
Study Uncovers Correlation Between Tooth Number and Diabetes Management in Patients
New Research Breaking Down Dental Health in Diabetes Patients
Recent collaborative research conducted by Shiga University of Medical Science and Sunstar Group sheds light on the concerning relationship between the number of teeth in diabetes patients and the importance of dental maintenance. Utilizing data from regular health check-ups and medical institutions, the study aimed to analyze the connection between dental visits, maintenance practices, and the prevalence of tooth loss among individuals with diabetes.
Throughout this comprehensive study, a significant trend emerged indicating that patients with poorly controlled blood sugar levels tend to lose more teeth compared to their peers who maintain a healthy glucose level. This finding emphasizes the critical role that regular dental care and blood sugar management play in the oral health of diabetes patients.
Overview of the Study
Objectives and Background
Maintaining a healthy set of teeth is crucial for individuals, particularly those suffering from diabetes, who face a higher risk of tooth loss. While previous studies provided self-reported data on this topic, there has been limited research utilizing large-scale medical databases. Sunstar Group, known for its explorative studies using such resources, has initiated this study to investigate the actual dental care received by diabetes patients and its implications on their oral health.
The extensive analysis encompassed data from 2015 to 2016, focusing on specific demographics. The study involved a sizable population sample of 705,542 individuals aged 20 to 74, and a specific cohort of 185,820 individuals aged 40 to 69, all of whom had adequate medical records to study both their dental habits and diabetes-related conditions.
Findings
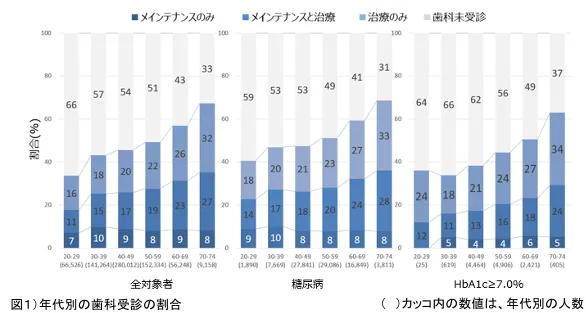
The research revealed alarming statistics. Only 46% of the entire population group engaged in regular dental check-ups, significantly declining in younger individuals: 34% for those in their 20s and 43% for those in their 30s. Among diabetic individuals, this trend continued, especially impactful on those with poor glucose control who reportedly attended dental appointments less frequently.
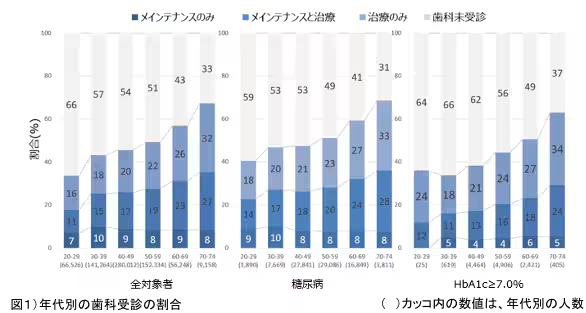
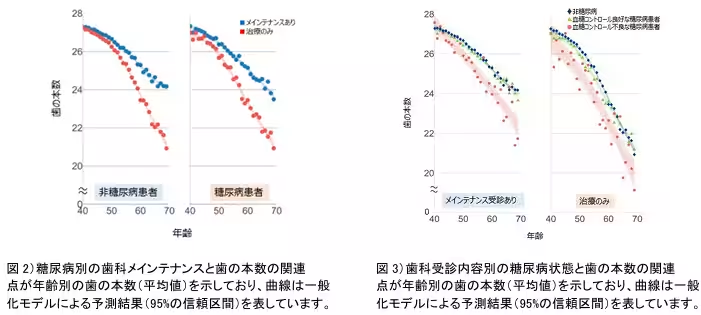
Interestingly, while healthy diabetes patients and non-diabetic individuals exhibited similar tooth counts, those with inadequate blood control demonstrated a stark difference even when maintaining their dentist visits. The data illustrated that regular dental maintenance was not just essential for overall health but was a significant factor in the prevention of tooth loss, particularly in diabetes patients.
Conclusions and Implications
The outcomes of this study elucidate the undeniable link between comprehensive dental care and blood sugar management. It is critical for diabetes patients to engage in both regular dental maintenance and effective blood sugar control to sustain their oral health. The implications suggest that there should be enhanced collaboration between healthcare providers and dental professionals to create a patient-centered preventive healthcare system.
This intricate analysis drives home the message that not only treatment but also proactive preventive measures can significantly influence health outcomes for diabetes patients. Ensuring a holistic approach towards managing health—where dental and medical care converge—will be a key takeaway as we move toward a future of improved patient care in diabetes management and oral health.


Topics Health)










【About Using Articles】
You can freely use the title and article content by linking to the page where the article is posted.
※ Images cannot be used.
【About Links】
Links are free to use.