
Understanding the Global CEO Salary Disparity: Japan vs Western Countries
Understanding the Global CEO Salary Disparity: Japan vs Western Countries
In a significant study conducted by HR Governance Leaders Inc., led by CEO Shigeru Uchikazaki, the compensation levels of CEOs in Japan, the United States, the United Kingdom, and Germany have been thoroughly analyzed. This research aims to shed light on the distinctive features of salary structures and designs, while facilitating a better understanding among stakeholders regarding global compensation practices.
Key Findings of the Research
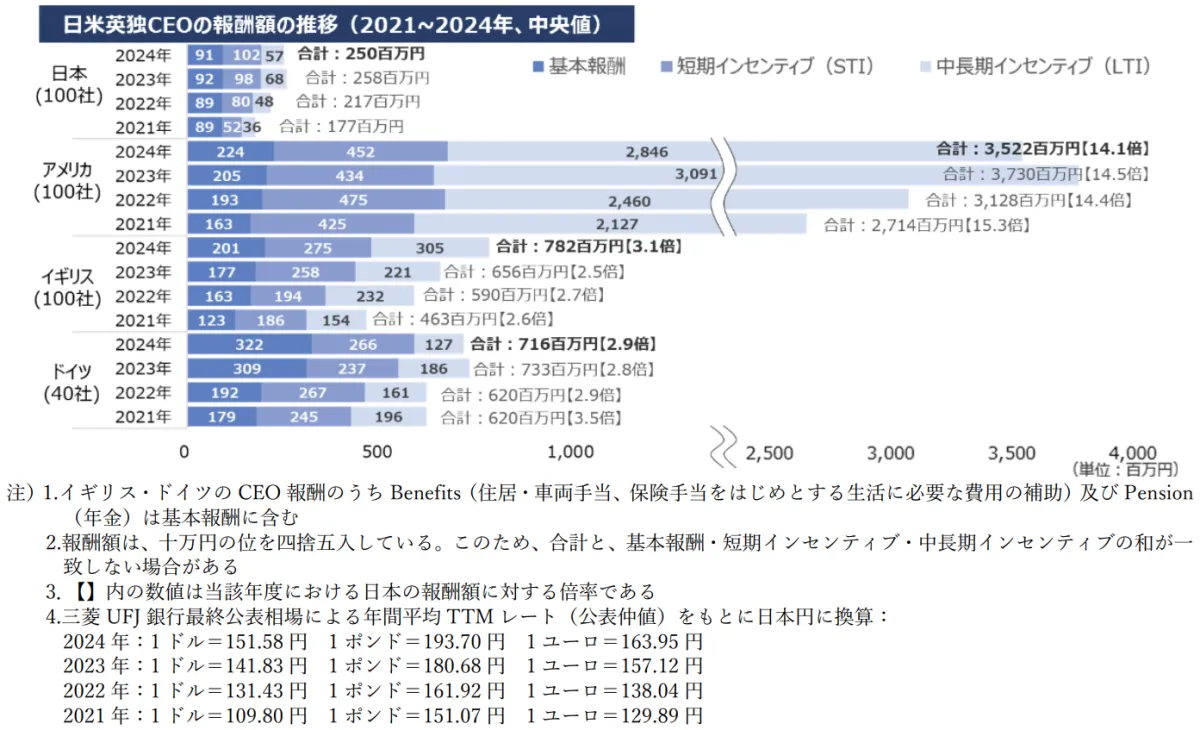
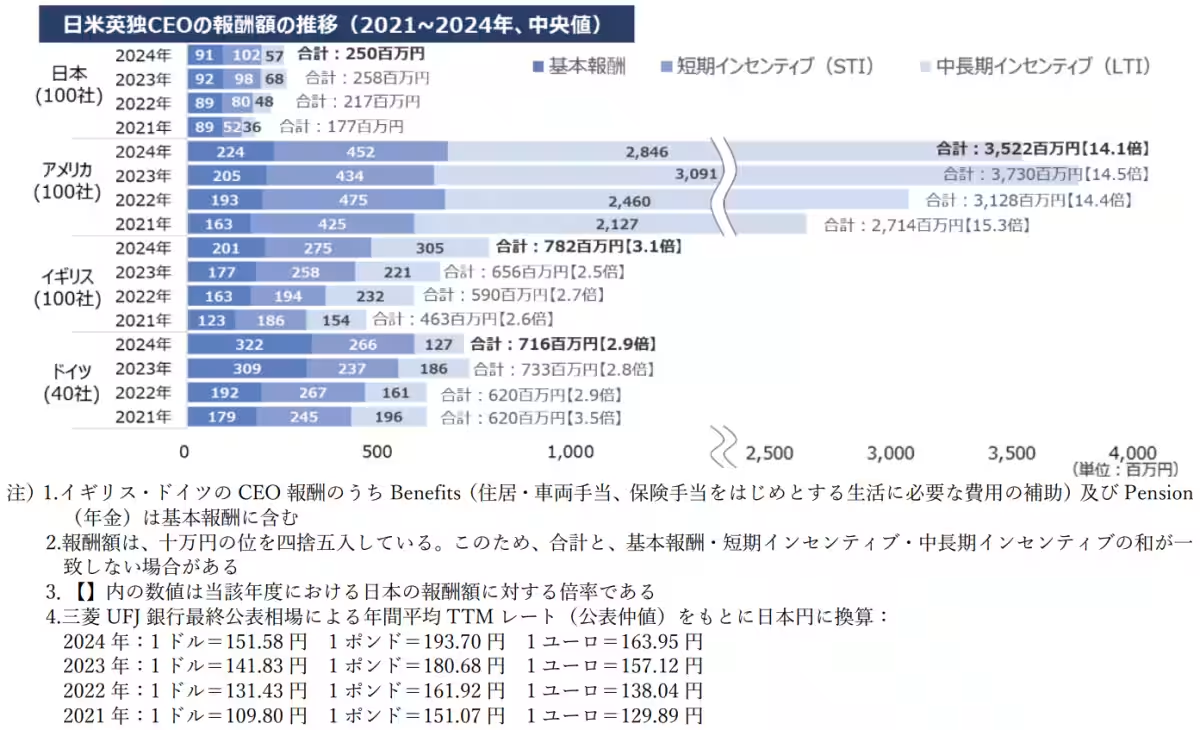
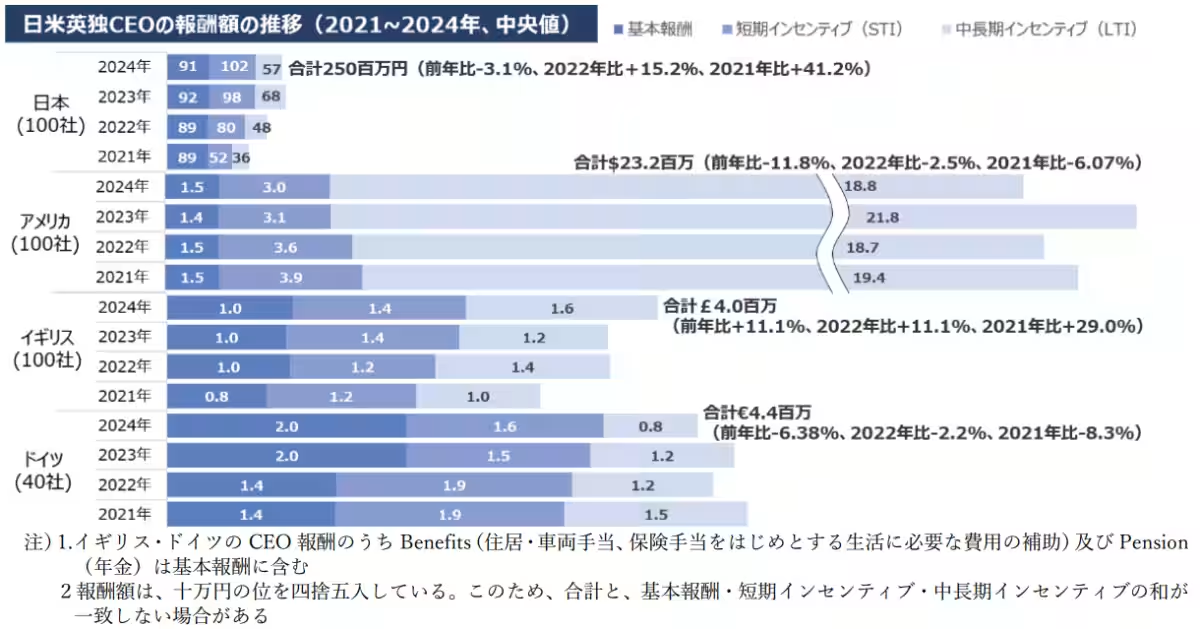
The median CEO compensation in 2024 is projected to be approximately 250 million yen in Japan, 3.52 billion yen in the United States, 780 million yen in the United Kingdom, and 720 million yen in Germany. The disparity between Japanese executives and their Western counterparts remains substantial and has grown significantly from 2021 to 2024: in the UK, the gap has expanded from about 2.5 times to 3.1 times; in Germany, it hovers near threefold; and the difference with the U.S. is around 14 to 15 times.
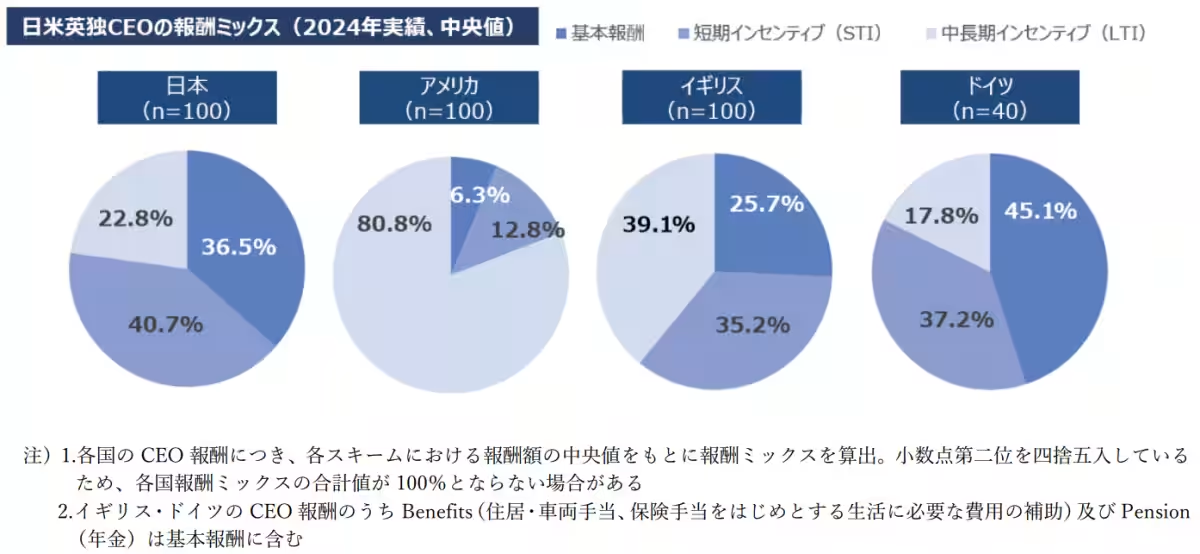
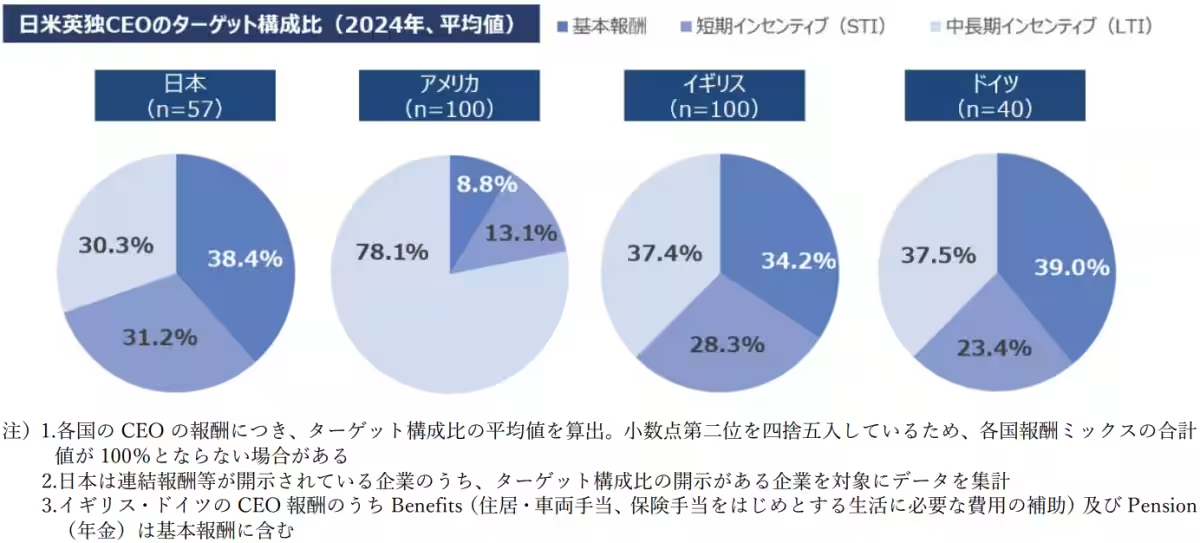
Japan's compensation mix reveals that 36.5% of remuneration constitutes base salary, which is the second highest after Germany but shows a lower proportion of Long-Term Incentives (LTI). However, compared to 2022, performance-linked pay has increased, demonstrating a shift in compensation trends.
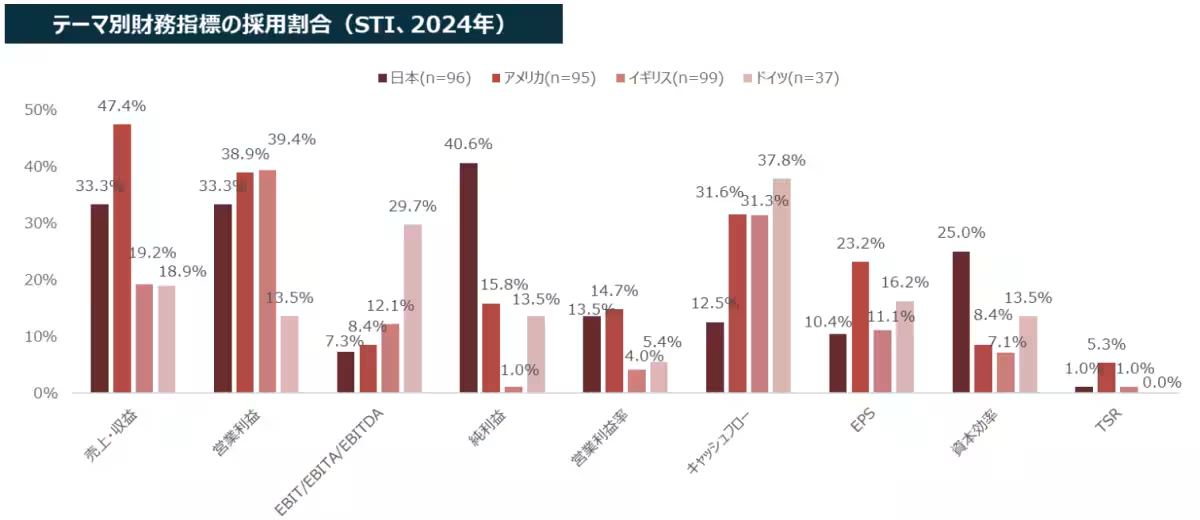
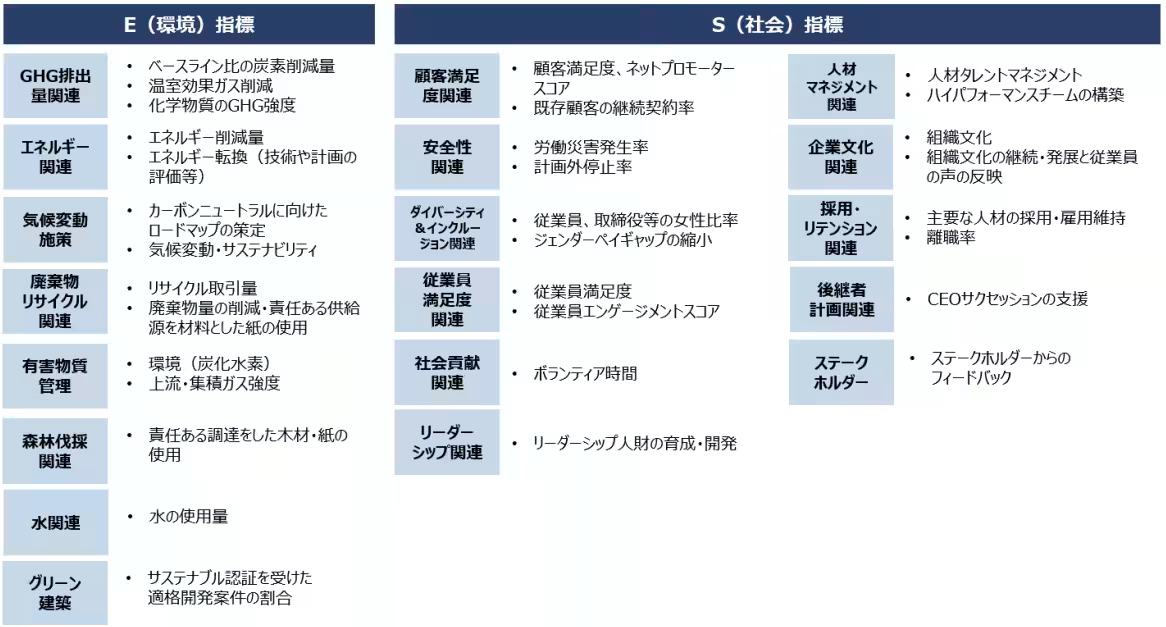
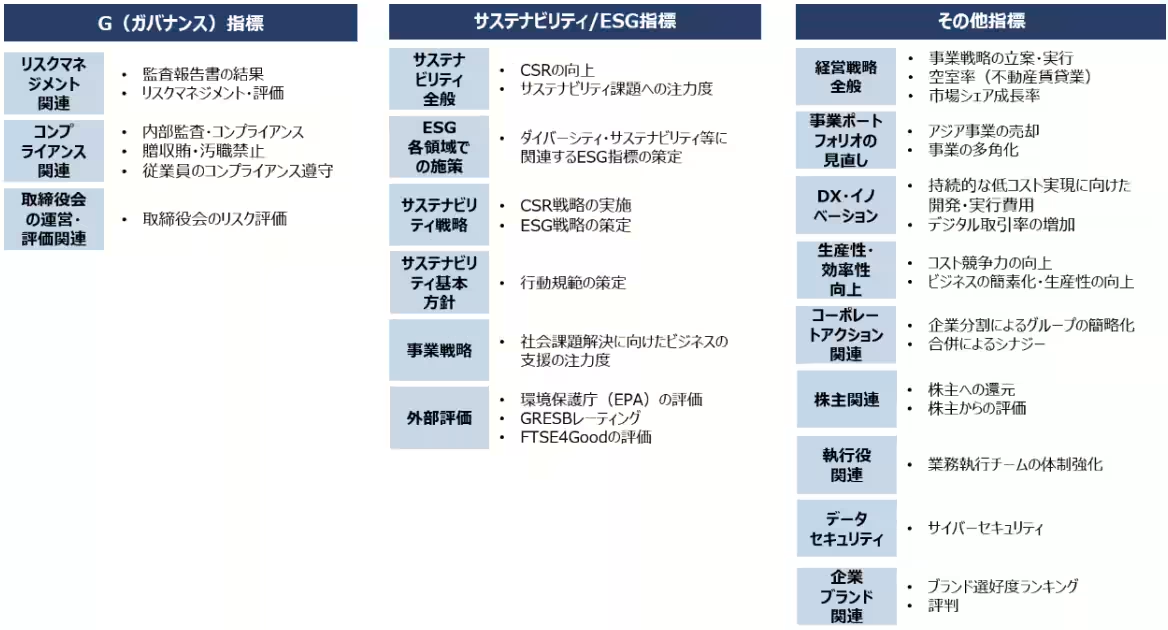
When examining financial metrics employed in Short-Term Incentives (STI), it becomes evident that Japan favors indicators linked to net profit and capital efficiency, while showing lower adoption of cash flow-related metrics. In contrast, Western nations, particularly the U.S., prioritize revenue and profit-related metrics.
Adoption of Financial Performance Metrics
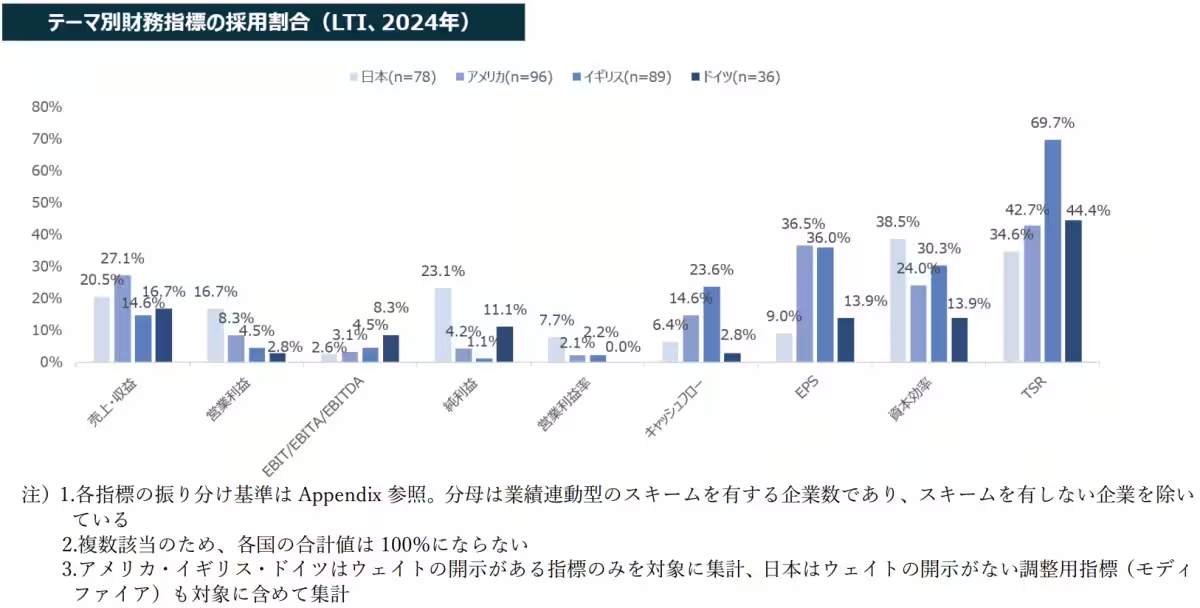
A detailed analysis of the adoption of financial metrics shows that in Japan, there is a high usage rate of capital efficiency metrics for LTI, reflecting a growing trend that mirrors Western practices. However, Japan's adoption rate for STI remains the lowest among the four regions. In the Western context, though STI adoption is declining, LTI utilization continues to increase.
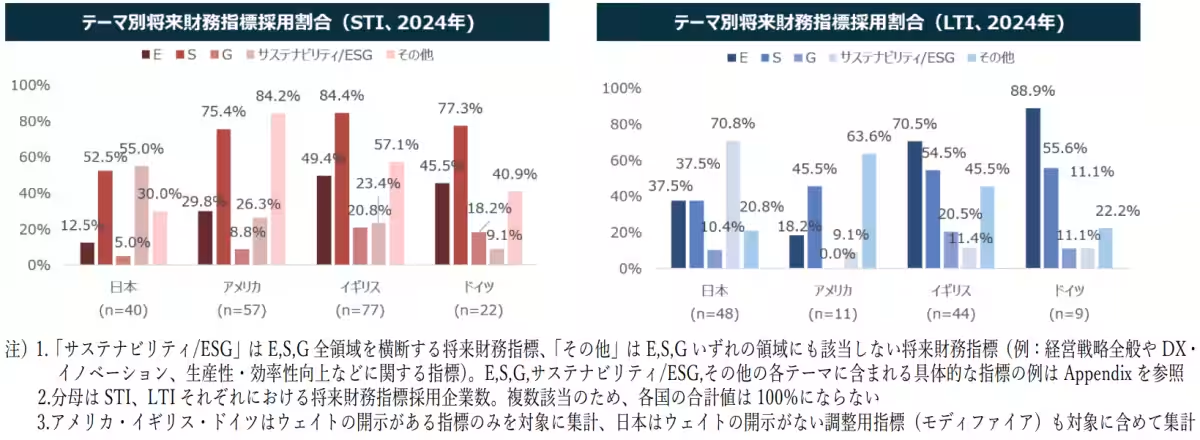
Future Financial Metrics in CEO Compensation
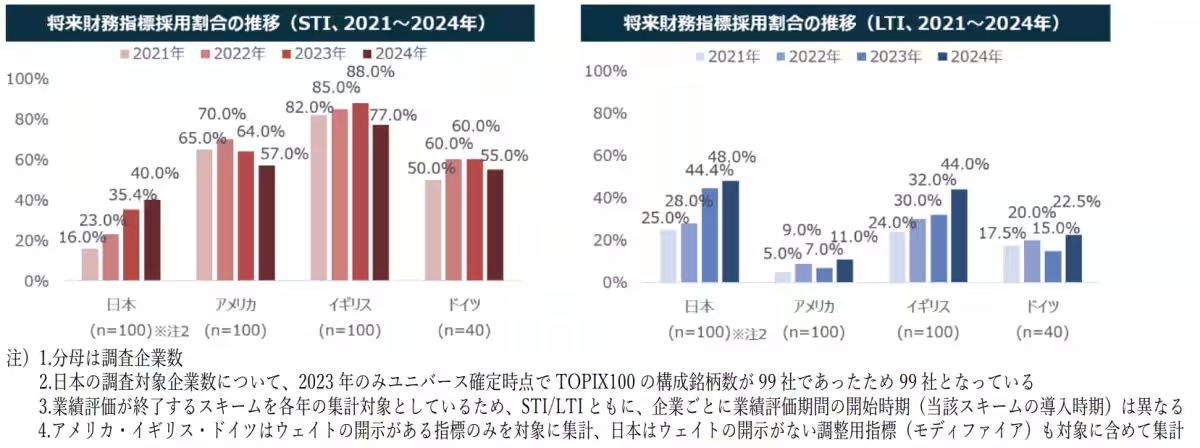
The adoption of future financial metrics as part of performance evaluation is on the rise in Japan, especially for LTI, with the STI adoption rate also reaching levels in the 40% range in 2024. This contrasts starkly with the Western norm, where LTI has seen a notable increase but STI continues to see a decline.
The study shows a high preference for sustainability-related indices in Japanese companies, with lower adoption of other specific metrics compared to Western companies where there is a general inclination towards “Other” category indicators.
Conclusion
Shigeru Uchikazaki remarked on these findings, emphasizing the need for Japanese companies to address the existing pay gap to attract global talent and remain competitive. He stressed the importance of developing a remuneration mix that supports long-term corporate value creation and encourages appropriate risk-taking among executive leadership.
HR Governance Leaders intends to continue serving as a resource for sustainability governance, assisting clients in aligning their compensation structures with strategic business goals. The ongoing

Topics Business Technology)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.