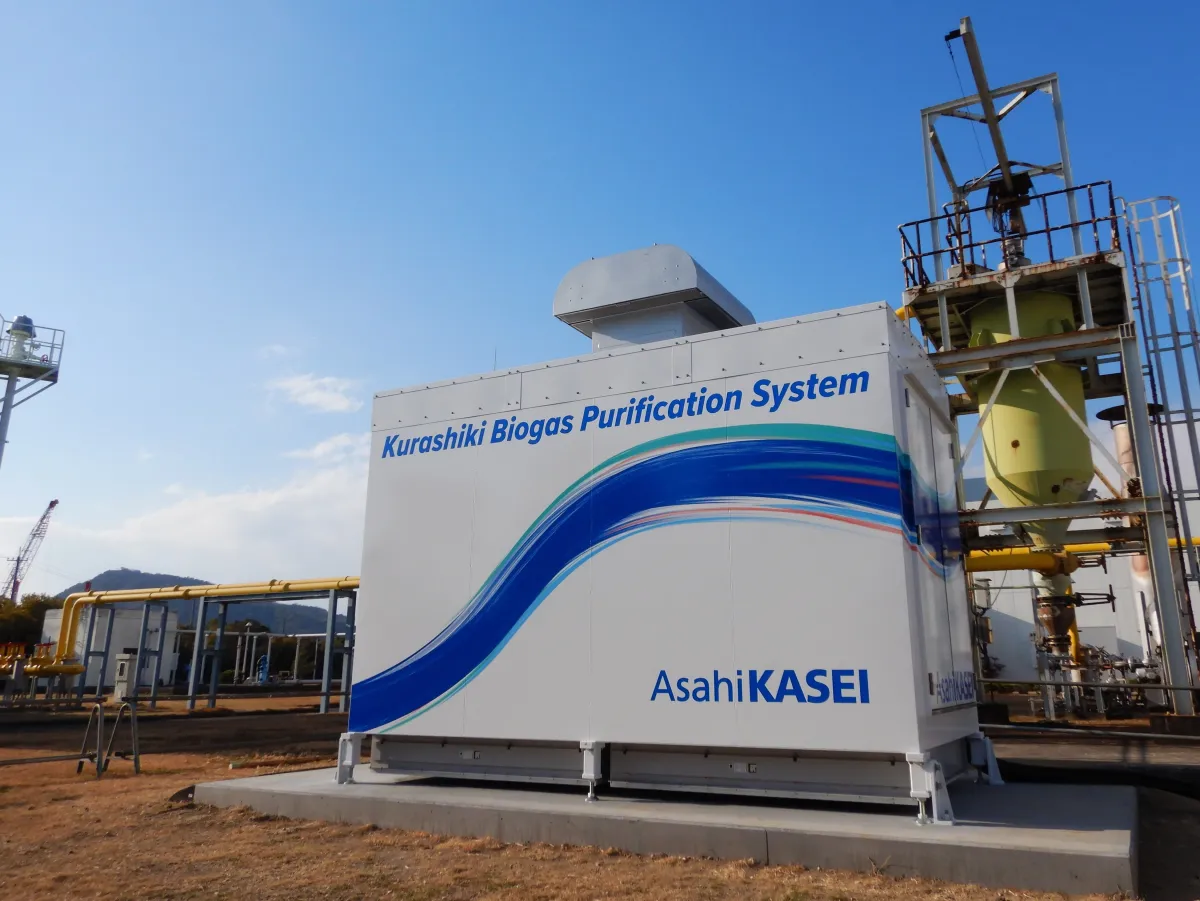
Asahi Kasei Corporation, headquartered in Chiyoda, Tokyo, has made significant strides in sustainable energy by initiating a comprehensive search for global partners to license its innovative biogas purification system. This move follows the successful preliminary evaluation of the system at the Kojima Wastewater Treatment Plant in Kurashiki City, Okayama Prefecture, where initial tests have demonstrated the ability to achieve both high purity and high recovery rates of methane.
The Social Significance of Biomethane Utilization
With global warming and energy security as pressing issues, the acceleration of renewable energy adoption has become a priority. Among various sources, biomethane derived from biogas stands out as a sustainable energy solution that can leverage existing natural gas infrastructures. As European countries increasingly embrace this technology, demand for injected biomethane into pipelines and bio-CNG is surging. In India, government policies are promoting the use of biogas as a solution to issues related to waste management and energy supply, particularly in rapidly urbanizing areas.
Overview of Asahi Kasei's Biogas Purification System
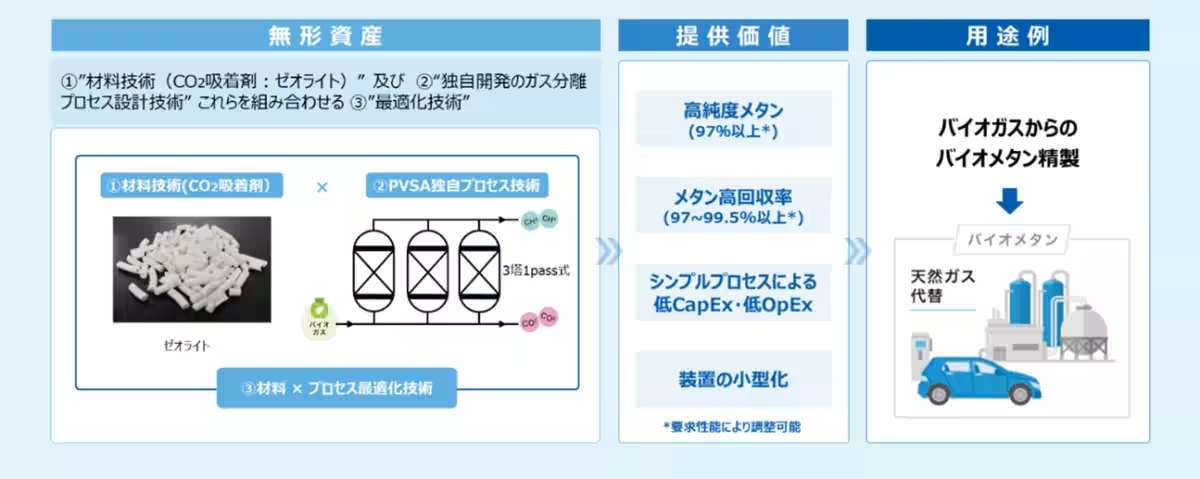
Asahi Kasei has a long history of expertise in catalyst development and gas separation technology, particularly in chemical production. The company has established unique technologies related to structural control and adsorption properties. Utilizing this knowledge, they have successfully developed a zeolite capable of selectively adsorbing CO₂. Combining the PVSA (Pressure Vacuum Swing Adsorption) process with zeolite technology, Asahi Kasei's biogas purification system efficiently removes CO₂ from biogas, resulting in the purification of biomethane with both high purity and recovery rates. This system not only supports the expanded use of biomethane as a renewable energy source but also helps achieve carbon neutrality.
Details of the Validation Test
Beginning in February 2025, Asahi Kasei has been conducting validation tests at the Kojima Wastewater Treatment Plant, using biogas generated from sewage sludge to verify the system's performance and stability under real gas conditions. Typically, achieving both high purity and high recovery has been a technological challenge, with these factors generally being a trade-off. However, this validation continuously monitors the ability to simultaneously meet these performance indicators in real gas environments.
Preliminary Evaluation Results
After about a month of continuous operations, the initial evaluation confirmed that the purity of the produced biomethane exceeded 97%, making it suitable for utilization in natural gas pipeline injections and as fuel for CNG (Compressed Natural Gas) vehicles. Additionally, the recovery rate was over 99.5%, demonstrating the capability to simultaneously achieve high purity and high recovery, addressing the key challenges in biomethane purification.
Future Plans
Asahi Kasei's biogas purification system is part of its co-creation initiative, TBC (Technology Value Business Creation), which focuses on leveraging intangible assets to create new business opportunities. The company aims for rapid social implementation in response to regional demands, particularly in Europe and India. To support this goal, ongoing performance verification and data accumulation from extended continuous operation tests in Kurashiki City are planned. Furthermore, partnerships with new companies and municipalities will be sought for validation at commercial scale, aiming for market introduction by 2027.
Under the philosophy of "Beginning the Change for a Better Future," Asahi Kasei is committed to creating intangible assets that provide societal value while working towards a better future for both people and the planet.
This article refers to several key terms: CNG (Compressed Natural Gas), a fuel made from high-pressure methane that has lower CO₂ emissions when compared to gasoline or diesel; PVSA (Pressure Vacuum Swing Adsorption), a technology that separates specific gases through alternating pressure and vacuum; and TBC (Technology Value Business Creation), Asahi Kasei's initiative to foster innovation through collaboration.

Topics Energy)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.