International Standardization Enhances Reliability of Nanoparticle Evaluation in Liquids
Enhancing Reliability of Nanoparticle Evaluation with International Standards
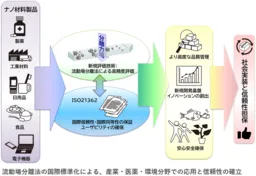
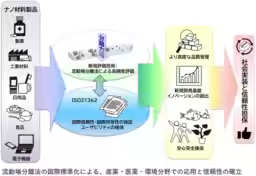
The introduction of the international standard ISO 21362:2026 marks a significant milestone in ensuring the reliability of quality and safety evaluations of nanoparticles used in various industries such as cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and material development. Developed by the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) in collaboration with researchers and equipment manufacturers globally, this standard addresses the challenges in quantifying nanoparticles dispersed in liquids accurately.
About ISO 21362:2026
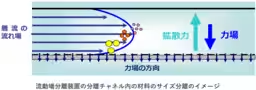
The focus of this standard is on the flow field separation method, which allows the evaluation of dispersed nanoparticles without any pre-treatment. By effectively separating nanoparticles based on their size and aggregation state, the method facilitates high-precision assessments while minimizing the influence of pre-treatment processes on the sample. This approach enables evaluations that are closer to the actual state of the samples, a crucial aspect in industries that prioritize safety.
Historically, the challenge around this method lay in its susceptibility to operational conditions, which could lead to variations in measurement results for the same sample. Recognizing this issue, AIST meticulously established common parameters through extensive collaboration with both domestic and international experts and comparative studies, thereby enhancing the reproducibility and reliability of measurements.
Practical Applications
ISO 21362:2026 provides a framework for various applications, including quality assurance in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals, novel material development, and the environmental assessment of micro- and nanoplastics. As standardized evaluation methods become globally shared, this will not only facilitate smoother research and development efforts but also bolster public trust in nanotechnology, contributing to a safer and more secure society.
Addressing Social Challenges
The presence of nanoparticles has become commonplace in our daily products ranging from cosmetics and pharmaceuticals to food packaging and electronic materials. However, accurately measuring the size and structure of these nanoparticles within liquid media posed significant technological challenges. This has made safety evaluations and quality assurance critical issues in industries relying on nanotechnology.
The flow field separation method shines as an innovative solution enabling the analysis of liquid-distributed nanoparticles without causing any damage. Despite being a promising technology, the original method faced hurdles due to variations arising from operational setups and equipment configurations. AIST's long-term collaboration with global researchers has led to optimized operational conditions and large-scale international comparison tests aimed at establishing universally acceptable benchmarks for quality analysis.
The Journey to Standardization
Historically, flow field separation methods were limited to categorizing polymers and particles by simple measures of molecular weight or size. However, as the need for accurate evaluation of dispersed nanoparticles emerged, AIST collaborated with various national and international partners to enhance the technology's efficacy. Notably, a major international research collaboration program, VAMAS, with the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) contributed to comparative tests involving over 20 global institutions to define critical parameters and establish reliable measurements.
In publishing ISO 21362:2026, the flow field separation method receives its first-ever international standard, enabling reliable evaluation of nanoparticles across several fields. It has also gained recognition from CEN in Europe and the FDA in the U.S., extending its applicability in regulatory frameworks internationally.
Future Prospects and Impact
With the establishment of this standard, industries such as cosmetics, electronics, coatings, and pharmaceuticals can now evaluate the aggregation and dispersion states of particles with high precision, maintaining international equivalency. This advancement not only enhances quality control and product development but also reduces technical barriers in compliance and trade, benefiting industries involved in international transactions.
Furthermore, the development of standard documentation and user guides will provide a more accessible environment for beginners and technical staff in the field, accelerating the adoption of the flow field separation method in practical applications. The collaboration for advanced measurement methods and the integration of new technologies is expected to broaden the application scope, particularly in bio and pharmaceutical sectors, while promoting deeper international technological collaboration.
- ---
Standard Overview: ISO 21362:2026
- - Title: Nanotechnologies — Analysis of nano-objects using asymmetrical flow and centrifugal field-flow fractionation.
- - Scope: This standard lays down the fundamental principles, prerequisites, and reporting requirements for evaluating nanoparticles in aqueous systems, employing both asymmetrical flow and centrifugal field-flow fractionation techniques.
Key Members Involved
- - Haruhisa Kato: Senior Researcher, Nanostructure Measurement Standard Group, AIST
For more details, visit the official Press Release.
Topics Consumer Products & Retail)









【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.