
AIST's Free Dataset Boosts Development of Bimanual Robot AI in Japan
AIST's Open Dataset for Bimanual Robot AI Development
In a groundbreaking initiative, the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) has unveiled a comprehensive dataset designed to accelerate the development of bimanual robot AI. Titled AIST-Bimanual Manipulation, this extensive dataset, available for free, aims to provide researchers and developers with the necessary tools to create robots capable of performing intricate tasks with both hands, mimicking human behavior.
Overcoming Challenges in Robotic Learning
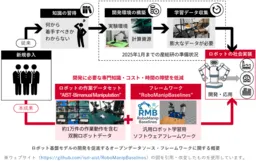
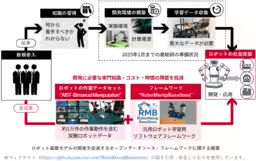
The journey towards effective robotic learning has often been hampered by several significant barriers, including a lack of starting points, absence of training data, and the high costs associated with setting up development environments. The AIST addresses these issues directly with the release of approximately 10,000 action sequences within the AIST-Bimanual Manipulation dataset, which integrates seamlessly with the previously issued software framework, RoboManipBaselines. This integration facilitates quicker initiation of research and development processes, thus lowering entry barriers for companies and institutions eager to delve into bimanual robot AI creation.
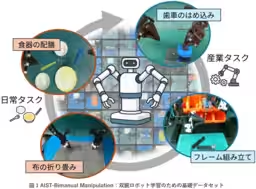
Notably, traditional robotic datasets have largely focused on single-arm tasks. The new dataset expands the scope by including complex human-like bimanual coordination tasks. For instance, it contains sequences of actions such as holding one object with one hand while manipulating another with the other. This strategy promises to assist industries grappling with labor shortages, particularly in manufacturing, logistics, and caregiving sectors.
The Societal Implications of Robotic Advancements
Japan is currently facing critical labor shortages exacerbated by an aging population, particularly in fields like manufacturing and caregiving where manual labor remains essential. The need for robots that can perform complex two-handed tasks is more crucial than ever. Tasks such as assembling components, adjusting packages in logistics, and household chores like folding laundry require the kind of dexterity that has previously posed significant challenges for robotics.
Given these societal pressures, large players in the AI space are increasingly investing in the development of foundational models for robots. While Japan also seeks to contribute to this global movement, companies often find themselves hindered by the financial burden of initial investments and a lack of technical expertise, creating a challenging environment for new entrants.
Furthermore, interest in Physical AI, which involves understanding actions and language, has surged globally. Japan, however, lacks the necessary extensive data and know-how to propel research and development in this domain. To combat this disparity, AIST aims to create an environment that is accessible even to beginners, facilitating early-stage practical applications of robotic technologies across key sectors.
Research Background and Achievements
Since launching the initiative to tackle real-world automation challenges in January 2025, AIST has worked diligently to bridge the gap between industrial demands and technological capabilities. The release of the AIST-Bimanual Manipulation dataset marks a significant milestone in actualizing this vision, representing a major leap in how datasets can be utilized to enhance robotic learning.
AIST's intelligent systems research team, including researchers like Tomohiro Motoda and Masaki Murooka, has concentrated on creating efficient methods for gathering large-scale data necessary for bimanual robotic tasks. This involves not only data collection but also developing software frameworks that enhance the usability and efficiency of robotic learning processes.
Features of the AIST-Bimanual Manipulation Dataset
The AIST-Bimanual Manipulation dataset comprises a wealth of 10,000 recorded tasks, drawing from scenarios that span daily life to industrial applications. This rich array of tasks allows for a more nuanced training regimen, enabling robots to learn complex coordinative actions that are second nature to humans.
To collect this data, AIST utilized a Leader-Follower remote operation system named ALOHA, where the motions of a human operator are replicated in real time by a robotic arm. During data collection, skilled operators performed various tasks, which were meticulously recorded to capture the subtleties of human-like movements.
RoboManipBaselines: An Open Framework for Robotic Learning
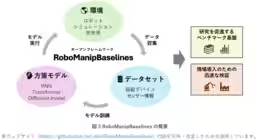
Alongside the dataset, AIST has rolled out RoboManipBaselines, a software framework designed to streamline the robotic learning process. This framework enables researchers to manipulate various simulators and actual robots through a unified interface, thereby facilitating the inclusion of new robots and learning methodologies as technology evolves.
Designed to be user-friendly, RoboManipBaselines allows users with minimal programming knowledge to engage in robotic training and evaluation, making it an invaluable resource for researchers in the field.
Future Directions and Research Expansion
The ultimate goal for AIST is to expand its dataset and software capabilities further to encompass a wider variety of tasks. The integration of natural language processing could transform how robots are controlled, leading to a comprehensive visual-language-action model that rose from the fundamental developments being made today.
As AIST forges ahead, its innovations promise not only to enhance Japan's standing in the global AI robotics arena but also to lay the groundwork for a future where robotic systems seamlessly augment human capabilities across numerous industries.
Additional Information
For those interested, both the RoboManipBaselines and AIST-Bimanual Manipulation datasets can be accessed through the following links:
This transformative step positions Japan's AI in bimanual robotics on the global stage, effectively responding to urgent labor challenges and pushing the boundaries of robotic capabilities.


Topics Consumer Technology)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.