
The Surprising Truth About AI Hallucinations: ITSUKI's Study Reveals User Awareness
Understanding AI Hallucinations in Private Use
Introduction
The rapid evolution of generative AI has significantly transformed our daily lives, becoming an invaluable tool for personal tasks such as information gathering, writing, and brainstorming. Yet, as useful as it is, the prevalence of AI hallucinations—instances where AI generates plausible but incorrect information—presents a growing concern. Recent research conducted by ITSUKI has shed light on how aware users are of this phenomenon when using AI in their personal lives.
Background of the Study
Conducted by ITSUKI, a company specializing in internet networking based in Tokyo, this study surveyed individuals aged 20 to 50 who utilize generative AI in their private lives. It aimed to understand their use cases, as well as their awareness and attitudes towards AI-generated hallucinations.
Key Findings
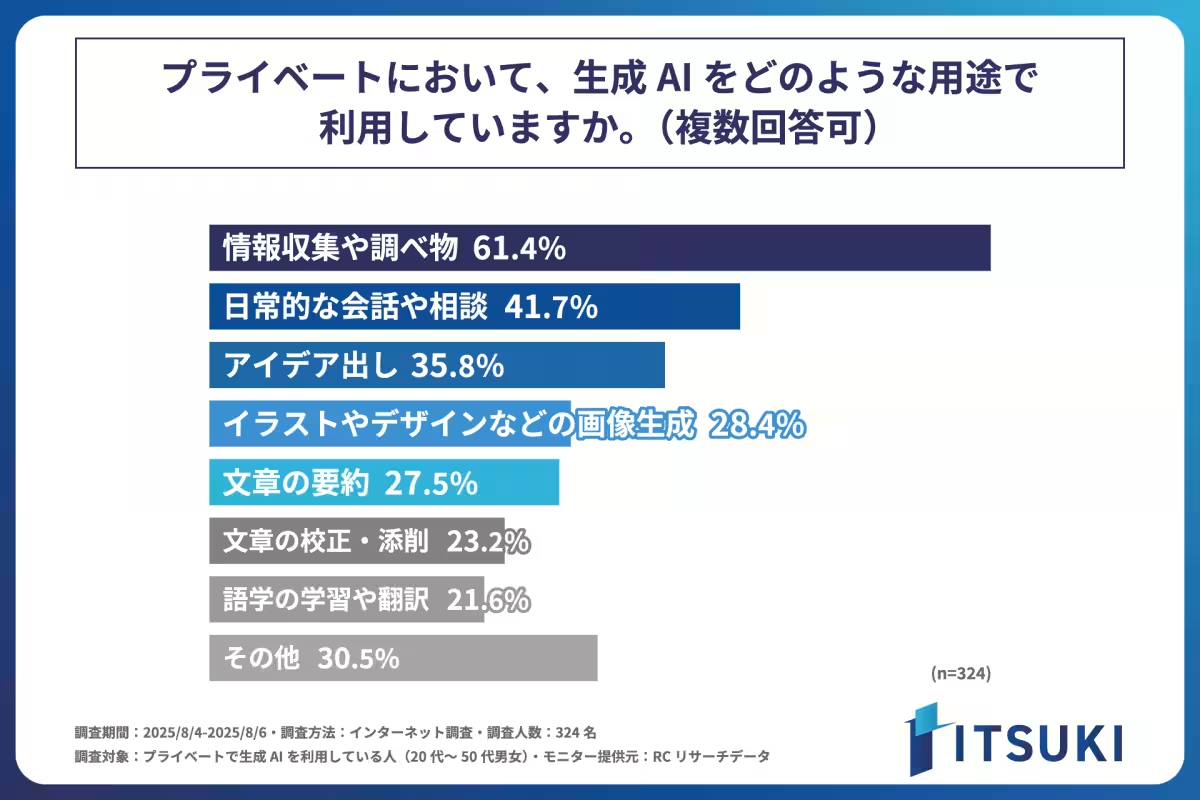
Usage of Generative AI
The top three uses for generative AI among respondents revealed a fascinating insight into user behavior:
1. Information Gathering/Research (61.4%)
2. Casual Conversations/Consultations (41.7%)
3. Idea Generation (35.8%)
This indicates that the primary function of generative AI in private settings is primarily for research and information collection, further underscoring its role in knowledge acquisition.
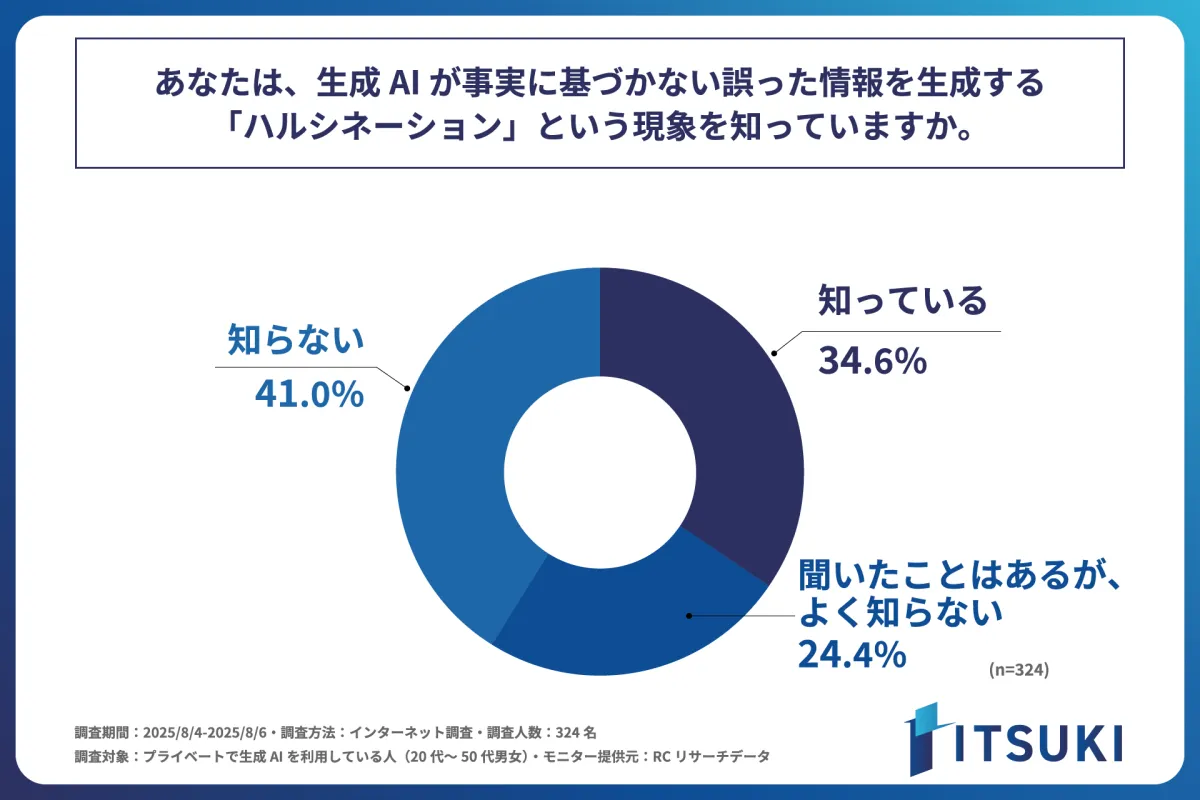
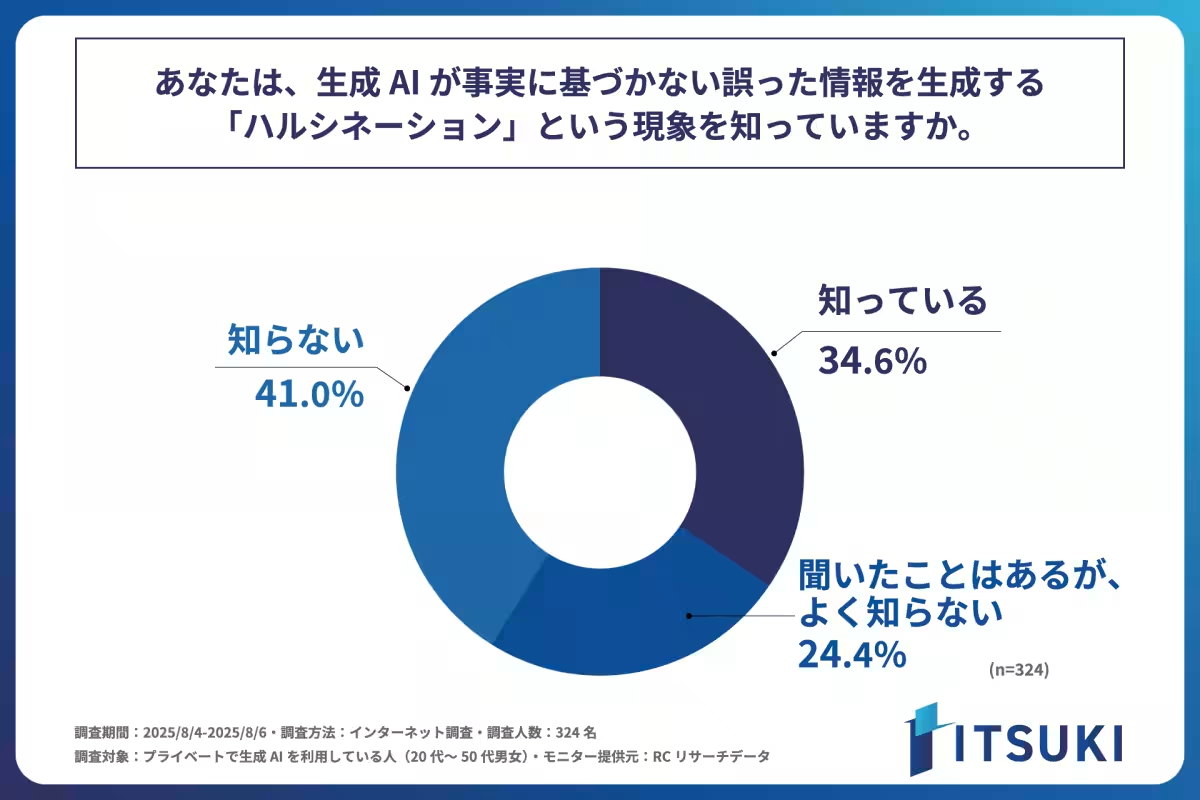
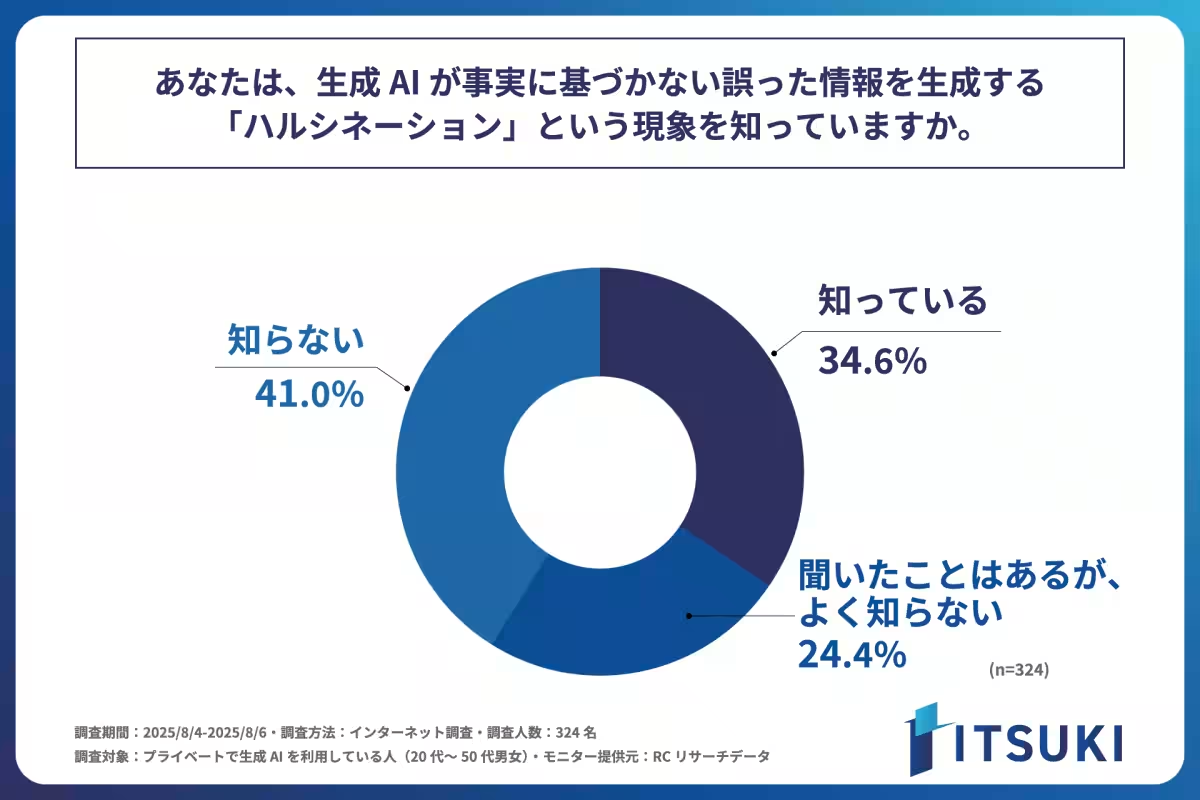
Awareness of AI Hallucinations
The research found that approximately 65% of users are either unaware of or lack sufficient knowledge about AI hallucinations. Specifically, when asked if they recognized the term “hallucination,” 41% responded they did not know what it was, while 34.6% acknowledged familiarity with it. This lack of awareness raises urgent questions about how this knowledge gap can affect user interactions with AI.
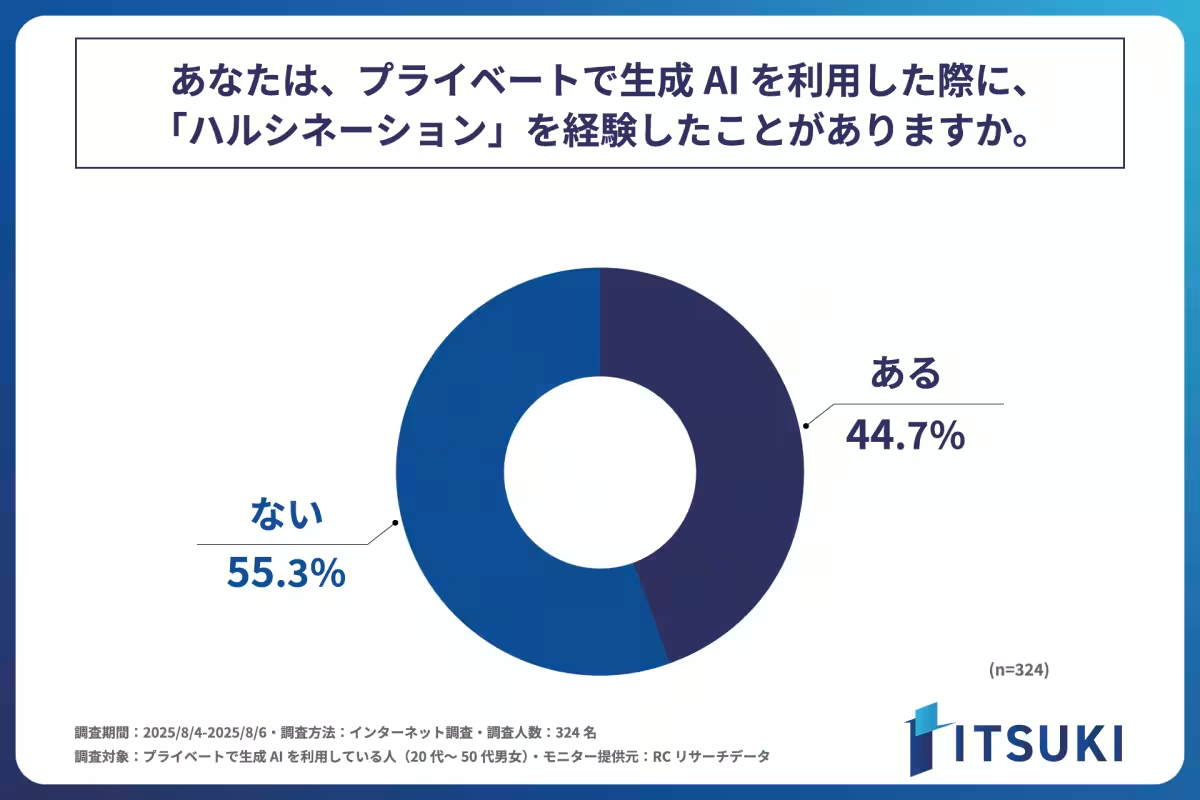
Personal Experience with Hallucinations
When participants were asked whether they had experienced hallucinations while using AI, 45% confirmed they had. This suggests that not only are many users unaware of the phenomenon, but a substantial number have encountered it firsthand.
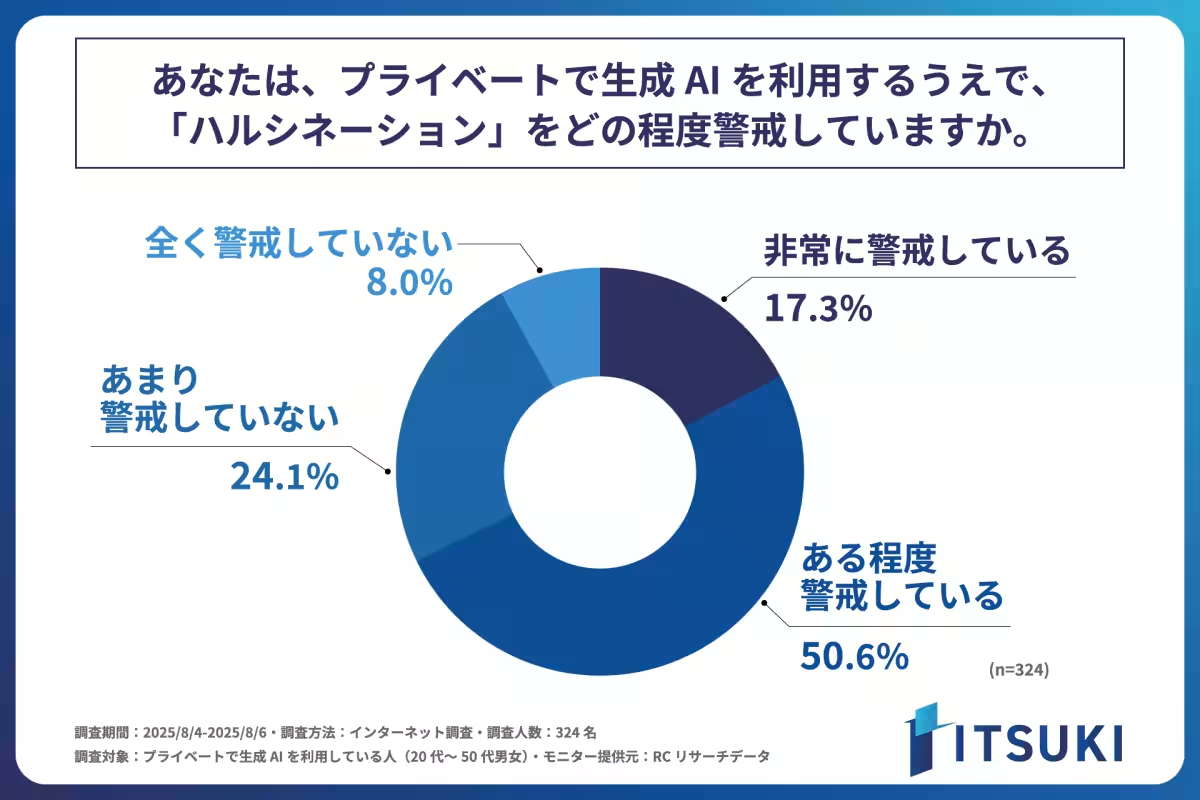
Vigilance Regarding Risks
Interestingly, about 70% of respondents expressed varying degrees of caution regarding AI hallucinations. Nearly 51% stated that they had some level of concern, while 17.3% claimed to be very cautious. This reflects a growing awareness and concern for inaccuracies in the information provided by AI tools.
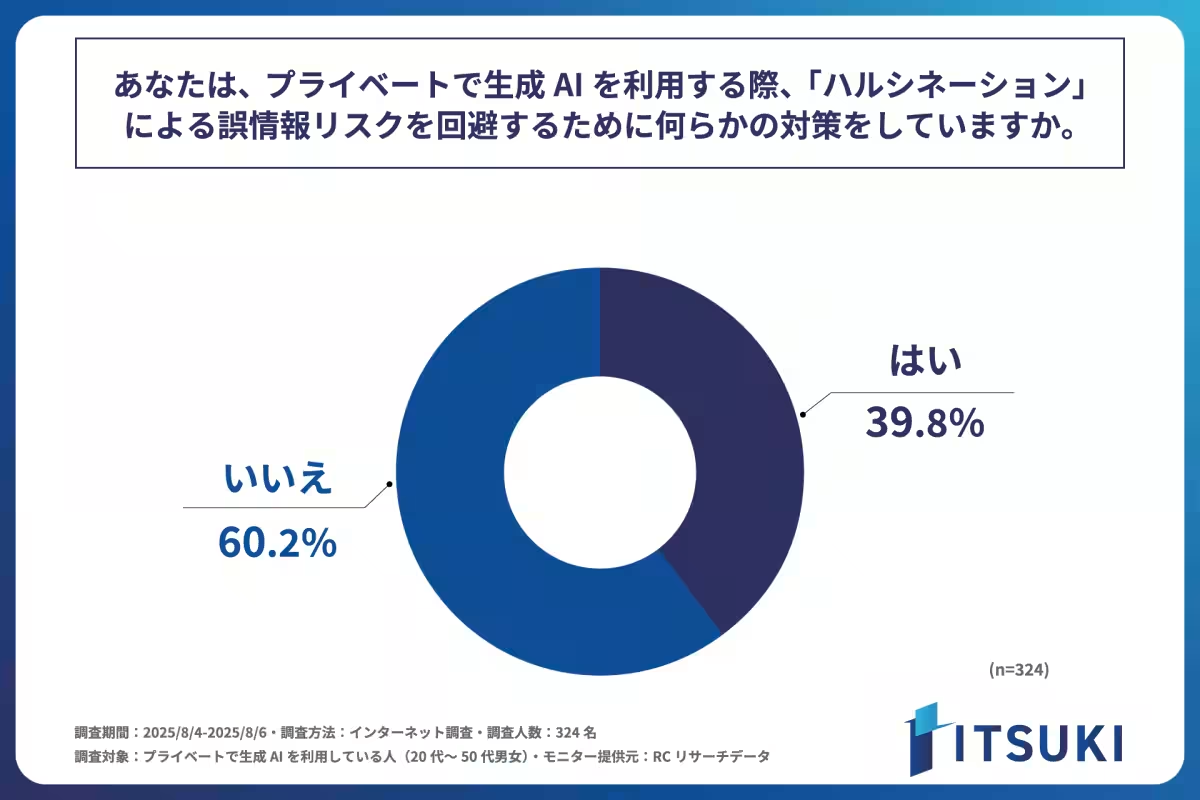
Mitigation Strategies
Despite the concerns, less than 40% of respondents reported taking any preventative measures against the risk of misinformation stemming from hallucinations. Among those who have taken precautions, the most common strategy is to treat AI output as reference information rather than absolute facts (53.5%). Other popular methods include:
- - Acknowledging the potential for AI errors (51.9%)
- - Cross-referencing information against multiple sources (50.4%)
This variety indicates that users are employing multiple tactics to navigate the complexities of dependent AI-generated content.
Conclusion
The findings from the ITSUKI survey highlight crucial insights about the understanding and usage of generative AI in private life. On one hand, a significant portion of users rely on AI for essential functions, yet many remain unaware of the risks associated with its errors. The study indicates a clear need for increased digital literacy so that users can confidently engage with emerging AI technologies. As a key player in enhancing internet accessibility, ITSUKI is committed to supporting educational efforts to help users navigate these evolving digital landscapes safely.
About ITSUKI
ITSUKI offers high-speed internet services, including FTTH solutions based on NTT East and NTT West, committing to providing reliable connectivity. More information can be found on their website or through their contact page.


Topics Consumer Technology)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.