

Tokyo Gas Group Launches Innovative Methane Measurement Research for Enhanced Carbon Credit Reliability
Tokyo Gas Group's Groundbreaking Research on Methane Measurement
Tokyo Gas Co. and Tokyo Gas Engineering Solutions (TGES) have embarked on an innovative research project aimed at simplifying and enhancing the measurement and visualization of methane concentration in natural environments using their proprietary laser methane detection technology. The study aims to establish a more reliable method for calculating carbon credits generated from methane reduction.
Objective of the Research
The core purpose of this research is to develop a high-precision technology for measuring methane emissions accurately, which contributes to a more trustworthy evaluation of carbon credits. By leveraging the unique capabilities of the Tokyo Gas Group's laser detection and computational fluid simulation techniques, this project seeks to create a straightforward approach to monitoring methane emissions, particularly in rice paddy fields.
Background
The importance of carbon neutrality is more pronounced than ever as both corporations and local governments strive to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The demand for highly trustworthy carbon credits is growing, especially in light of ongoing international efforts to establish regulatory frameworks for carbon credit generation and use. Existing challenges in the verification and utilization of carbon credits necessitate a solution that is not only effective but also reliable in capturing methane emissions accurately.
Innovative Techniques Deployed
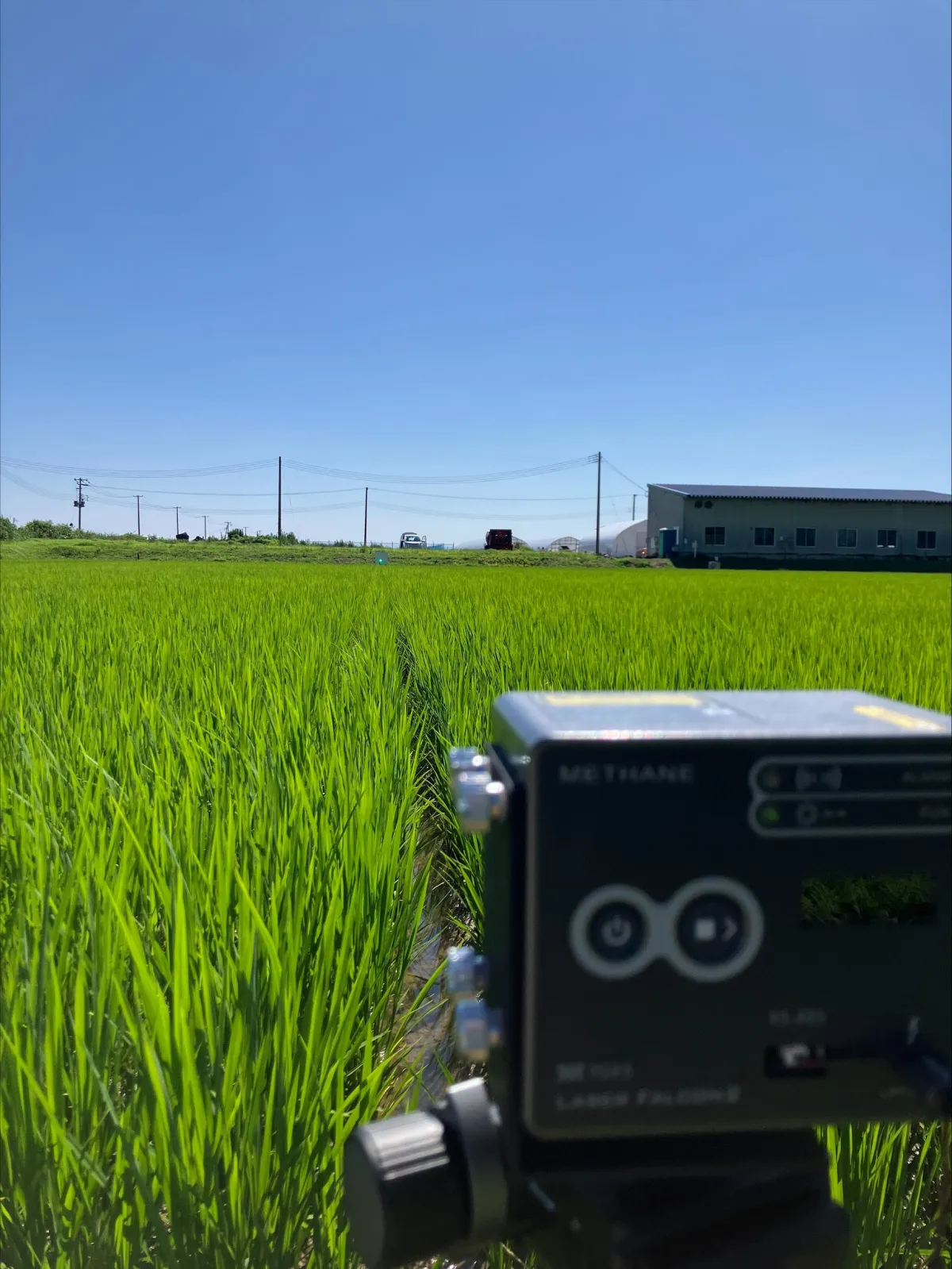
The laser methane detection technology works by emitting infrared laser light that is absorbed by methane gas. By analyzing the amount of laser light that is absorbed after bouncing off surfaces like the ground, the presence and concentration of methane can be detected almost instantaneously. This technology has been widely used for leak detection in urban gas systems.
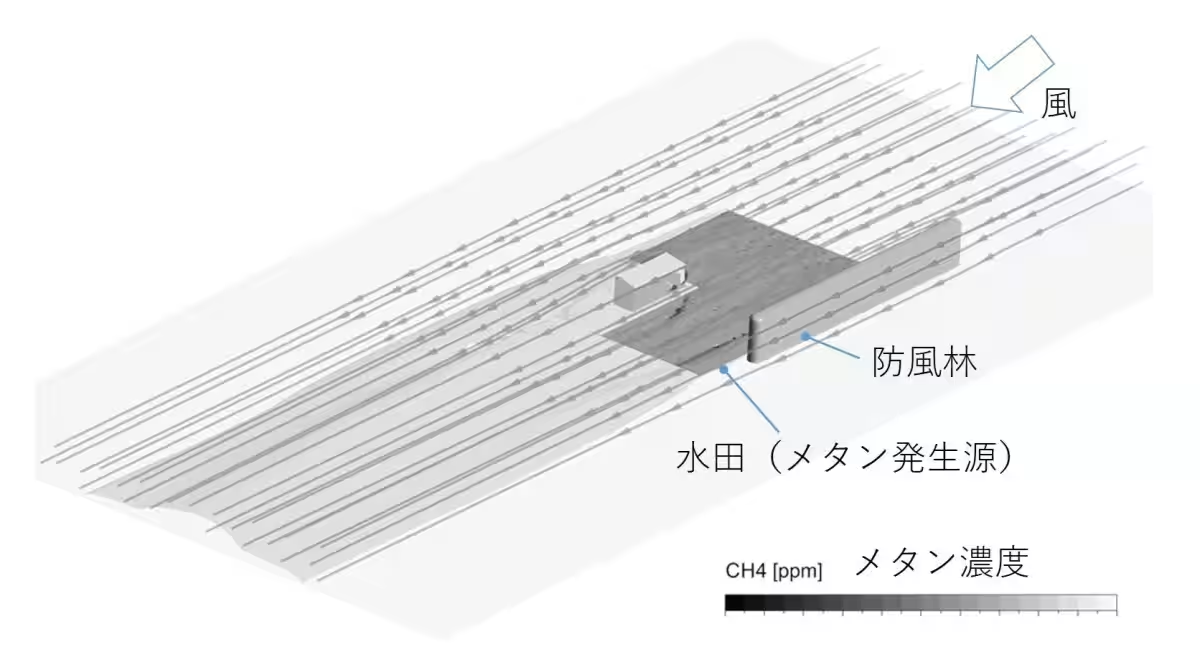
The research will utilize this laser data, combined with TGES's experience in high-precision fluid simulation, to model the dispersion of methane from rice paddies under varying environmental conditions. This approach will allow for the accurate assessment of methane emission reduction efforts and, consequently, the carbon credits that result from them.

(Image Caption: Measuring apparatus used in rice paddy methane emission assessment)
Future Prospects
The establishment of this technology is expected to streamline and enhance the measurement of methane emissions across broader natural landscapes. This innovative method will support various methodologies for generating carbon credits, including techniques such as Alternate Wetting and Drying (AWD), which is aimed at reducing methane emissions from rice paddies. Through this initiative, the Tokyo Gas Group aims to contribute significantly to the reliability of carbon credits generated through sustainable practices.
Commitment to Carbon Neutrality
Aligning with their management vision,



Topics Environment)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.