
Unlocking the Molecular Mechanisms Behind Continuous Plant Growth
Unlocking the Molecular Mechanisms Behind Continuous Plant Growth
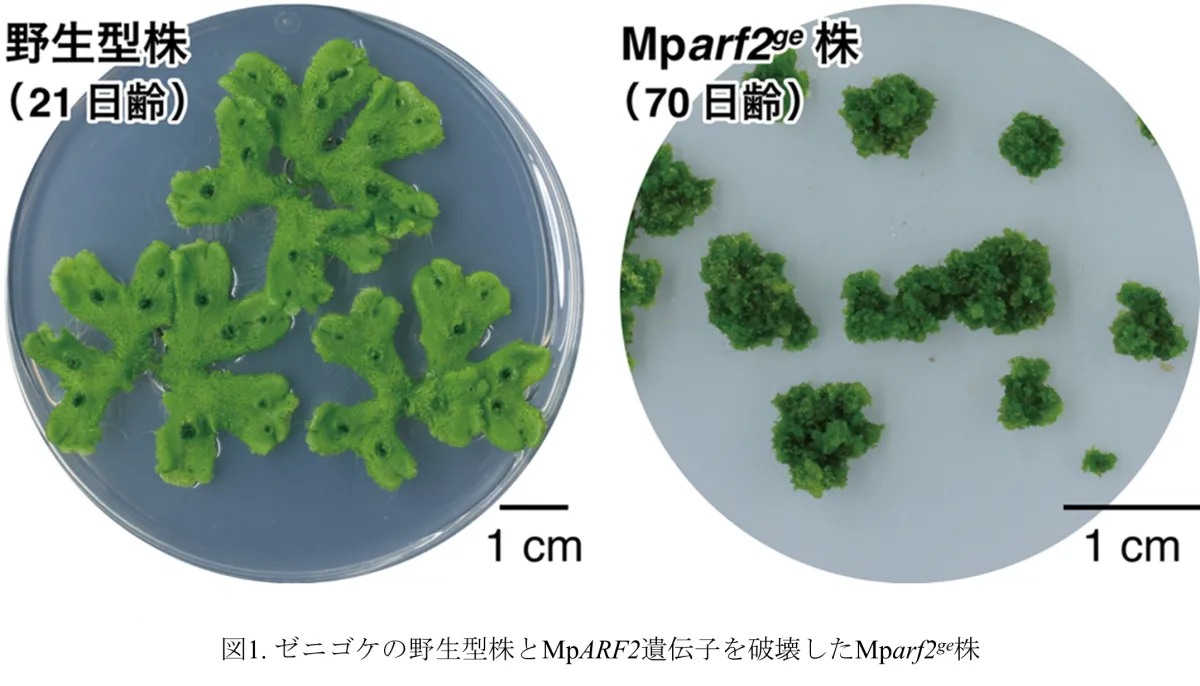
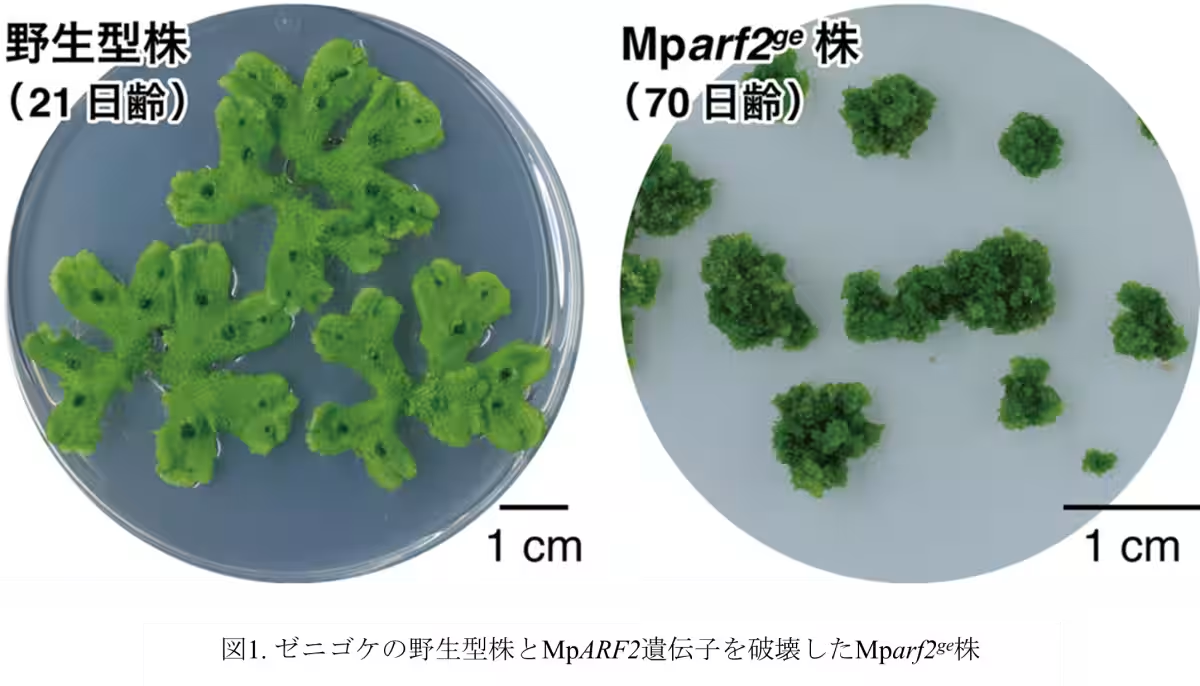
Recent advancements in plant biology have unveiled the molecular underpinnings that enable plants to sustain remarkable and perpetual growth throughout their life cycles. A study conducted by a team of researchers from Tokyo University of Science and institutions like Monash University and Cambridge University has brought new insights into the role of the transcription factor MpARF2 in this phenomenon.
Understanding the Mechanism of Continuous Growth
The study focused on the moss Marchantia polymorpha, which serves as an ideal model organism due to its simplicity compared to flowering plants. Researchers discovered that the transcription factor MpARF2 plays a pivotal role in modulating the effects of the plant hormone auxin, which is critical for the differentiation and development of plant organs.
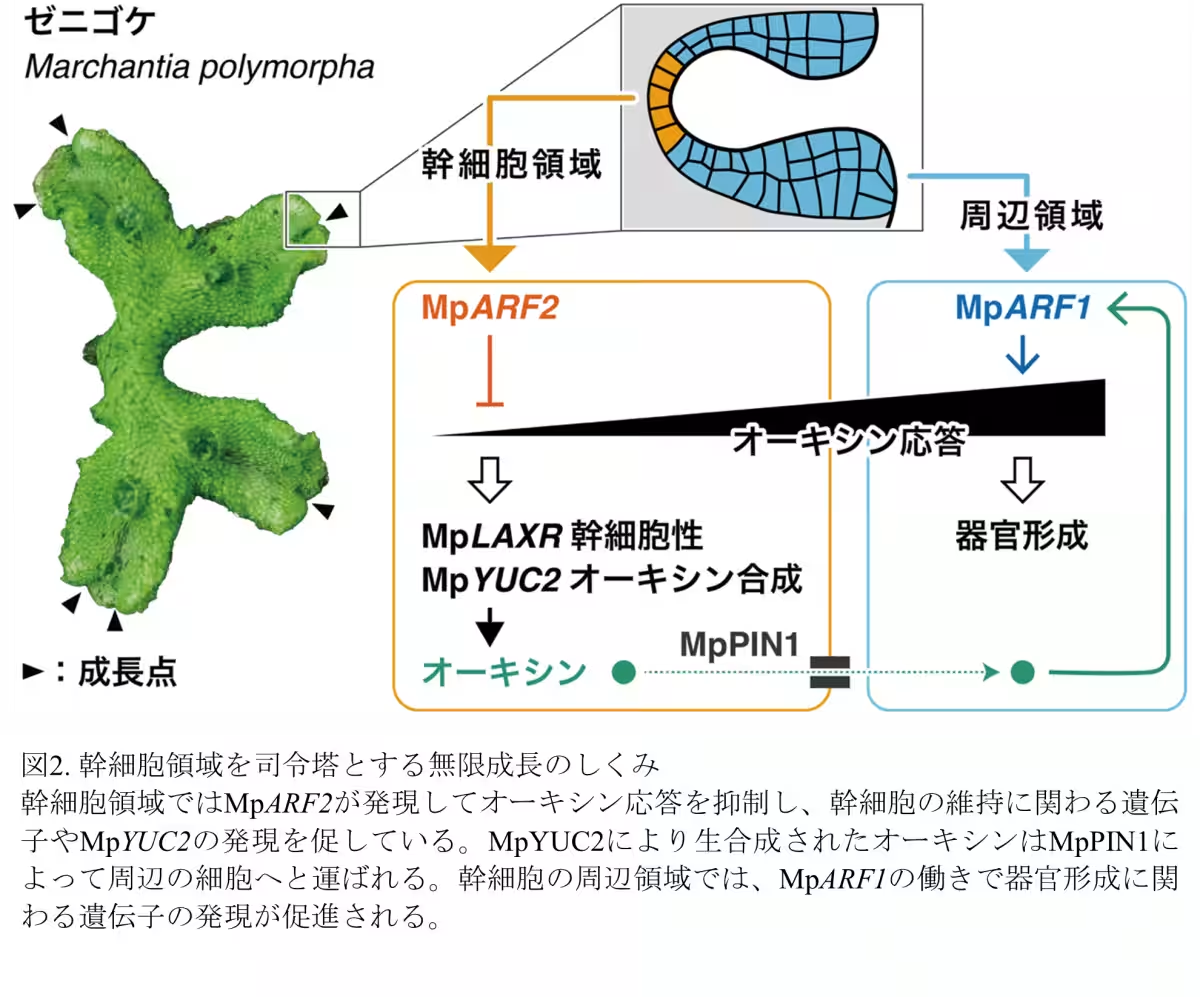
MpARF2 is predominantly expressed in the stem cell region of the plant, where it acts as a repressor of auxin responses. Interestingly, while it limits auxin response in the stem cell area, MpARF2 simultaneously activates auxin biosynthesis enzymes, promoting the production of auxin itself. This auxin, synthesized in the stem cell region, is then transported by auxin transporter proteins to the surrounding areas, facilitating organ formation.
Essentially, the stem cell region functions as an organizer, directing the differentiation of adjacent cells while remaining unresponsive to the signals it produces. This unique characteristic is underpinned by the core function of MpARF2.
Research Methodology
The research was spearheaded by Professor Ryuichi Nishihama from Tokyo University of Science, alongside a diverse team of graduate students and experts in various biological fields. By employing advanced genetic analysis and state-of-the-art techniques like RNA sequencing, the team analyzed the expression profiles of MpARF2 under different growth conditions.
Initial investigations revealed that MpARF2 is highly expressed in immature or regenerating plants, an indication of its crucial role in stem cell maintenance and growth point organization. Using genetic modification techniques, researchers suppressed the function of MpARF2, which ultimately led to the loss of the stem cell region and halted growth, signifying its essential role in stem cell formation and retention.
The Role of Auxin and Its Transport
Through further experiments, it became evident that MpARF2's suppression of auxin response was significant. Mutant plants with impaired MpARF2 exhibited heightened sensitivity to externally applied auxin, favoring an increased expression of genes associated with auxin response. This provided substantial evidence for MpARF2's inhibitory role in modulating auxin signaling at the genetic level.
Most notably, researchers identified a critical relationship between MpARF2 and MpYUC2, a gene coding for an auxin biosynthesis enzyme. The findings demonstrated that MpARF2 positively regulates MpYUC2, further controlling the overall auxin levels in the plant, which is vital for achieving optimal growth.
Implications of the Research Findings
The groundbreaking findings published in Current Biology help elucidate the fundamental principles of plant growth and development. As it stands, the discovery that stem cells can generate signals without responding to them opens new avenues for exploring artificial regulation in agricultural practices. By leveraging the inherent mechanisms of plant growth, we could develop innovative strategies to enhance crop resilience and productivity.
The study also poses important questions for the future: Is this regulatory mechanism of stem cell organization consistent across other plant species or has it evolved differently? Exploring these questions promises to deepen our understanding of plant development and diversity.
In summary, the research unveils a sophisticated architecture of plant growth management through the intricate roles of MpARF2 in stem cell organization, marking a significant leap towards harnessing these biological principles for agricultural biotechnology advancements.
- ---
This study highlights the sophisticated intricacies governing plant growth and raises stimulating prospects for future research aimed at translating this knowledge into practical applications within agriculture and beyond.
Topics Other)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.